|
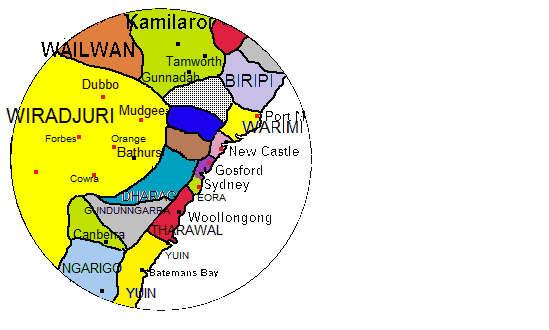
Yuin–Kuric Languages
The Yuin–Kuric languages are a group of mainly extinct Australian Aboriginal languages traditionally spoken in the south east of Australia. They belong in the Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan family.AIATSIS Language and Peoples Thesaurus , accessed 23 Jan 2010. These languages are divided into the Yuin, Kuri, and Yora groups, although exact classifications vary between researchers. Yuin–Kuric languages were spoken by the original inhabitants of what are now the cities of Sydney and Canberra. The name of this grouping was coined by Wilhelm Schmidt (linguist), Wilhelm Schmidt in 1919, and it refers to the two groups which define the geographical extent of the subgroup. The labels of all three subgroups reflect the word for 'man' or 'Aboriginal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral Sea, Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory and Jervis Bay Territory are Enclave and exclave, enclaves within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. , the population of New South Wales was over 8.3 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Almost two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. The Colony of New South Wales was founded as a British penal colony in 1788. It originally comprised more than half of the Australian mainland with its Western Australia border, western boundary set at 129th meridian east in 1825. The colony then also includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharawal Languages
Tharawal, also spelt Thurawal and Dharawal, is a small family of mostly extinct Australian Aboriginal languages once spoken along the South Coast (New South Wales), South Coast of New South Wales. Number of languages in the group According to Robert M. W. Dixon, Bob Dixon (2002), four Tharawal languages are attested, though he does not accept them as related: *Tharawal language, Tharawal *Dhurga language, Dhurga *Dyirringanj language, Dyirringanj *Thawa language, Thawa Claire Bowern (2011) lists three, among the Yuin languages:Bowern, Claire. 2011.How Many Languages Were Spoken in Australia?, ''Anggarrgoon: Australian languages on the web'', December 23, 2011correctedFebruary 6, 2012) * Dharawal * Dhurga * Thawa Speakers Peoples who spoke these languages include: Clans and Families of The Northern Dharawal *Noron-Geragal *Targarigal *Goonamattagal *Wodi Wodi *Gweagal (Geawegal) South Coast (New South Wales), New South Wales south coast group *Dharawal *Dhurga people, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awabakal Language
Awabakal (also Awabagal or the Hunter River – Lake Macquarie, often abbreviated HRLM language) is an Australian Aboriginal language that was spoken around Lake Macquarie (New South Wales), Lake Macquarie and Newcastle, New South Wales, Newcastle in New South Wales. The name is derived from ''Awaba'', which was the native name of the lake. It was spoken by Awabakal and Wonnarua peoples. It was studied by missionary Lancelot Threlkeld in the 19th century, who wrote a grammar of the language, but the spoken language had died out before 21st-century language revival, revival efforts. Classification Awabakal is a Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama–Nyungan language, most closely related to the Worimi language, within the Yuin–Kuric languages, Yuin–Kuric group of Pama–Nyungan. History Awabakal was studied by the Reverend Lancelot Threlkeld from 1825 until his death in 1859, producing a grammar and dictionary in ''An Australian Grammar'' in 1834. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worimi Language
The Gathang language, also spelt Gadjang, Kattang, Kutthung, Gadhang, Gadang and previously known as Worimi (also spelt Warrimay), is an Australian Aboriginal language or group of dialects. The three known dialects are Birrbay, Guringay, and Warrimay, which are used by the Worimi, Guringay, and Birrbay peoples. It went extinct during the latter half of the 20th century, but has been revived in the 21st century. History and status After the colonisation of Australia, many of the hundreds of Aboriginal languages fell into disuse. The Worimi people comprised 18 clan groups (''ngurras''), all of whom spoke Gathang. The four ngurras of the Port Stephens area moved to the settlement at Carrington to work at the Australian Agricultural Company, and over the years lost their language and culture as they learnt European ways. Many Worimi people were forced into missions and reserves. In 1887: E.M. Curr published the first word list of the Gathang language, which had been compiled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worimi Languages
Worimi is a small family of two to five mostly extinct Australian Aboriginal languages of New South Wales. * Awabakal, spoken around Lake Macquarie in New South Wales. Awabakal was studied by Reverend Lancelot Threlkeld from 1825 until his death in 1859, assisted by Biraban, the tribal leader, and parts of the Bible were translated into the language. For example, the ''Gospel of Mark'' begins: "Kurrikuri ta unni Evanelia Jesu úmba Krist koba, Yenal ta noa Eloi úmba." The language is currently in early stages of revival. * Gadjang (Worimi), previously extinct, in the early stages of revitalisation, spoken by the Worimi people, from the eastern Port Stephens and Great Lakes The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ... regions of coastal New South Wales. The languages ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkinjung Language
Darkinjung (Darrkinyung; many other spellings; see below) is an Australian Aboriginal language, the traditional language of the Darkinjung people. While no audio recordings of the language survive, several researchers have compiled wordlists and grammatical descriptions. It has been classified as a language no longer fully spoken and it can be classified as needing a language renewal program. It was spoken adjacent to Dharuk, Wiradhuri, Gamilaraay, and Awabakal. The Darkinjung tribe occupied a small part of southeastern Australia inside what is now the New South Wales area. They likely inhabited a considerable tract of land within Hunter, Northumberland, and Cook counties. Alternate names The name of the language has various spellings as recorded by both Mathews and W.J. Enright, among others, who worked of documentation from the 19th century: * ''Darkinjang'' (Tindale 1974) * ''Darkinjung'' * ''Darkiñung'' (Mathews 1903) * ''Darrkinyung'' * ''Darginjang'' * ''Darginyung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney Language
The Dharug language, also spelt Darug, Dharuk, and other variants, and also known as the Sydney language, Gadigal language ( Sydney city area), is an Australian Aboriginal language of the Yuin–Kuric group that was traditionally spoken in the region of Sydney, New South Wales, until it became extinct due to effects of colonisation. It is the traditional language of the Dharug people. The Dharug population has greatly diminished since the onset of colonisation. The term Eora language has sometimes been used to distinguish a coastal dialect from hinterland dialects, but there is no evidence that Aboriginal peoples ever used this term, which simply means "people". Some effort has been put into reviving a reconstructed form of the language. Name The speakers did not use a specific name for their language prior to settlement by the First Fleet. The coastal dialect has been referred to as Iyora (also spelt as Iora or Eora), which simply means "people" (or Aboriginal people), whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friendly Female Koala
Friendly may refer to: Places * Friendly, West Yorkshire, a settlement in Calderdale, West Yorkshire, England * Friendly, Maryland, an unincorporated community in the United States * Friendly, Eugene, Oregon, a neighborhood in the United States * Friendly, West Virginia, a town in the United States * Friendly Islands or Tonga Other uses * Environmentally friendly, goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that claim reduced, minimal, or no harm upon ecosystems or the environment * Friendly (surname) * Friendly (musician), Australian-born musician * Friendly (sport) or exhibition game, a game of association football or bandy that has no consequence in a wider competition * Friendly's, an American restaurant chain * Friendly Center, a shopping mall in Greensboro, North Carolina, United States * Friendly Hall, a building on the University of Oregon campus * Friendly High School, a public high school in Fort Washington, Maryland, United States * Friendly number, in mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandangara People
The Gandangara people, also spelled Gundungara, Gandangarra, Gundungurra and other variations, are an Aboriginal Australian people in south-eastern New South Wales, Australia. Their traditional lands include present day Goulburn, Wollondilly Shire, The Blue Mountains and the Southern Highlands. Name The ethnonym ''Gundangara'' combines lexical elements signifying both "east" and "west". Language The first attempt at a brief description of the Gundangara language was undertaken by R. H. Mathews in 1901. The language is classified as a subset of the Yuin-Kuric branch of the Pama-Nyungan language family, and is very close to Ngunnawal. Country The Gandangara lived throughout an area covering an estimated in the south-east region of New South Wales. According to Norman Tindale, their lands encompassed Goulburn and Berrima, running down the Nepean River (''Wollondilly'') until the vicinity of Camden. This includes the catchments of the Wollondilly and Coxs rivers, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngunnawal People
The Ngunnawal people, also spelt Ngunawal, are an Aboriginal people of southern New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory in Australia. Language Ngunnawal and Gundungurra are Australian Aboriginal languages from the Pama-Nyungan family, the traditional languages of the Ngunnawal and Gandangara peoples respectively. The two varieties are very closely related, being considered dialects of the one (unnamed) language, in the technical, linguistic sense of those terms. One classification of these varieties groups them with Ngarigo, as one of several Southern Tableland languages of New South Wales. Country When first encountered by European colonisers in the 1820s, the Ngunawal-speaking Indigenous people lived around this area. Their tribal country according to the early ethnographer, R. H. Mathews, stated their country extended from Goulburn to Yass and Boorowa southwards as far as Lake George to the east and Goodradigbee to the west. To the south of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngarigo People
The Ngarigo people (also spelt Garego, Ngarego, Ngarago, Ngaragu, Ngarigu, Ngarrugu or Ngarroogoo) are Aboriginal Australian people of southeast New South Wales, whose traditional lands also extend around the present border with Victoria. They are named for their language, Ngarigo, which in the 19th century was said to be spoken by the Nyamudy people (also known as Namwich or Yammoitmithang). Language Ngarigu has been classified by linguist Robert Dixon as one of two Aboriginal Australian languages of the Southern New South Wales Group, the other being Ngunawal/Gundungurra. It was spoken in the area of Tumut by the Walgalu, in the Canberra-Queanbeyan- Upper Murrumbidgee region by people variously called the ''Nyamudy'', the ''Namwich'' or the ''Yammoitmithang'', and also as far south as Victoria's Omeo district. The heartland of Ngarigo speakers, in a more restricted sense, was Monaro. John Lhotsky, Charles du Vé, John Bulmer, George Augustus Robinson, Alfred W. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |