|
DGX-1
The Nvidia DGX (Deep GPU Xceleration) represents a series of servers and workstations designed by Nvidia, primarily geared towards enhancing deep learning applications through the use of general-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU). These systems typically come in a rackmount format featuring high-performance x86 server CPUs on the motherboard. The core feature of a DGX system is its inclusion of 4 to 8 Nvidia Tesla GPU modules, which are housed on an independent system board. These GPUs can be connected either via a version of the SXM socket or a PCIe x16 slot, facilitating flexible integration within the system architecture. To manage the substantial thermal output, DGX units are equipped with heatsinks and fans designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This framework makes DGX units suitable for computational tasks associated with artificial intelligence and machine learning models. Models Pascal - Volta DGX-1 DGX-1 servers feature 8 GPUs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVLink
NVLink is a wire-based serial multi-lane near-range communications protocol, communications link developed by Nvidia. Unlike PCI Express, a device can consist of multiple NVLinks, and devices use mesh networking to communicate instead of a central hub (network science), hub. The protocol was first announced in March 2014 and uses a proprietary high-speed signaling interconnect (NVHS). Principle NVLink is developed by Nvidia for data and control code transfers in processor systems between CPUs and GPUs and solely between GPUs. NVLink specifies a point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point connection with data rates of 20, 25 and 50 Gbit/s (v1.0/v2.0/v3.0+ resp.) per differential pair. For NVLink 1.0 and 2.0 eight differential pairs form a "sub-link" and two "sub-links", one for each direction, form a "link". Starting from NVlink 3.0 only four differential pairs form a "sub-link". For NVLink 2.0 and higher the total data rate for a sub-link is 25 GB/s and the tota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem, it designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing, and system on a chip units (SoCs) for mobile computing and the automotive market. Nvidia is also a leading supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software. Nvidia outsources the manufacturing of the hardware it designs. Nvidia's professional line of GPUs are used for edge-to-cloud computing and in supercomputers and workstations for applications in fields such as architecture, engineering and construction, media and entertainment, automotive, scientific research, and manufacturing design. Its GeForce line of GPUs are aimed at the consumer market and are used in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
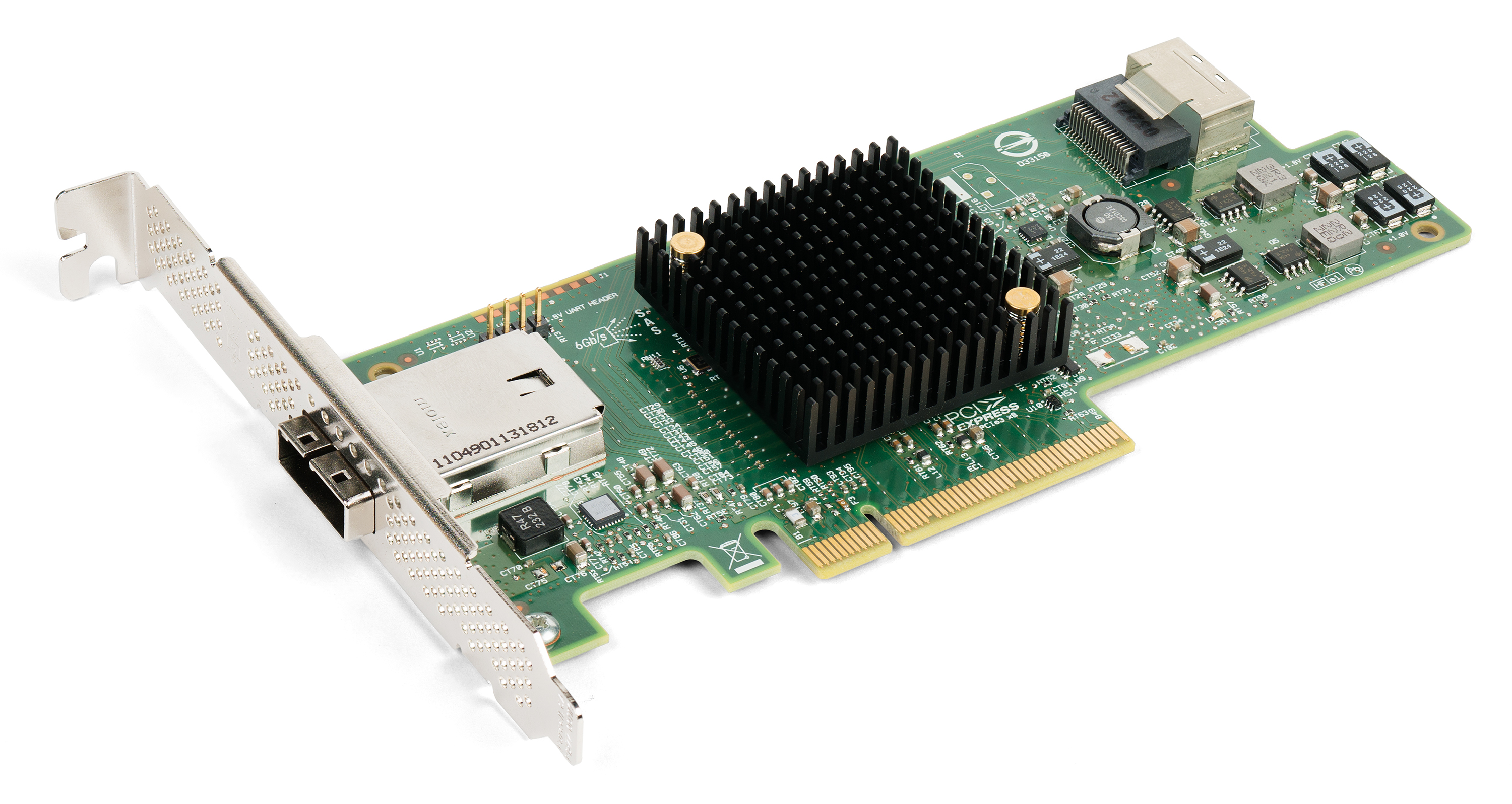
SXM (socket)
SXM (Server PCI Express Module) is a high bandwidth socket solution for connecting Nvidia Compute Accelerators to a system. Each generation of Nvidia Tesla since the P100 models, the DGX computer series and the HGX boards come with an SXM socket type that realizes high bandwidth, power delivery and more for the matching GPU daughter cards. Nvidia offers these combinations as an end-user product e.g. in their models of the DGX system series. Current socket generations are SXM for Pascal based GPUs, SXM2 and SXM3 for Volta based GPUs, SXM4 for Ampere based GPUs, and SXM5 for Hopper based GPUs. These sockets are used for specific models of these accelerators, and offer higher performance per card than PCIe equivalents. The DGX-1 system was the first to be equipped with SXM-2 sockets and thus was the first to carry the form factor compatible SXM modules with P100 GPUs and later was unveiled to be capable of allowing upgrading to (or being pre-equipped with) SXM2 modules with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta (microarchitecture)
Volta is the codename, but not the trademark, for a graphics processing unit, GPU microarchitecture developed by Nvidia, succeeding Pascal (microarchitecture), Pascal. It was first announced on a roadmap in March 2013, although the first product was not announced until May 2017. The architecture is named after 18th–19th century Italian chemist and physicist Alessandro Volta. It was Nvidia's first chip to feature Tensor Cores, specially designed cores that have superior deep learning performance over regular CUDA cores. The architecture is produced with TSMC's 14 nm process, 12 nm FinFET process. The Ampere (microarchitecture), Ampere microarchitecture is the successor to Volta. The first graphics card to use it was the datacenter Nvidia Tesla, Tesla V100, e.g. as part of the Nvidia DGX-1 system. It has also been used in the Quadro GV100 and Titan V. There were no mainstream GeForce graphics cards based on Volta. After two USPTO proceedings, on July 3, 2023 Nvidia lost the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (microarchitecture)
Pascal is the codename for a GPU microarchitecture developed by Nvidia, as the successor to the Maxwell (microarchitecture), Maxwell architecture. The architecture was first introduced in April 2016 with the release of the Tesla P100 (GP100) on April 5, 2016, and is primarily used in the GeForce 10 series, starting with the GeForce GTX 1080 and GTX 1070 (both using the GP104 GPU), which were released on May 27, 2016, and June 10, 2016, respectively. Pascal was manufactured using TSMC's 14 nm process, 16 nm FinFET process, and later Samsung's 14 nanometer, 14nm FinFET process. The architecture is named after the 17th century French mathematician and physicist, Blaise Pascal. In April 2019, Nvidia enabled a software implementation of DirectX Raytracing on Pascal-based cards starting with the GTX 1060 6 GB, and in the GeForce 16 series, 16 series cards, a feature reserved to the Turing-based RTX series up to that point. Details In March 2014, Nvidia announced that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere (microarchitecture)
Ampere is the codename for a graphics processing unit (GPU) microarchitecture developed by Nvidia as the successor to both the Volta and Turing architectures. It was officially announced on May 14, 2020, and is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère. Nvidia announced the Ampere architecture GeForce 30 series consumer GPUs at a GeForce Special Event on September 1, 2020. Nvidia announced the A100 80 GB GPU at SC20 on November 16, 2020. Mobile RTX graphics cards and the RTX 3060 based on the Ampere architecture were revealed on January 12, 2021. Nvidia announced Ampere's successor, Hopper, at GTC 2022, and "Ampere Next Next" ( Blackwell) for a 2024 release at GPU Technology Conference 2021. Details Architectural improvements of the Ampere architecture include the following: * CUDA Compute Capability 8.0 for A100 and 8.6 for the GeForce 30 series * TSMC's 7 nm FinFET process for A100 * Custom version of Samsung's 8 nm pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfiniBand
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology. Between 2014 and June 2016, it was the most commonly used interconnect in the TOP500 list of supercomputers. Mellanox (acquired by Nvidia) manufactures InfiniBand host bus adapters and network switches, which are used by large computer system and database vendors in their product lines. As a computer cluster interconnect, IB competes with Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Intel Omni-Path. The technology is promoted by the InfiniBand Trade Association. History InfiniBand originated in 1999 from the merger of two competing designs: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture (MCA). They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus, which replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVMe
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via the PCI Express bus. The initial ''NVM'' stands for '' non-volatile memory'', which is often NAND flash memory that comes in several physical form factors, including solid-state drives (SSDs), PCIe add-in cards, and M.2 cards, the successor to mSATA cards. NVM Express, as a logical-device interface, has been designed to capitalize on the low latency and internal parallelism of solid-state storage devices. Architecturally, the logic for NVMe is physically stored within and executed by the NVMe controller chip that is physically co-located with the storage media, usually an SSD. Version changes for NVMe, e.g., 1.3 to 1.4, are incorporated within the storage media, and do not affect PCIe-compatible components such as motherboards and CPUs. By its design, NVM Expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-performance Computing
High-performance computing (HPC) is the use of supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems. Overview HPC integrates systems administration (including network and security knowledge) and parallel programming into a multidisciplinary field that combines digital electronics, computer architecture, system software, programming languages, algorithms and computational techniques. HPC technologies are the tools and systems used to implement and create high performance computing systems. Recently, HPC systems have shifted from supercomputing to computing clusters and grids. Because of the need of networking in clusters and grids, High Performance Computing Technologies are being promoted by the use of a collapsed network backbone, because the collapsed backbone architecture is simple to troubleshoot and upgrades can be applied to a single router as opposed to multiple ones. HPC integrates with data analytics in AI engineering workflows to generate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Cooling
file:KKP Auslauf.jpg, Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and non-toxic; however, it can contain impurities and cause corrosion. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and power stations. Water coolers utilising Convection (heat transfer), convective heat transfer are used inside high-end personal computers to lower the temperature of CPUs and other components. Other uses include the cooling of lubricant oil in pumps; for cooling purposes in heat exchangers; for cooling buildings in Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, HVAC and in chillers. Mechanism Advantages Water is inexpensive, non-toxic, and available over most of the earth's surface. Liquid cooling offers higher thermal conductivity than air cooling. Water has unusually hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |