|
DENSO Corporation
is a global automotive components manufacturer headquartered in the city of Kariya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. After becoming independent from Toyota Motor, the company was founded as in 1949. About 25% of the company is owned by Toyota. Despite being a part of the Toyota Group of companies, as of the year ending March 2016, sales to the Toyota Group accounted for less than 50% of total revenue (44% of revenue originated from other car manufacturers in Japan, Germany, the U.S. and China). In 2023, DENSO was the second largest auto parts supplier in the world. In 2022, DENSO was listed at #278 on the Fortune Global 500 list with a total revenue of $49.0 billion and 167,950 employees. DENSO consisted of 200 consolidated subsidiaries (64 in Japan, 23 in North America, 32 in Europe, 74 in Asia, and seven in Oceania and other regions). Name The name is a blend word of the Japanese terms for and . Operations The company develops and manufactures various auto parts, including g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Company
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of share capital, stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (listing (finance), listed company), which facilitates the trade of shares, or not (unlisted public company). In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are ''private'' enterprises in the ''private'' sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets. Public companies are formed within the legal systems of particular states and so have associations and formal designations, which are distinct and separate in the polity in which they reside. In the United States, for example, a public company is usually a type of corporation, though a corporation need not be a public company. In the United Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, at the centre of the land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second-least populated after Antarctica. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of Input/output, inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems. They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact. PLCs were first developed in the automobile manufacturing industry to provide flexible, rugged and easily programmable controllers to replace hard-wired relay logic systems. Dick Morley, who invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
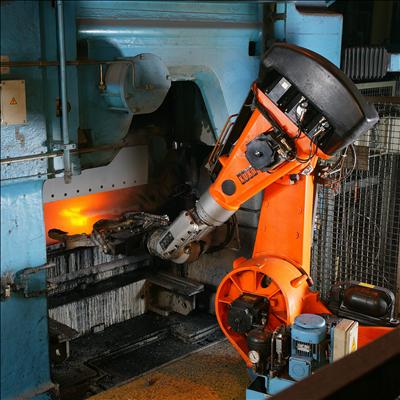
Industrial Robot
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes. Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circular economy, disassembly, Automated storage and retrieval system, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, Palletizer, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can assist in material handling. In the year 2023, an estimated 4,281,585 industrial robots were in operation worldwide according to International Federation of Robotics, International Federation of Robotics (IFR). Types and features There are six types of industrial robots. Articulated robots Articulated robots are the most common industrial robots. They look like a Arm, human arm, which is why they are also called robotic arm or Manipulator (device), manipulator arm. Their articu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode Reader
A barcode reader or barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes and send the data they contain to computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens, and a light sensor for translating optical impulses into electrical signals. Additionally, nearly all barcode readers contain ''decoder'' circuitry that can analyse the barcode's image data provided by the sensor and send the barcode's content to the scanner's output port. Types of barcode scanners Technology Barcode readers can be differentiated by technologies as follows: Pen-type readers Pen-type readers consist of a light source and photodiode that are placed next to each other at the tip of a pen. To read a barcode, the person holding the pen must move the tip of it across the bars at a relatively uniform speed. The photodiode measures the intensity of the light reflected back from the light source as the tip crosses each bar and space in the printed code. The photodiode g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anjō
is a Cities of Japan, city in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 188,693 in 76,087 households, and a population density of 2,193 persons per km². The total area of the city was . Geography Anjō is situated in southern Aichi Prefecture, approximately from central Nagoya, in the center of the Okazaki Plain, on the west bank of the Yahagi River. Japan National Route 1, National Route 1 and Japan National Route 23, National Route 23 provide the main east-west access through the city, with Aichi Prefectural Route 48 running between the two. Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Anjō is 15.6 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1576 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.7 °C, and lowest in January, at around 4.4 °C. Demographics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, chaturanga, xiangqi, Indian chess, and janggi. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Shogi was the earliest historical chess-related game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This ''drop rule'' is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th-century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the 6th century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while a direct ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spark Plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air mixture by an electric spark, while containing combustion pressure within the engine. A spark plug has a metal threaded shell, electrically isolated from a central electrode by a ceramic insulator. The central electrode, which may contain a resistor, is connected by a heavily insulated wire to the output terminal of an ignition coil or magneto. The spark plug's metal shell is screwed into the engine's cylinder head and thus electrically grounded. The central electrode protrudes through the porcelain insulator into the combustion chamber, forming one or more spark gaps between the inner end of the central electrode and usually one or more protuberances or structures attached to the inner end of the threaded shell and designated the ''si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbag
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate in milliseconds during a collision and then deflate afterwards. It consists of an airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. The purpose of the airbag is to provide a vehicle occupant with soft cushioning and restraint during a collision. It can reduce injuries between the flailing occupant and the vehicle's interior. The airbag provides an energy-absorbing surface between the vehicle's occupants and a steering wheel, instrument panel, body pillar, headliner, and windshield. Modern vehicles may contain up to ten airbag modules in various configurations, including driver, passenger, side-curtain, seat-mounted, door-mounted, B- and C-pillar mounted side-impact, knee bolster, inflatable seat belt, and pedestrian airbag modules. During a crash, the vehicle's crash sensors provide crucial information to the airbag electronic controller unit (ECU), including colli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
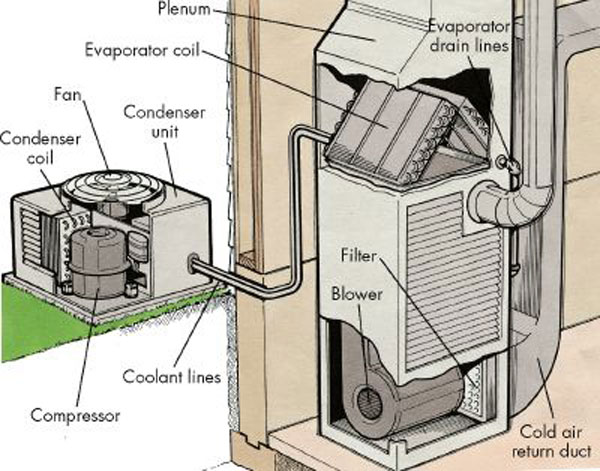
Climate Control
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids. Hybrid powertrains are designed to switch from one power source to another to maximize both fuel efficiency and energy efficiency. In hybrid electric vehicles, for instance, the electric motor is more efficient at producing torque, or turning power, while the combustion engine is better for maintaining high speed. Improved efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced running costs relative to non-hybrid vehicles are three primary benefits of hybridization. Vehicle types Two-wheeled and cycle-type vehicles Mopeds, electric bicycles, and even electric kick scooters are a simple form of a hybrid, powered by an internal combustion engine or electric motor and the rider's muscles. Early prototype motorcycles in the late 19th century used the same principle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compression (physics), compression; thus, the diesel engine is called a compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Introduction Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air combined with residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation, "EGR"). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases air temperature inside the Cylinder (engine), cylinder so that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. The torque a dies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |