|
DEC Rainbow
The Rainbow 100 is a microcomputer introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1982. This desktop unit had a monitor similar to the VT220 and a dual-CPU box with both Zilog Z80 and Intel 8088 CPUs. The Rainbow 100 was a triple-use machine: VT100 mode (industry standard terminal for interacting with DEC's own VAX), 8-bit CP/M mode (using the Z80), and CP/M-86 or MS-DOS mode using the 8088. It ultimately failed to succeed in the marketplace which became dominated by the simpler IBM PC and its clones which established the industry standard as compatibility with CP/M became less important than IBM PC compatibility. Writer David Ahl called it a disastrous foray into the personal computer market. The Rainbow was launched along with the similarly packaged DEC Professional and DECmate II which were also not successful. The failure of DEC to gain a significant foothold in the high-volume PC market would be the beginning of the end of the computer hardware industry in New Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until he was forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the early 1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the Programmed Data Processor, PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
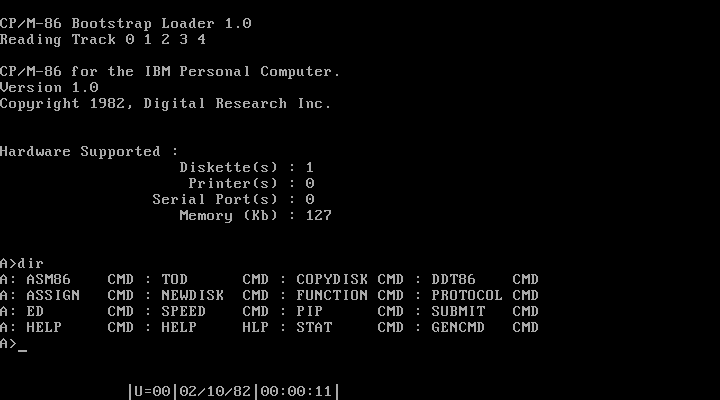
CP/M-86
CP/M-86 is a discontinued version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well. History Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for the IBM PC, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC V20
The NEC V20 is a microprocessor that was designed and produced by NEC. It is both pin compatible and object-code compatible with the Intel 8088, with an instruction set architecture (ISA) similar to that of the Intel 80188 with some extensions. The V20 was introduced in March 1984. Features The V20's die comprised 63,000 transistors; more than double the 29,000 of the 8088 CPU. The chip was designed for a clock duty cycle of 50%, compared to the 33% duty cycle used by the 8088. The V20 has two 16-bit wide internal databuses, allowing two data transfers to occur concurrently. Differences like that meant that a V20 could typically complete more instructions in a given time than an Intel 8088 running at the same frequency. The V20 was fabricated in 2-micron CMOS technology. Early versions ran at speeds of 5, 8, and 10 MHz. In 1990, an upgrade to the fabrication process technology resulted in the V20H and V20HL, with improved performance and reduced power consumption. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
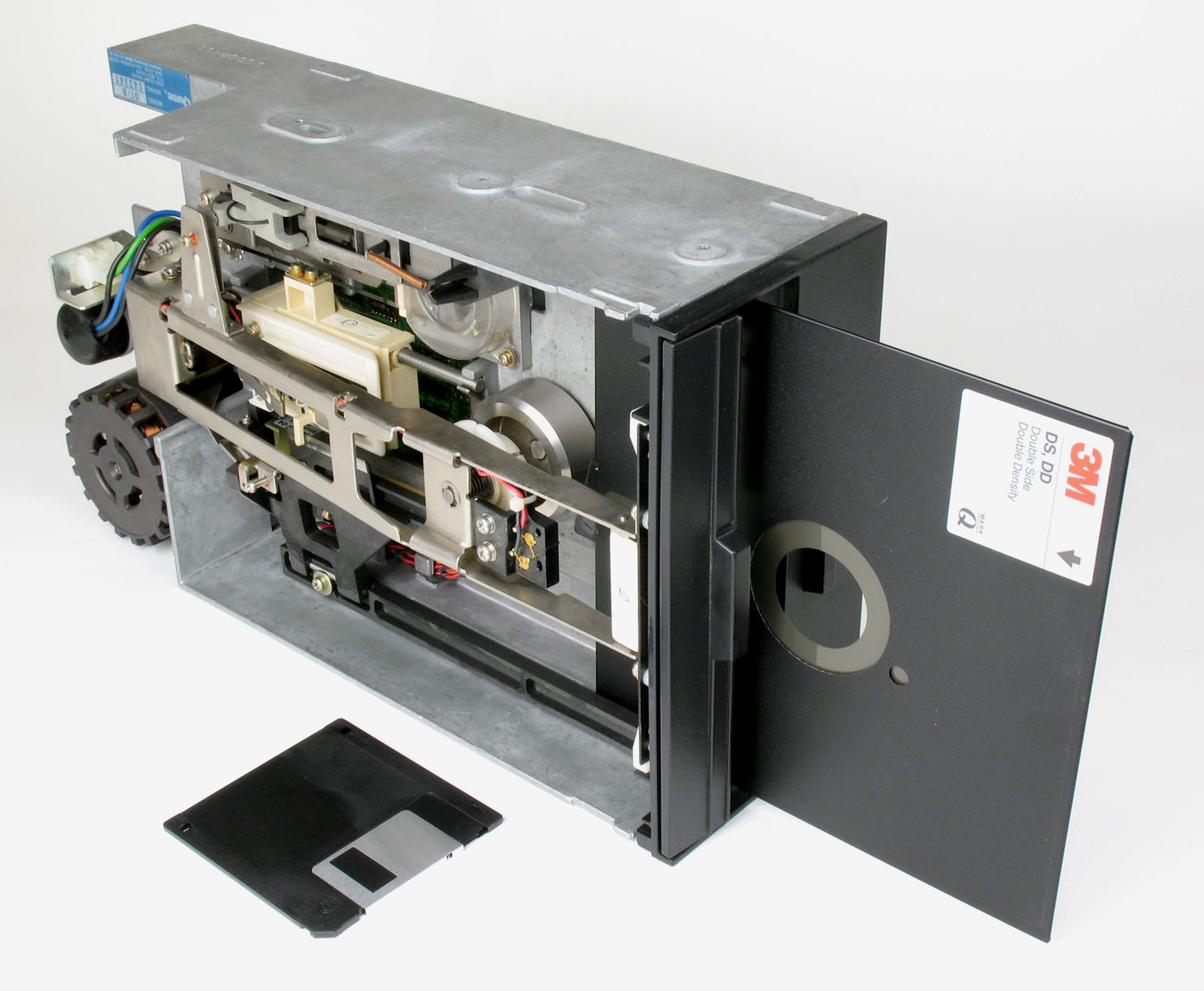
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winchester Disk
IBM manufactured magnetic disk storage devices from 1956 to 2003, when it sold its hard disk drive business to Hitachi. Both the hard disk drive (HDD) and floppy disk drive (FDD) were invented by IBM and as such IBM's employees were responsible for many of the innovations in these products and their technologies. The basic mechanical arrangement of hard disk drives has not changed since the IBM 1301. Disk drive performance and characteristics are measured by the same standards now as they were in the 1950s. Few products in history have enjoyed such spectacular declines in cost and physical size along with equally dramatic improvements in capacity and performance. IBM manufactured 8-inch floppy disk drives from 1969 until the mid-1980s, but did not become a significant manufacturer of smaller-sized, 5.25- or 3.5-inch floppy disk drives (the dimension refers to the diameter of the floppy disk, not the size of the drive). IBM always offered its magnetic disk drives for sale but did no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolics
Symbolics, Inc., is a privately held American computer software maker that acquired the assets of the former manufacturing company of the identical name and continues to sell and maintain the Open Genera Lisp (programming language), Lisp system and the Macsyma computer algebra system.Symbolics Sales by David Schmidt History Symbolics, Inc. was a computer manufacturer head ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automation, and energy and sustainability solutions (ESS). Honeywell also owns and operates Sandia National Laboratories under contract with the U.S. Department of Energy. Honeywell is a Fortune 500 company, ranked 115th in 2023. In 2024, the corporation had a global workforce of approximately 102,000 employees. As of 2023, the current chairman and chief executive officer is Vimal Kapur. The corporation's name, Honeywell International Inc., is a product of the merger of Honeywell Inc. and AlliedSignal in 1999. The corporation headquarters were consolidated with AlliedSignal's headquarters in Morristown, New Jersey. The combined company chose the name "Honeywell" because of the considerable brand recognition. Honeywell was a component of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computervision
Computervision, Inc. (CV) was an early pioneer in Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing ( CAD/CAM). Computervision was founded in 1969 by Marty Allen and Philippe Villers, and headquartered in Bedford, Massachusetts, United States. Its early products were built on a Data General Nova platform. Starting around 1975, Computervision built its own "CGP" (Computervision Graphics Processor) Nova-compatible 16-bit computers with added instructions optimized for graphics applications and using its own operating system known as Computervision Graphic Operating System (CGOS). In the 1980s, Computervision rewrote their code to operate on Unix-based platforms. Computervision was acquired by Prime Computer in 1988 for $434 million. Prime subsequently adopted the Computervision name. On December 12, 1998 Parametric Technology Corporation acquired Computervision. CADDS product history Computervision's first product, CADDS-1, was aimed at the printed circuit board layout and 2-D draftin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Computer
Prime Computer, Inc. was a Natick, Massachusetts-based producer of minicomputers from 1972 until 1992. With the advent of Personal computer, PCs and the decline of the minicomputer industry, Prime was forced out of the market in the early 1990s, and by the end of 2010 the trademarks for both PRIME and PRIMOS no longer existed. The alternative spellings "PR1ME" and "PR1MOS" were used as brand names or logos by the company. Founders The company was started by seven founders, some of whom worked on the Multics project at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT. * Robert Baron (president) * Sidney Halligan (VP Sales) * James Campbell (Director of Marketing) * Joseph Cashen (VP Hardware Engineering) * Robert Berkowitz (VP Manufacturing) * William Poduska (VP Software Engineering) * John Carter (Director of Human Resources) The company started with the motto ''"Software First"''. Poduska left in 1981, to start Apollo Computer.Alfred Dupont Chandler, Takashi Hikino, Andrew Von Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Laboratories
Wang Laboratories, Inc., was an American computer company founded in 1951 by An Wang and G. Y. Chu. The company was successively headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts (1954–1963), Tewksbury, Massachusetts (1963–1976), Lowell, Massachusetts (1976–1995), and finally Billerica, Massachusetts. At its peak in the 1980s, Wang Laboratories had annual revenues of US$3 billion and employed over 33,000 people. It was one of the leading companies during the time of the Massachusetts Miracle. The company was directed by An Wang, who was described as an "indispensable leader" and played a personal role in setting business and product strategy until his death in 1990. The company went through transitions between different product lines, beginning with typesetters, calculators, and word processors, then adding computers, copiers, and laser printers. Wang Laboratories filed for bankruptcy protection in August 1992. After emerging from bankruptcy, the company changed its name to Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General
Data General Corporation was an early minicomputer firm formed in 1968. Three of the four founders were former employees of Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Their first product, 1969's Data General Nova, was a 16-bit minicomputer intended to both outperform and cost less than the equivalent from DEC, the 12-bit PDP-8. A basic Nova system cost two-thirds or less than a similar PDP-8 while running faster, offering easy expandability, being significantly smaller, and proving more reliable in the field. Combined with Data General RDOS (DG/RDOS) and programming languages like Data General Business Basic, Novas provided a multi-user platform far ahead of many contemporary systems. A series of updated Nova machines were released through the early 1970s that kept the Nova line at the front of the 16-bit mini world. The Nova was followed by the Data General Eclipse, Eclipse series which offered much larger memory capacity while still being able to run Nova code without modification. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of general-purpose computer mostly developed from the mid-1960s, built significantly smaller and sold at a much lower price than mainframe computers . By 21st century-standards however, a mini is an exceptionally large machine. Minicomputers in the traditional technical sense covered here are only small relative to generally even earlier and much bigger machines. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching, as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end-use application. During the two-decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 minicomputer vendor companies formed. Only a half-dozen remained by the mid-1980s. When single-chip CPU microprocessors appeared in the 1970s, the defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |