|
Trichomycteridae
Trichomycteridae is a family of catfishes commonly known as pencil catfishes or parasitic catfishes. This family includes the candiru fish (''Vandellia cirrhosa''), feared by some people for its alleged habit of entering into the urethra of humans. They are one of the few parasitic chordates. Another species is the life monsefuano (''Trichomycterus punctulatus'') which was important to the Moche culture and still an important part of Peruvian cuisine.FondazioneslowfoodLife monsefuano.Retrieved 28 April 2017. This family is prohibited from being imported into various parts of the United States. Taxonomy The Trichomycteridae comprise about 42 genera and 286 species described. It is the second-most diverse family of the superfamily Loricarioidea. Numerous species still remain undescribed, such as the human-biting candiru. The monophyly of Trichomycteridae is well-supported. The family is divided into eight subfamilies. The only subfamily that is not monophyletic is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ituglanis
''Ituglanis'' is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family (biology), family Trichomycteridae native to South America. Their greatest diversity seems to occur in the Amazon River basin.Datovo, A. & Landim, M.I. (2005)''Ituglanis macunaima'', a new catfish from the rio Araguaia basin, Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae).''Neotropical Ichthyology, 3 (4): 455–464.'' Most species inhabit leaf litter, with several species Cavefish, living in caves. This genus was first erected for nine species previously classified in ''Trichomycterus''.Sarmento-Soares, L.M., Martins-Pinheiro, R.F., Aranda, A.T. & Chamon, C.C. (2006)''Ituglanis cahyensis'', a new catfish from Bahia, Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae).''Neotropical Ichthyology, 4 (3): 309-318.'' ''Ituglanis'' is believed to be a monophyly, monophyletic group. There may be two monophyletic groups within this genus. ''Ituglanis'' is currently considered a member of the subfamily Trichomycterinae though its position as a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
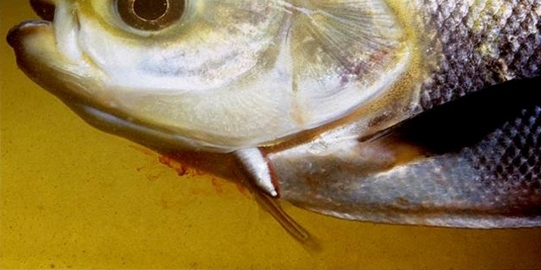
Vandellia Cirrhosa
Candiru (''Vandellia cirrhosa''), also known as cañero, toothpick fish, or vampire fish, is a species of parasitic freshwater catfish in the family Trichomycteridae native to the Amazon basin where it is found in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. The name "candiru" is also used to refer to the entire genus '' Vandellia''. This species is known for an alleged tendency to invade and parasitize the human urethra and other bodily openings; however, despite ethnological reports dating back to the late 19th century, the first documented case of the removal of a candiru from a human urethra did not occur until 1997, and even that incident has remained a matter of controversy. Description ''Vandellia cirrhosa'' is a small, freshwater catfish. Members of the genus ''Vandellia'' can reach up to in standard length, but some others can grow to around . The fish has an elongated body with an anterior dorsal fin and pelvic fin, and an anal fin slightly larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoglanidinae
The Sarcoglanidinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera: '' Ammoglanis'', '' Malacoglanis'', '' Microcambeva'', '' Sarcoglanis'', '' Stauroglanis'', and '' Stenolicmus''. Taxonomy The subfamily Sarcoglanidinae was first established in 1966 for ''Sarcoglanis simplex'' and ''Malacoglanis gelatinosus''. A third species of the subfamily – ''Stauroglanis gouldingi'', was described about 25 years later. Descriptions of additional species have followed, though most genera remain monotypic. The relationships of the genus ''Ammoglanis'' with other sarcoglanidines are not well-established; however, this genus is currently included within Sarcoglanidinae. This subfamily has been proposed to have a sister group relationship to Glanapteryginae. Like the members of this subfamily, many glanapterygines are sand-dwelling fish. Distribution and habitat All genera except ''Microcambeva'' are endemic to the Amazon River; ''Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers", with some seemingly not having them. Siluriformes as a whole are Fish scale, scale-less, with neither the Armoured catfish, armour-plated nor the naked species having scales. This order of fish are Autapomorphy, defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish range in size and behavior from the three List of largest fish, largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivorous and scavenging bottom feeders, down to tiny ectoparasitic species known as the Candiru (fish), candirus. In the Southern United States, catfish species may be known by a variety of slang names, such as "mud cat", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copionodontinae
The Copionodontinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes two genera, '' Copionodon'' and '' Glaphyropoma''. Classification Copionodontines are remarkably primitive in body form, and lack many of the synapomorphies previously used to diagnose the family Trichomycteridae. Little doubt exists that the Copionodontinae form a monophyletic group, diagnosed by several unambiguous synapomorphies, including a unique dentition composed of spatulate teeth not seen anywhere else in the Trichomycteridae. A few characters also support the genera ''Copionodon'' and ''Glaphyropoma'' as monophyletic subunits. Distribution and ecology Copionodontines occur exclusively in the Chapada Diamantina; though the plateau is drained by four river basins, so far, these fish are exclusively found in drainages associated with the Paraguaçu River The Paraguaçu River () is a river in Bahia state, located in eastern Brazil. It runs from the Chapada D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichogeninae
''Trichogenes'' is a genus of pencil catfishes. It is currently the only genus within the subfamily ''Trichogeninae''. A third species, ''T. beagle'', was described in 2020 from archival material of unknown origin. The occurrence of the new species in the wild is unknown. Etymology The name ''Trichogenes'' is composed of the words 'Tricho', referring to its family, the Trichomycteridae, and 'genes', referring to the genus '' Helogenes'' due to its superficial resemblance to the latter. Distribution ''Trichogenes'' species are endemic to Brazil. Species There are currently three recognized species in this genus: * '' Trichogenes beagle'' * '' Trichogenes claviger'' de Pinna, Helmer, Britski & Nunes, 2010 * ''Trichogenes longipinnis ''Trichogenes longipinnis'' (the long-finned cambeva), is a species of catfish (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. ''T. longipinnis'' is endemic to coastal streams in the Atlantic forest between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomycterinae
The Trichomycterinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera, '' Bullockia'', '' Hatcheria'', '' Rhizosomichthys'', and '' Eremophilus'', all monotypic, '' Silvinichthys'' with seven species, and '' Trichomycterus'', with over 170 species. The former five genera are diagnosed by putatively apomorphic characters, whereas ''Trichomycterus'' is defined by the lack of those specializations and is likely not monophyletic. This subfamily has historically served as much of a wastebasket for trichomycterids that lack the specializations of the other subfamilies. Species of Trichomycterinae dwell in headwaters and small, cold clear water streams running over stony beds. Due to the patchy distribution of their habitats, trichomycterines generally have restricted geographic distributions, thus display a high level of endemism Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glanapteryginae
The Glanapteryginae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes four genera, '' Glanapteryx'', '' Listrura'', '' Pygidianops'', and '' Typhlobelus''. Phylogeny Monophyly of the subfamily is supported by five synapomorphies involving reductions in the fins, caudal skeleton, and laterosensory system. It has been proposed that the sister group to this subfamily is the Sarcoglanidinae. ''Listrura'' is the sister group to the remainder of the subfamily. ''Glanapteryx'' is sister to a clade formed by the sister taxa ''Pygidianops'' and ''Typhlobelus''. Distribution ''Glanapteryx'', ''Pygidianops'', and ''Typhlobelus'' are distributed in the Orinoco and Amazon River basins. ''Listrura'' species are from Brazil, outside of the Amazon River basin. However, the distribution of glanapterygines may be greater than previously thought. Description Most of the subfamily is constituted by 'miniaturized' species. Though miniaturized fish usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegophilinae
The Stegophilinae are a subfamily of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes 12 genera: '' Acanthopoma'', '' Apomatoceros'', '' Haemomaster'', '' Henonemus'', '' Homodiaetus'', '' Megalocentor'', '' Ochmacanthus'', '' Parastegophilus'', '' Pareiodon'', '' Pseudostegophilus'', '' Schultzichthys'', and '' Stegophilus''. A monophyletic group within the Stegophilinae is supported by two characteristics of the lateral line, including ''Acanthopoma'', ''Henonemus'', ''Megalocentor'', ''Pareiodon'', ''Parastegophilus'', and ''Pseudostegophilus''. ''Acanthopoma'' and ''Henonemus'' have a sister group relationship. The Stegophilinae are widely distributed in the main South American river basins, including the Amazon, Orinoco, São Francisco, Paraná-Paraguay, and those of southern Brazil. Eight of the genera are distributed in Venezuela. Stegophilines are sometimes considered candirú, so are considered parasites or semiparasites, because of their pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleronema (fish)
''Scleronema'' is a genus of pencil catfishes native to South America. They are a member of the subfamily Trichomycterinae. Species of Scleronema are geographically distributed in the La Plata basin and Atlantic coastal drainages from Southern Brazil, Southern Paraguay, Northeastern Argentina and Uruguay. They inhabit rivers or streams with sand or gravel-bottoms across the Pampa grasslands. In Greek, Scleronema means "hard filament." Species There are currently three recognized species in this genus: * '' Scleronema angustirostre'' ( Devincenzi, 1942) * '' Scleronema minutum'' ( Boulenger, 1891) * '' Scleronema operculatum'' C. H. Eigenmann, 1917 ''S. minutum'' and ''S. operculatum'' both originate from Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loricarioidea
Loricarioidei is a suborder of catfishes ( order Siluriformes). It contains the six families Trichomycteridae, Nematogenyiidae, Callichthyidae, Scoloplacidae, Astroblepidae, and Loricariidae. Some schemes also include Amphiliidae. This superfamily, including Amphiliidae, includes about 156 genera and 1,187 species. Taxonomy Loricarioidea was previously considered a part of Siluroidei, a clade of all catfishes excluding Diplomystidae. In Nelson, 2006, this grouping is sister to the superfamily Sisoroidea. However, in a recent molecular analysis, it was determined that the suborder Loricarioidei (not including Amphiliidae) is sister to a group including Diplomystidae and Siluroidei. Amphiliidae, in this analysis, was found to be much more closely related to Mochokidae or Malapteruridae. It is disputed whether Loricarioidea or Diplomystidae are the most basal group of catfish, with molecular studies favoring the former while morphological studies favor the latter. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |