|
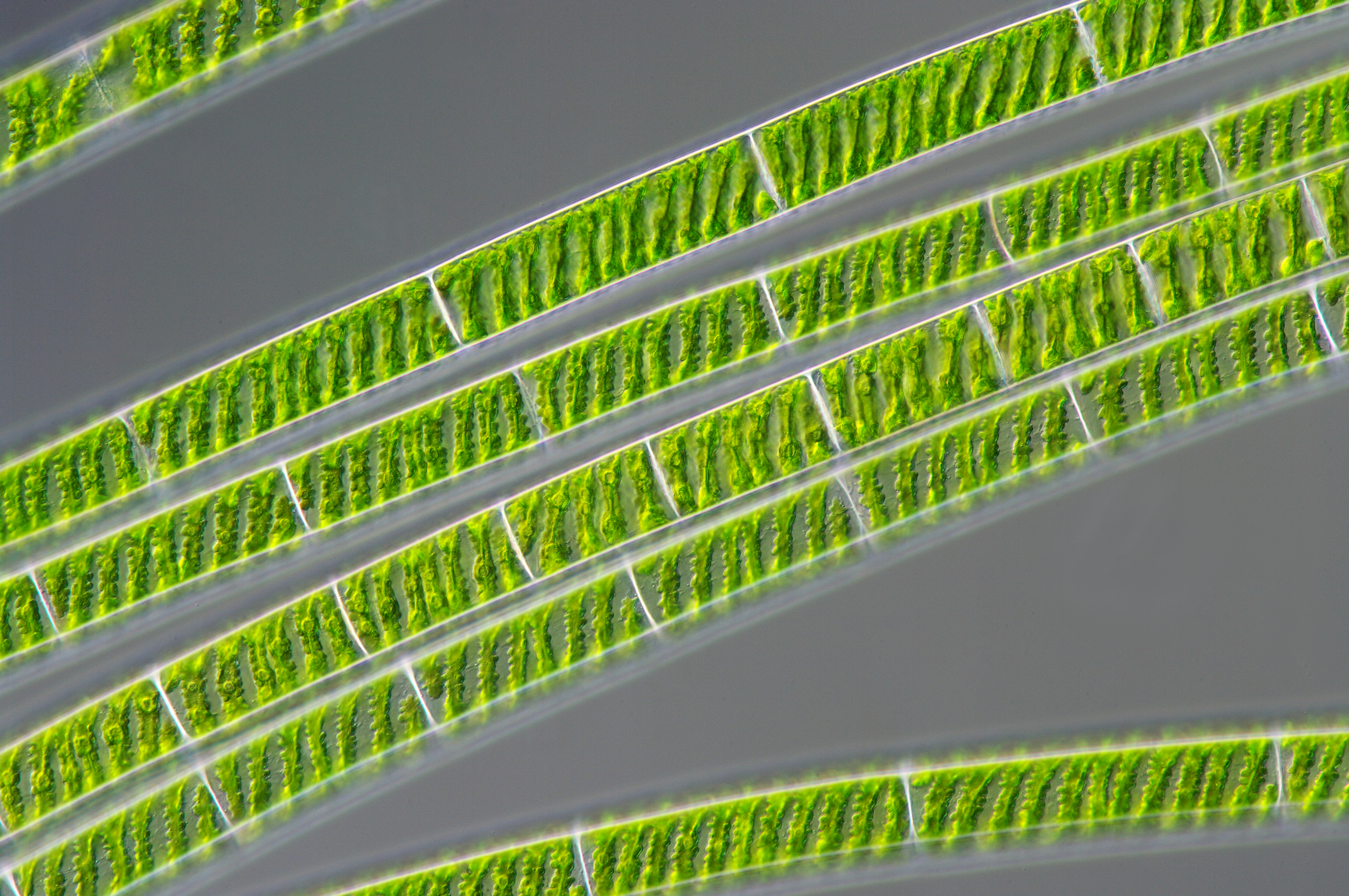
Zygnematales
The Zygnematales ( (''zygós'') and νῆμα (''nḗma'') ( nom.), νήματος (''nḗmatos'') ( gen.)), also called the Conjugatales, are an order of green algae, comprising several thousand different species in two families. The larger family Zygnemataceae, with well-known genera such as ''Zygnema'' and ''Spirogyra'', includes members that grow as unbranched filaments, which grow longer through normal cell division. This group includes the desmids. Most members of both families live in freshwater, and form an important component of the algal scum that grows on or near plants and rocks. Systematically they fall within the division Charophyta/ Streptophyta, in which the land plants ( Embryophyta) emerged. Sexual reproduction in Zygnematales takes place through a process called ''conjugation''. Here filaments of opposite gender line up, and tubes form between corresponding cells. The male cells then become amoeboid and crawl across, or sometimes both cells crawl into the tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmids
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids (''Gr.'' ''desmos'', bond or chain), are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled (sometimes filamentous or colonial) microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional. The desmids belong to the class Zygnematophyceae. Although they are sometimes grouped together as a single family Desmidiaceae, most classifications recognize three to five families, usually within their own order, Desmidiales. The Desmidiales comprise around 40 genus, genera and 5,000 to 6,000Brook, Alan J., 1981. ''The Biology of Desmids'', page 1. (Berkeley: University of California Press). species, found mostly but not exclusively in fresh water. In general, desmids prefer acidic waters (pH between 4.8 and 7.0), so many species may be found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmidiales
Desmidiales, commonly called the desmids (''Gr.'' ''desmos'', bond or chain), are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants ( Embryophyta) emerged. Desmids consist of single-celled (sometimes filamentous or colonial) microscopic green algae. Because desmids are highly symmetrical, attractive, and come in a diversity of forms, they are popular subjects for microscopists, both amateur and professional. The desmids belong to the class Zygnematophyceae. Although they are sometimes grouped together as a single family Desmidiaceae, most classifications recognize three to five families, usually within their own order, Desmidiales. The Desmidiales comprise around 40 genera and 5,000 to 6,000Brook, Alan J., 1981. ''The Biology of Desmids'', page 1. (Berkeley: University of California Press). species, found mostly but not exclusively in fresh water. In general, desmids prefer acidic waters (pH between 4.8 and 7.0), so many species may be found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netrium
''Netrium'' is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaenia'' .... The species of this genus are found in Europe, America and Australia. Species: *'' Netrium digitus'' *'' Netrium interruptum'' *'' Netrium lamellosum'' *'' Netrium naegelii'' *'' Netrium obesus'' *'' Netrium oblongum'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1231838 Zygnematales Charophyta genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryophyte
The embryophytes () are a clade of plants, also known as Embryophyta (Plantae ''sensu strictissimo'') () or land plants. They are the most familiar group of photoautotrophs that make up the vegetation on Earth's dry lands and wetlands. Embryophytes have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of freshwater charophyte green algae as a sister taxon of Charophyceae, Coleochaetophyceae and Zygnematophyceae. Embryophytes consist of the bryophytes and the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). Embryophytes have diplobiontic life cycles. The embryophytes are informally called "land plants" because they thrive primarily in terrestrial habitats (despite some members having evolved secondarily to live once again in semiaquatic/ aquatic habitats), while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. Embryophytes are complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptophyta
Streptophyta (), informally the streptophytes (, from the Greek ''strepto'' 'twisted', for the morphology of the sperm of some members), is a clade of plants. The composition of the clade varies considerably between authors, but the definition employed here includes land plants and all green algae except the Chlorophyta and the more basal Prasinodermophyta. Classifications The composition of Streptophyta and similar groups (Streptophytina, Charophyta) varies in each classification. Some authors include only the Charales and Embryophyta (e.g., Streptophyta, Streptophytina); others include more groups (e.g., Charophyta, Streptophyta, Streptobionta); some authors use this broader definition, but exclude the Embryophyta (e.g., Charophyta, Charophyceae, Streptophycophytes). The clade Streptophyta includes both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Streptophyta contains the freshwater charophyte green algae and all land plants that reproduce sexually by conjugation. ''Mesostigma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirogyra
''Spirogyra'' (common names include water silk, mermaid's tresses, and blanket weed) is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. ''Spirogyra'' species, of which there are more than 500, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. ''Spirogyra'' measures approximately 10 to 150 micrometres in width (though not usually more than 60) and may grow to several centimetres in length. Distribution ''Spirogyra'' can be been found on every continent on Earth, including Antarctica. It is freshwater algae, found rivers, ponds, and other such bodies of water. Taxonomy The genus Spirogyra was named by German naturalist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1820. The lectotype, ''Spirogyra'' ''porticalis'' was designated in 1952 by Paul C. Silvia. Reproduction ''Spirogyra'' can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In vegetative reproduction, fragmentation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Alga
The green algae (: green alga) are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/ Streptophyta. The land plants ( Embryophytes) have emerged deep within the charophytes as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid (spherical), and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesotaeniaceae
The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaenia'' was found to be a Basal (phylogenetics), basal green alga. Genera The Mesotaeniaceae includes the following genera: * ''Ancylonema'' Berggren, 1872 * ''Cylindrocystis'' Meneghini ex De Bary, 1858 * ''Geniculus'' Prescott, 1967 * ''Mesotaenium'' Nägeli, 1849 * ''Netrium'' (Nägeli) Itzigsohn & Rothe, 1856 * ''Nucleotaenium'' Gontcharov & Melkonian, 2010 * ''Planotaenium'' (Ohtani) Petlovany & Palamar-Mordvintseva, 2009 * ''Roya (alga), Roya'' West & G.S.West, 1896 * ''Tortitaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1998 Synonyms: * ''Endospira'' Brébisson, nom. inval., is a synonym of Spirotaenia * ''Entospira'' Kuntze, 1898 is a synonym of ''Spirotaenia'' * ''Polytaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1997, nom. illeg., is a synonym of ''Tortitaenia'' References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar Hertwig, Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other Anisogamy, anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm, sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a cell potency, totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetics, epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygnema
''Zygnema'' is a genus of freshwater filamentous thalloid alga comprising about 100 species. A terrestrial species, ''Z. terrestre'', is known from India. ''Zygnema'' grows as a free-floating mass of filaments, although young plants may be found anchored to streambeds with a holdfast. The filaments form a yellow-green to bright green colored tangled mat, and are composed of elongate barrel-shaped cells, each with two star-shaped (stellate) chloroplast A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...s arrayed along the axis of the cell. Species Some species include: * ''Z. atrocoeruleum'' * ''Z. binuclearioides'' * ''Z. carinthiacum'' * ''Z. carteri'' * ''Z. circumcarinatum'' * ''Z. coeruleum'' * ''Z. conspicuum'' * ''Z. cruciatum'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |