|
Tropical Cyclones In 2021
During 2021, tropical cyclones formed in seven major bodies of water, commonly known as tropical cyclone basins. Tropical cyclones will be assigned names by various weather agencies if they attain maximum sustained winds of . During the year, 136 systems have formed and 94 were named, including one subtropical depression and excluding one system, which was unofficial. Cyclones Gulab and Shaheen, One storm was given two names by the same Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre, RSMC. The most intense storm of the year was Typhoon Surigae, with maximum 10-minute sustained wind speeds of and a minimum pressure of . The deadliest tropical cyclone was Typhoon Rai, which caused 410 fatalities in the Philippines and 1 in Vietnam, while the costliest was Hurricane Ida, which caused an estimated $75.25 billion United States dollar, USD in damage after striking Louisiana and the Northeastern United States. Like last year, 2021 had an above average amount of tropical cyclones globally. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Danilo (2021)
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine Effect of Sun angle on climate, directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or Polar regions of Earth, polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Axial tilt#Earth, Earth's axial tilt; the width of the tropics (in latitude) is twice the tilt. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). Due to the overhead sun, the tropics insolation, receive the most solar energy over the course of the year, and consequently have the highest temperatures on the planet. Even when not directly overhead, the sun is still close to overhead throughout the year, therefore the tropics also have the lowest seasonal variation on the planet; "winter" and "summer" lose their temperature contrast. Instead, seasons are more commonly divided Season#Tropical, by precipitation variations than by temperature variations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifteenth-most populous country. One of two communist states in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulated Cyclone Energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used to compare overall activity of tropical cyclones, utilizing the available records of windspeeds at six-hour intervals to synthesize storm duration and strength into a single index value. The ACE index may refer to a single storm or to groups of storms such as those within a particular month, a full season or combined seasons. It is calculated by summing the square of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds, as recorded every six hours, but only for windspeeds of at least tropical storm strength (≥ 34 kn; 63 km/h; 39 mph); the resulting figure is divided by 10,000 to place it on a more manageable scale. The calculation originated as the Hurricane Destruction Potential (HDP) index, which sums the squares of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds while at hurricane strength, at least 64 knots (≥ 119 km/h; 74 mph) at six-hour recorded intervals across an entire season. The HDP index was later modified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclones In 2003
During 2003, tropical cyclones formed within seven different tropical cyclone basins, located within various parts of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. During the year, a total of 129 systems formed with 85 of these developing further and were tropical cyclone naming, named by the responsible warning centre. The strongest tropical cyclone of the year was Cyclone Inigo, which was estimated to have a minimum barometric pressure of and was tied with Cyclone Gwenda for being the most intense recorded cyclone in the List of Australian region cyclone seasons, Australian region in terms of pressure, with the possible exception of Cyclone Mahina. So far, 26 Saffir-Simpson scale, Category 3 tropical cyclones formed, including six Saffir-Simpson scale, Category 5 tropical cyclones formed in 2003, tying Tropical cyclones in 2021, 2021. The accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index for the 2003 (seven basins combined), as calculated by Colorado State University was 833 units. Tropical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffir–Simpson Scale
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) is a tropical cyclone intensity scale that classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds. This measuring system was formerly known as the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, or SSHS. To be classified as a hurricane, a tropical cyclone must have one-minute-average maximum sustained winds at above the surface of at least 74 mph (64 kn, 119 km/h; Category 1). The highest classification in the scale, Category 5, consists of storms with sustained winds of at least 157 mph (137 kn, 252 km/h). The classifications can provide some indication of the potential damage and flooding a hurricane will cause upon landfall. The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale is based on the highest wind speed averaged over a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
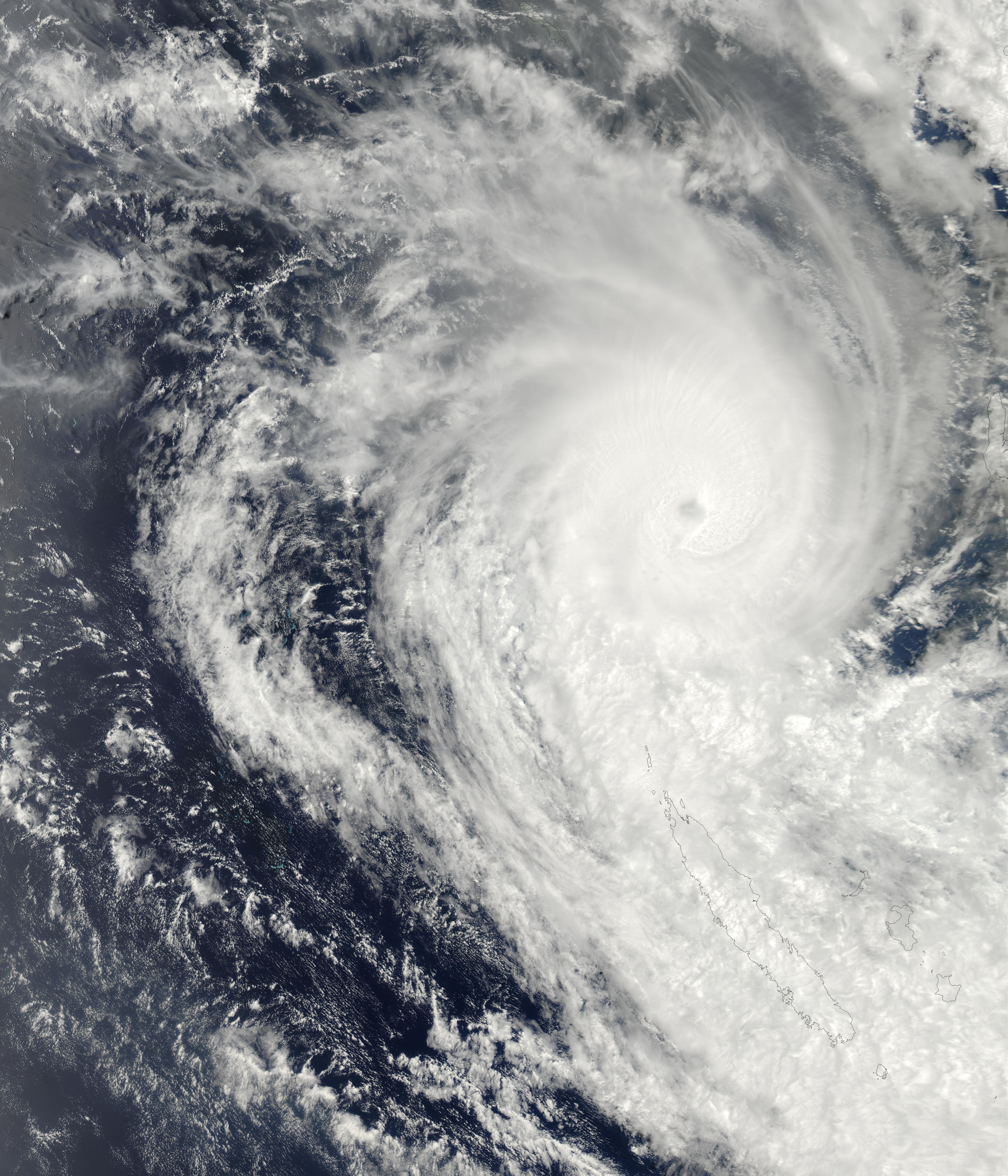
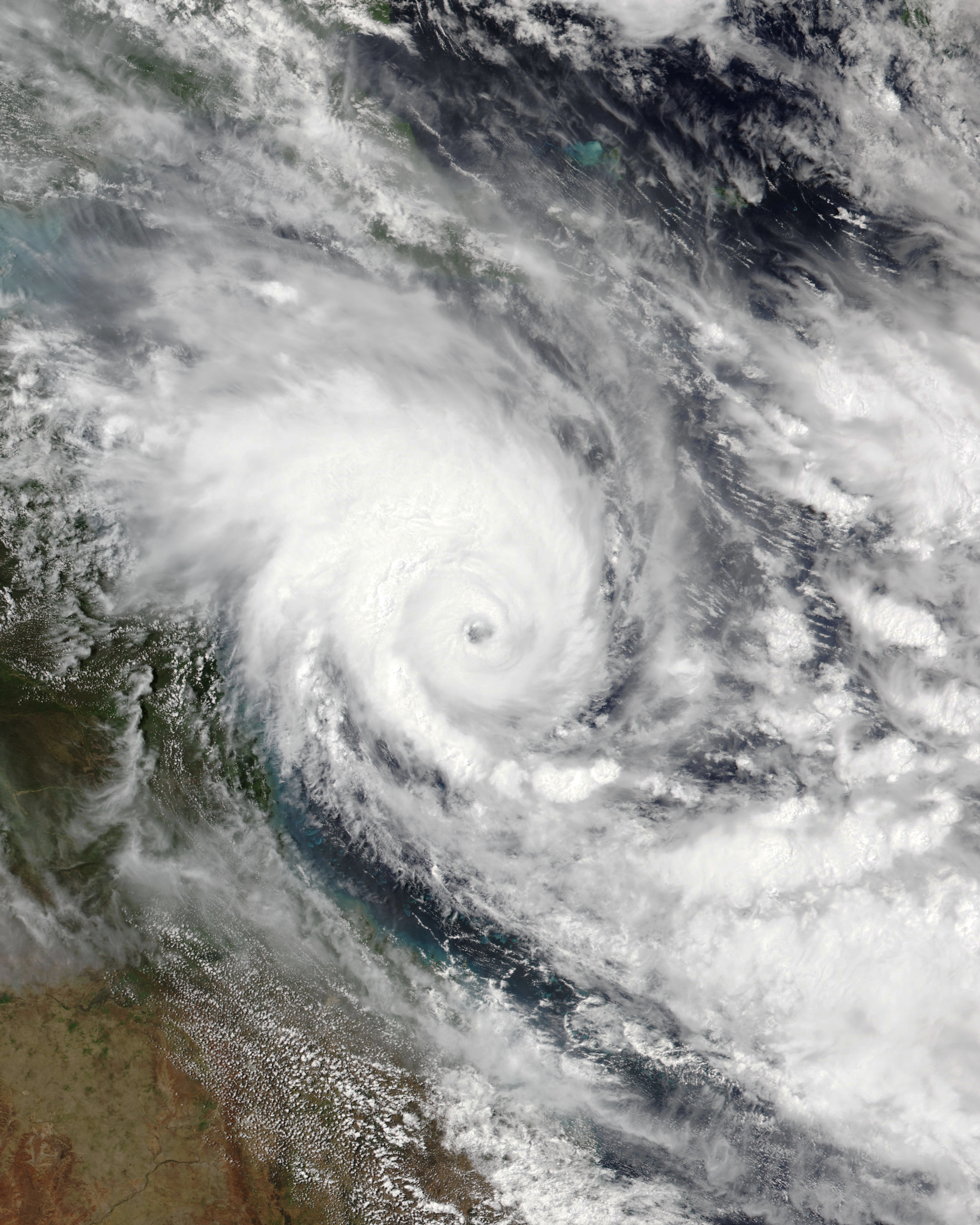
Cyclone Niran
Severe Tropical Cyclone Niran was a very powerful tropical cyclone that brought severe impacts to extreme Northeastern Australia and nearly made landfall in New Caledonia in February and March 2021. The sixth tropical cyclone and the second severe tropical cyclone of the 2020–21 Australian region cyclone season, while being the third severe tropical cyclone of the annual South Pacific cyclone season, Niran was the second Category 5 severe tropical cyclone in the South Pacific cyclone season, following Cyclone Yasa. The cyclone formed from a tropical low in the Coral Sea on 27 February. The tropical low gradually intensified while stalling offshore of Queensland for several days, although disorganized at the time. Early on 3 March, Niran pulled away from the coast of Australia, while it started undergoing rapid intensification. Eventually, Niran reached its peak intensity as a Category 5 tropical cyclone on both the Australian Tropical Cyclone Scale and the Saffir–Simpson scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Faraji
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2023 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2023 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an above-average and deadly season, becoming the most active since 2019 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, 2019, with nine depressions and six cyclonic storms forming. It was the deadliest since 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, 2017, mostly due to Cyclone Mocha, and had the second-highest accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) in the basin, after the 2019 cyclone season, which was itself the second most active North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone, North Indian Ocean cyclone season on record in terms of cyclonic storms. The 2023 season also had the most extremely severe cyclonic storms on record, tying with 1999 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, 1999 and 2019. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with the peak from May to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2021 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active Pacific hurricane season, with above-average activity in terms of number of named storms, but below-average activity in terms of major hurricanes, as 19 named storms, 8 hurricanes, and 2 major hurricanes formed in all. It also had a near-normal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE). The season officially began on May 15, 2021 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean (east of from 140°W), and on June 1, 2021, in the Central Pacific (from 140°W to the International Date Line) in the Northern Hemisphere. The season ended in both regions on November 30, 2021. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific and are adopted by convention. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated by the formation of Tropical Storm Andres on May 9, which was the earliest forming tropical storm on record in the Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 2021 Atlantic hurricane season was the third-most active Atlantic hurricane season on record in terms of number of tropical cyclones, although many of them were weak and short-lived. With 21 named storms forming, it became the second season in a row and third overall in which the designated 21-name list of storm names was exhausted. Seven of those storms strengthened into hurricanes, four of which reached major hurricane intensity, which is slightly above-average. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period in each year when most Atlantic tropical cyclones form. However, subtropical or tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the development of Tropical Storm Ana on May 22, making this the seventh consecutive year in which a storm developed outside of the official season. Three named storms formed in June, tying the record for the most to develop i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic coast of North America, the region borders Canada to its north, the Southern United States to its south, the Midwestern United States to its west, and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The Northeast is one of the four regions defined by the U.S. Census Bureau for the collection and analysis of statistics. The Census Bureau defines the region as including the six New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont, and three lower North-Eastern states of New Jersey, New York (state), New York, and Pennsylvania. Some expanded definitions of the region include Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic locations such as Delaware, Maryland, Northern Virginia, and Washington, D.C. The regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |