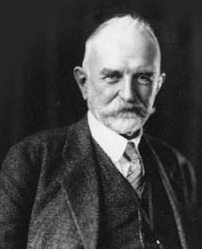|
Urban Sociology
Urban sociology is the sociological study of cities and urban life. One of the field’s oldest sub-disciplines, urban sociology studies and examines the social, historical, political, cultural, economic, and environmental forces that have shaped urban environments. Like most areas of sociology, urban sociologists use statistical analysis, observation, archival research, census data, social theory, interviews, and other methods to study a range of topics, including poverty, racial residential segregation, economic development, migration and demographic trends, gentrification, homelessness, blight and crime, urban decline, and neighborhood changes and revitalization. Urban sociological analysis provides critical insights that shape and guide urban planning and policy-making. The philosophical foundations of modern urban sociology originate from the work of sociologists such as Karl Marx, Ferdinand Tönnies, Émile Durkheim, Max Weber and Georg Simmel who studied and theorized t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Singapore National Day Parade 2011 Fireworks
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert E
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioural Sciences
Behavioural science is the branch of science concerned with human behaviour.Hallsworth, M. (2023). A manifesto for applying behavioural science. ''Nature Human Behaviour'', ''7''(3), 310-322. While the term can technically be applied to the study of behaviour amongst all living organisms, it is nearly always used with reference to humans as the primary target of investigation (though animals may be studied in some instances, e.g. invasive techniques). The behavioural sciences sit in between the conventional natural sciences and social studies in terms of scientific rigor. It encompasses fields such as psychology, neuroscience, linguistics, and economics.Sanders, M., Snijders, V., & Hallsworth, M. (2018). Behavioural science and policy: where are we now and where are we going?. ''Behavioural Public Policy'', ''2''(2), 144-167. Scope The behavioural sciences encompass both natural and social scientific disciplines, including various branches of psychology, neuroscience and bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Inference
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is sampled from a larger population. Inferential statistics can be contrasted with descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics is solely concerned with properties of the observed data, and it does not rest on the assumption that the data come from a larger population. In machine learning, the term ''inference'' is sometimes used instead to mean "make a prediction, by evaluating an already trained model"; in this context inferring properties of the model is referred to as ''training'' or ''learning'' (rather than ''inference''), and using a model for prediction is referred to as ''inference'' (instead of ''prediction''); se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subculture Theories
A subculture is a group of people within a cultural society that differentiates itself from the values of the conservative, standard or dominant culture to which it belongs, often maintaining some of its founding principles. Subcultures develop their own norms and values regarding cultural, political, and sexual matters. Subcultures are part of society while keeping their specific characteristics intact. Examples of subcultures include hippies, hipsters (which include 1940s original parent subculture), goths, steampunks, bikers, punks, skinheads, gopnik, hip-hoppers, metalheads, cosplayers, otaku, otherkin, furries, hackers and more. The concept of subcultures was developed in sociology and cultural studies. Subcultures differ from countercultures. Definitions The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines subculture, in regards to sociological and cultural anthropology, as "an identifiable subgroup within a society or group of people, esp. one characterized by beliefs or interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (social)
A social norm is a shared standard of acceptance, acceptable behavior by a group. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into wikt:rule, rules and laws. Social normative influences or social norms, are deemed to be powerful drivers of human behavioural changes and well organized and incorporated by major theories which explain human behaviour. Institutions are composed of multiple norms. Norms are shared social beliefs about behavior; thus, they are distinct from "ideas", "attitudes", and "values", which can be held privately, and which do not necessarily concern behavior. Norms are contingent on context, social group, and historical circumstances. Scholars distinguish between regulative norms (which constrain behavior), constitutive norms (which shape interests), and prescriptive norms (which prescribe what actors ''ought'' to do). The effects of norms can be determined by a logic of appropriateness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roles
A role (also rôle or social role) is a set of connected behaviors, rights, obligations, beliefs, and norms as conceptualized by people in a social situation. It is an expected or free or continuously changing behavior and may have a given individual social status or social position. It is vital to both functionalist and interactionist understandings of society. Social role theory posits the following about social behavior: # The division of labour in society takes the form of the interaction among heterogeneous specialized positions, we call roles. # Social roles included appropriate and permitted forms of behavior and actions that recur in a group, guided by social norms, which are commonly known and hence determine the expectations for appropriate behavior in these roles, which further explains the position of a person in the society. # Roles are occupied by individuals, who are called actors. #When individuals approve of a social role (i.e., they consider the role legit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabula Rasa
''Tabula rasa'' (; Latin for "blank slate") is the idea of individuals being born empty of any built-in mental content, so that all knowledge comes from later perceptions or sensory experiences. Proponents typically form the extreme "nurture" side of the nature versus nurture debate, arguing that humans are born without any "natural" psychological traits and that all aspects of one's personality, social and emotional behaviour, knowledge, or sapience are later imprinted by one's environment onto the mind as one would onto a wax tablet. This idea is the central view posited in the theory of knowledge known as empiricism. Empiricists disagree with the doctrines of innatism or rationalism, which hold that the mind is born already in possession of specific knowledge or rational capacity. Etymology ''Tabula rasa'' is a Latin phrase often translated as ''clean slate'' in English and originates from the Roman '' tabula'', a wax-covered tablet used for notes, which was blanked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of United States cities by population, third-most populous city in the United States after New York City and Los Angeles. As the county seat, seat of Cook County, Illinois, Cook County, the List of the most populous counties in the United States, second-most populous county in the U.S., Chicago is the center of the Chicago metropolitan area, often colloquially called "Chicagoland" and home to 9.6 million residents. Located on the shore of Lake Michigan, Chicago was incorporated as a city in 1837 near a Chicago Portage, portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River, Mississippi River watershed. It grew rapidly in the mid-19th century. In 1871, the Great Chicago Fire destroyed several square miles and left more than 100,000 homeless, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbolic Interaction
Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to humans' particular use of shared language to create common symbols and meanings, for use in both intra- and interpersonal communication. It is particularly important in microsociology and social psychology. It is derived from the American philosophy of pragmatism and particularly from the work of George Herbert Mead, as a pragmatic method to interpret social interactions. According to Mead, symbolic interactionism is "The ongoing use of language and gestures in anticipation of how the other will react; a conversation". Symbolic interactionism is "a framework for building theory that sees society as the product of everyday interactions of individuals". In other words, it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds, and in return, how these worlds shape individual behaviors. It is a framework that help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Herbert Mead
George Herbert Mead (February 27, 1863 – April 26, 1931) was an American philosopher, Sociology, sociologist, and psychologist, primarily affiliated with the University of Chicago. He was one of the key figures in the development of pragmatism. He is regarded as one of the founders of symbolic interactionism, and was an important influence on what has come to be referred to as the Chicago school (sociology), Chicago School of Sociology. Biography George Herbert Mead was born on February 27, 1863, in South Hadley, Massachusetts. He was raised in a Protestantism, Protestant, middle-class family comprising his father, Hiram Mead, his mother, Elizabeth Storrs Mead (née Billings), and his sister Alice. His father was a former Congregationalist pastor from a lineage of farmers and clergymen and who later held the chair in Sacred Rhetoric and Pastoral Theology at Oberlin College's theological seminary. Elizabeth taught for two years at Oberlin College and subsequently, from 1890 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Geography
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography which studies spatial relationships between human communities, cultures, economies, and their interactions with the environment, examples of which include urban sprawl and urban redevelopment. It analyzes spatial interdependencies between social interactions and the environment through Qualitative geography, qualitative and Quantitative geography, quantitative methods. This multidisciplinary approach draws from sociology, anthropology, economics, and environmental science, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the intricate connections that shape lived spaces. History The Royal Geographical Society was founded in England in 1830. The first professor of geography in the United Kingdom was appointed in 1883, and the first major geographical intellect to emerge in the UK was Halford John Mackinder, appointed professor of geography at the London School of Economics in 1922. The National Geographic Societ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |