|
DGCR8
The microprocessor complex subunit DGCR8 ''( DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8)'' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene. In other animals, particularly the common model organisms '' Drosophila melanogaster'' and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', the protein is known as ''Pasha'' (partner of Drosha). It is a required component of the RNA interference pathway. Function The subunit DGCR8 is localized to the cell nucleus and is required for microRNA (miRNA) processing. It binds to the other subunit Drosha, an RNase III enzyme, to form the microprocessor complex that cleaves a primary transcript known as pri-miRNA to a characteristic stem-loop structure known as a pre-miRNA, which is then further processed to miRNA fragments by the enzyme Dicer. DGCR8 contains an RNA-binding domain and is thought to bind pri-miRNA to stabilize it for processing by Drosha. DGCR8 is also required for some types of DNA repair. Removal of UV-induced DNA photoproducts, during tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor Complex
The microprocessor complex is a protein complex involved in the early stages of processing microRNA (miRNA) and RNA interference (RNAi) in animal cells. The complex is minimally composed of the ribonuclease enzyme Drosha and the dimeric RNA-binding protein DGCR8 (also known as Pasha in non-human animals), and cleaves primary miRNA substrates to pre-miRNA in the cell nucleus. Microprocessor is also the smaller of the two multi-protein complexes that contain human Drosha. Composition The microprocessor complex consists minimally of two proteins: Drosha, a ribonuclease III enzyme; and DGCR8, a double-stranded RNA binding protein. (DGCR8 is the name used in mammalian genetics, abbreviated from "DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8"; the homologous protein in model organisms such as flies and worms is called ''Pasha'', for ''Pa''rtner of Dro''sha''.) The stoichiometry of the minimal complex was at one point experimentally difficult to determine, but it has been demonstrated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
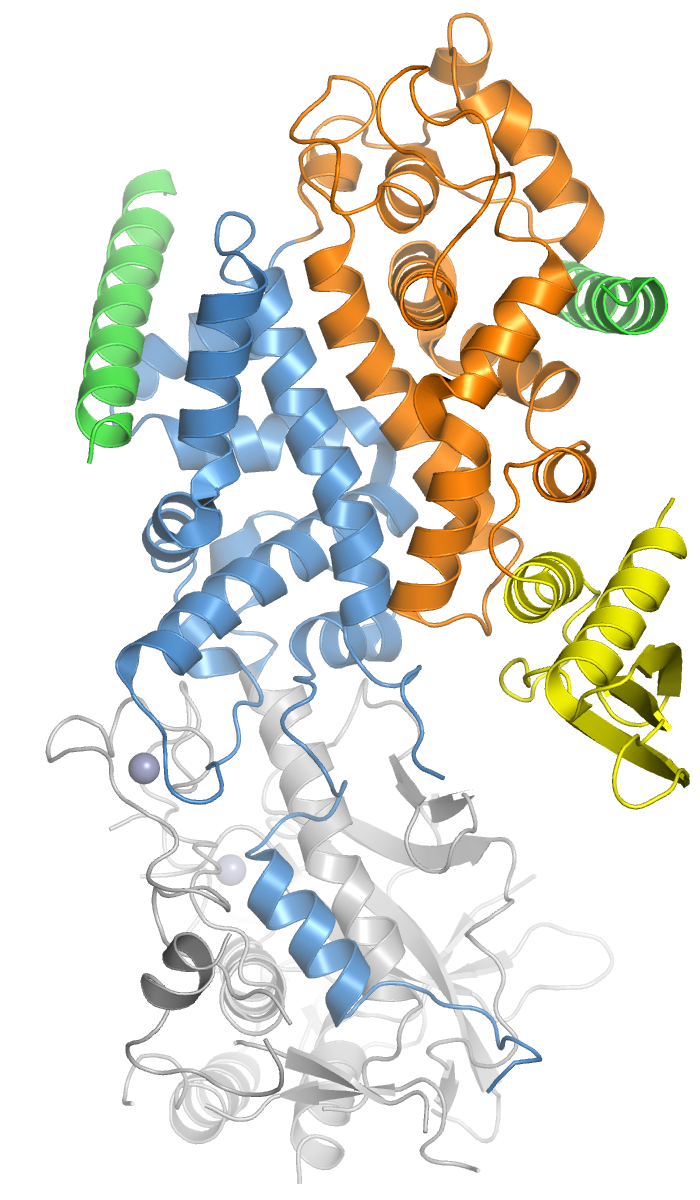
Drosha
Drosha is a Class 2 ribonuclease III enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DROSHA'' (formerly ''RNASEN'') gene. It is the primary nuclease that executes the initiation step of miRNA processing in the nucleus. It works closely with DGCR8 and in correlation with Dicer. It has been found significant in clinical knowledge for cancer prognosisSlack FJ, Weidhaas JB (December 2008). "MicroRNA in cancer prognosis". ''The New England Journal of Medicine.'' 359 (25): 2720-2. and HIV-1 replication.Swaminathan, G., Navas-Martín, S., & Martín-García, J. (2014). MicroRNAs and HIV-1 infection: antiviral activities and beyond. ''Journal of molecular biology'', ''426''(6), 1178-1197. History Human Drosha was cloned in 2000 when it was identified as a nuclear dsRNA ribonuclease involved in the processing of ribosomal RNA precursors. The other two human enzymes that participate in the processing and activity of miRNA are the Dicer and Argonaute proteins. Recently, proteins like Drosha ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs base-pair to complementary sequences in mRNA molecules, then gene silence said mRNA molecules by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of mRNA by shortening its poly(A) tail, or (3) translation of mRNA into proteins. This last method of gene silencing is the least efficient of the three, and requires the aid of ribosomes. miRNAs resemble the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. The human genome may encode over 1900 miRNAs, although more recent analysis s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DiGeorge Syndrome
DiGeorge syndrome, also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a syndrome caused by a microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 22. While the symptoms can vary, they often include congenital heart problems, specific facial features, frequent infections, developmental delay, learning problems and cleft palate. Associated conditions include kidney problems, schizophrenia, hearing loss and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or Graves' disease. DiGeorge syndrome is typically due to the deletion of 30 to 40 genes in the middle of chromosome 22 at a location known as ''22q11.2''. About 90% of cases occur due to a new mutation during early development, while 10% are inherited from a person's parents. It is autosomal dominant, meaning that only one affected chromosome is needed for the condition to occur. Diagnosis is suspected based on the symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing. Although there is no cure, treatment can improve symptoms. This often includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicer
Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into short double-stranded RNA fragments called small interfering RNA and microRNA, respectively. These fragments are approximately 20–25 base pairs long with a two-base overhang on the 3′-end. Dicer facilitates the activation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is essential for RNA interference. RISC has a catalytic component Argonaute, which is an endonuclease capable of degrading messenger RNA (mRNA). Discovery Dicer was given its name in 2001 by Stony Brook PhD student Emily Bernstein while conducting research in Gregory Hannon's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Bernstein sought to discover the enzyme responsible for generating small RNA fragments from double-stranded RNA. Dicer's ability to generate around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase III
Ribonuclease III (RNase III or RNase C)(BREND3.1.26.3 is a type of ribonuclease that recognizes dsRNA and cleaves it at specific targeted locations to transform them into mature RNAs. These enzymes are a group of endoribonucleases that are characterized by their ribonuclease domain, which is labelled the RNase III domain. They are ubiquitous compounds in the cell and play a major role in pathways such as RNA precursor synthesis, RNA Silencing, and the ''pnp'' autoregulatory mechanism. Types of RNase III The RNase III superfamily is divided into four known classes: 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each class is defined by its domain structure.Liang Y-H, Lavoie M, Comeau M-A, Elela SA, Ji X. Structure of a Eukaryotic RNase III Post-Cleavage Complex Reveals a Double- Ruler Mechanism for Substrate Selection. Molecular cell. 2014;54(3):431-444. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.006. Class 1 RNase III *Class 1 RNase III enzymes have a homodimeric structure whose function is to cleave dsRNA into multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it ''Rhabditides elegans.'' Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular and developmental biology of ''C. elegans'', which has since been extensively used as a model organism. It was the first multice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or " pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |