|
Romodanovsky Family
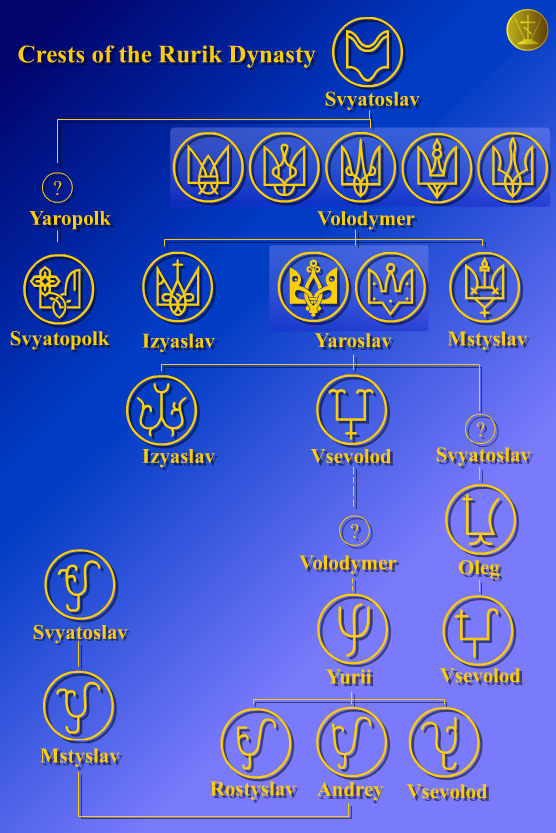
The House of Romodanovsky () was a Russian noble family descending from sovereign rulers of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma. Their progenitor was Prince Vasily Fyodorovich Starodubsky (Василий Фёдорович Стародубский) who changed his name to Romodanovsky after his ''votchina'' (estate) of Romodanovo. They claimed descent from the Rurikids. Although the family was one of the first Rurikids to enter the service of the prince of Moscow, it was in the 17th century that they finally rose to the highest ranks of Muscovite Russia. Early members Among Vasily's sons, one was Ivan III's okolnichi, another sat in the Boyar Duma during Vasily III's reign. Their nephew was sent by Ivan the Terrible as a Russian ambassador to Copenhagen. The latter's nephew, Prince Ivan Petrovich Romodanovsky, was killed by the Kalmucks on his way from Persia Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU COA Romodanovsky
Ru, ru, or RU may refer to: Russia * Russia (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code) * Russian language (ISO 639 alpha-2 code) * .ru, the Internet country code top-level domain for Russia China * Rù (入), the entering tone in Chinese language phonetics * Rú (儒), a Chinese language term for Confucianism * Ru (surname) (茹), a Chinese surname * Ru River (汝), in Henan, China * Ru ware, a type of Chinese pottery Educational institutions * Rajasthan University in Rajasthan, India * Radboud University Nijmegen, in Nijmegen, Netherlands * Radford University, in Virginia, USA * Rai University in Gujarat, India * Rajshahi University in Bangladesh * Rama University in India * Ramkhamhaeng University in Thailand * Rangoon University in Burma * Regis University in Colorado, USA * Reykjavík University Iceland * Rhodes University in Grahamstown, South Africa * Rockefeller University in New York, USA * Rockhurst University in Missouri, USA * Roosevelt University in Chicago, Illinois, USA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starodub-on-the-Klyazma
Starodub-on-the-Klyazma ( rus, Староду́б-на-Кля́зьме, p=stərɐˈdub nə ˈklʲæzʲmʲɪ) was a prominent urban centre of Russian Opolye from the 12th until the 14th century. Like so many towns in the vicinity, it was named by migrating population for a southern city they came from, in this case, for Starodub in Severia. The town was on the bank of the Klyazma River about twelve kilometres from the modern-day Kovrov. Nowadays, the village of Klyazminsky Gorodok stands on the spot. During the Mongol invasion of Russia, the youngest of Vsevolod III's sons, Ivan, made Starodub his seat (1238). His descendants ruled the tiniest of Russian principalities for more than a century, desperately trying to fend off attacks by two powerful neighbours—Muscovy and Nizhny Novgorod. Their ephemeral power came to an end in the 1370s, when the town was eventually annexed by Dmitry Donskoy. Thereupon numerous scions of Starodub dynasty moved to Moscow, where they for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votchina
A ''votchina'' ( , ) or ''otchina'' ( – from the word for ''father'') was a land estate that could be inherited. The term ''votchina'' was also used to describe the lands of a prince (''knyaz''). The system disappeared in Russia largely due to reforms in the 18th-century. Terminology In medieval sources, noble landowners and princes would often refer to a ''votchina'' or ''otchina'' in connection to their own lands. The term ''votchina'' is now generally used in Russian historical terminology in reference to the main form of feudal landownership. From the 15th century, there were two legally distinct forms of land that could be owned by Russian nobles: a ''votchina'' (hereditary land) and ''pomestye'' (service land). Service lands were given on condition of service, and so it reverted to the state upon the owner's death, while hereditary lands were considered to be family property. However, by the 16th century, it was common for sons or nephews to take over service land when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rurikids
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' and its principalities following its disintegration. The ''Romanovichi'' ruled the southwestern territories, which were unified by Roman the Great and his son Daniel, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV as the king of Ruthenia. Galicia–Volhynia was eventually annexed by Poland and Lithuania. The northern and northeastern territories were unified by the ''Daniilovichi'' of Moscow; by the 15th century, Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde and assumed the title of sovereign of all Russia. Ivan IV was crowned as the tsar of all Russia, where the Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were eventually succeeded by the House of Romanov. As a rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Moscow
The Grand Prince of Moscow (), known as the Prince of Moscow until 1389, was the ruler of the Grand Principality of Moscow. The Moscow principality was initially established in the 13th century as an appanage within the Vladimir-Suzdal grand principality. By the late 14th century, the grand principality became a family possession of the princes of Moscow; the monarch bore the title of ''grand prince of Vladimir and Moscow'' and later the title of ''grand prince of Vladimir, Moscow and all Russia''. History The grand principality of Vladimir-Suzdal fell apart into feuding appanages over the course of the 13th century. The princes of Moscow were descendants of Daniel. As Daniel never became grand prince of Vladimir before he died in 1303, this meant that according to traditional succession practices, his descendants were ''izgoi'': his son and successor Yury of Moscow had no legitimate claim to the throne of Vladimir. This is why Tokhta Khan granted Mikhail of Tver the grand princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscovite Russia
The Grand Principality of Moscow, or Muscovy, known as the Principality of Moscow until 1389, was a late medieval Russian monarchy. Its capital was the city of Moscow. Originally established as a minor principality in the 13th century, the grand principality was transformed into a centralized Russian state in the late 15th century. Moscow became a separate principality when Daniel (), the youngest son of Alexander Nevsky, received the city and surrounding area as an appanage. By the end of the 13th century, Moscow had become one of the leading principalities within the Vladimir grand principality, alongside Tver. A struggle between the princes of Moscow and Tver began after Mikhail of Tver became grand prince in 1304. Yury () contested the title and was later made grand prince in 1318 by the khan of the Golden Horde, who held suzerainty over the princes. However, Yury lost the title four years later. Ivan I () regained the title of grand prince and was able to colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan III
Ivan III Vasilyevich (; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1462 until his death in 1505. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his blind father Vasily II before he officially ascended the throne. He multiplied the territory of his state through conquest, purchase, inheritance and the seizure of lands from his dynastic relatives, and laid the foundations of the centralized Russian state. He also renovated the Moscow Kremlin and introduced a new legal code. Ivan is credited with ending the dominance of the Tatars over Russia; his victory over the Great Horde in 1480 formally restored its independence. Ivan began using the title tsar, and used the title tentatively until the Habsburgs recognized it. While officially using "tsar" in his correspondence with other monarchs, he was satisfied with the title of grand prince at home. Through marriage to Sophia Palaiologina, Ivan made the double-hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okolnichi
Okolnichy (, ) was an old Russian court official position. According to the ''Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary'', directives on the position of ''okolnichy'' date back to the 14th century. Judging by the Muscovite records from the 16th and 17th centuries, ''okolnichy'' were entrusted with the same business in administration as boyars, with the only difference that they were placed second to boyars everywhere. While lower than boyars, it was one of the highest ranks (or positions) close to the tsar in the courts of the Moscow rulers until the government reform undertaken by Peter the Great. The word is derived from the Russian word () meaning 'close, near', in this case 'sitting close to the Tsar'. In the mid-16th century the role became second (subordinate) to boyars.Чины в Московском государстве // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyar Duma
A duma () is a History of Russia, Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions. The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were formed across Russia. The first formally constituted state duma was the State Duma (Russian Empire) , Imperial State Duma introduced to the Russian Empire by Emperor Nicholas II in 1905. The Emperor retained an absolute veto and could dismiss the State Duma at any time for a suitable reason. Nicholas dismissed the First State Duma (1906) within 75 days; January 1907 Russian legislative election , elections for a second Duma took place the following year. The Russian Provisional Government dissolved the last Imperial State Duma (the fourth Duma) in 1917 during the Russian Revolution. Since 1993, the State Duma () has functioned as the lower legislative house of the Russian Federation. Etymology The Russian word is inherited from the Proto- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily III
Vasili III Ivanovich (; 25 March 14793 December 1533) was Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1505 until his death in 1533. He was the son of Ivan III and Sophia Paleologue and was christened with the name Gavriil (). Following on the ambitions of his predecessor Ivan, Vasili conquered Pskov, Ryazan and Smolensk as well as strengthening Russian influence in Kazan and to the Volga region. Several nobles were either exiled, sentenced or executed for criticizing his policies. Foreign affairs Vasili III maintained the policies initiated by his father Ivan III, focusing much of his reign on consolidating the territorial gains achieved by Ivan. Vasili annexed the last surviving autonomous provinces: Pskov in 1510, appanage of Volokolamsk in 1513, principalities of Ryazan in 1521 and Novgorod-Seversky in 1522. Vasili also took advantage of the difficult position of Sigismund of Poland to capture Smolensk, the great eastern fortress of Lithuania (siege started 1512, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan The Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (; – ), commonly known as Ivan the Terrible,; ; monastic name: Jonah. was Grand Prince of Moscow, Grand Prince of Moscow and all Russia from 1533 to 1547, and the first Tsar of all Russia, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia from 1547 until his death in 1584. Ivan's reign was characterised by Russia's transformation from a medieval state to a fledgling empire, but at an immense cost to its people and long-term economy. Ivan IV was the eldest son of Vasili III of Russia, Vasili III by his second wife Elena Glinskaya, and a grandson of Ivan III of Russia, Ivan III. He succeeded his father after his death, when he was three years old. A group of reformers united around the young Ivan, crowning him as tsar in 1547 at the age of 16. In the early years of his reign, Ivan ruled with the group of reformers known as the Chosen Council and established the ''Zemsky Sobor'', a new assembly convened by the tsar. He also revised the Sudebnik of 1550, legal code and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |