|
Rhipiduridae
The family Rhipiduridae are small insectivorous birds of Australasia, Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent that includes the fantails and silktails. Taxonomy and systematics The family contains 55 species which are divided into four genera: * Subfamily Rhipidurinae: **''Rhipidura'' – typical fantails (51 species) *Subfamily Lamproliinae: **'' Chaetorhynchus'' – drongo fantail **'' Eutrichomyias'' – cerulean flycatcher **''Lamprolia The silktails are a group of birds endemic to Fiji. The two species ( Taveuni silktail and Natewa silktail) are placed in the genus ''Lamprolia''. They look superficially like a diminutive bird-of-paradise but are actually closely related to the ...'' – silktails (2 species) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q847173 Bird families Birds of Oceania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerulean Flycatcher
The cerulean flycatcher (''Eutrichomyias rowleyi'') is a medium-sized (up to 18 cm long), blue passerine with bright cerulean blue plumage, a bare white orbital ring, dark brown Iris (anatomy), iris, bluish black Beak, bill and pale blue-grey below. The young has a shorter tail and grey underparts. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Eutrichomyias''. Although it resembles a monarch flycatcher, it is actually related to the fantails. Taxonomy and systematics The scientific name commemorates the British explorer and ornithologist George Dawson Rowley. The cerulean flycatcher was originally described in the genus ''Zeocephus'', and until recently was known as the cerulean paradise-flycatcher. Alternate names include Rowley's flycatcher and Rowley's paradise-flycatcher. Although initially classified in Monarch flycatcher, Monarchidae, a 2017 study involving sequencing of DNA from the type specimen found that it was a member of the fantail family Rhipiduridae, being cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetorhynchus
The drongo fantail (''Chaetorhynchus papuensis''), also known as the pygmy drongo, is a species of passerine bird endemic to the island of New Guinea. It is the only species in the genus ''Chaetorhynchus''. The species was long placed within the drongo family Dicruridae, but it differs from others in that family in having twelve rectrices instead of ten. Molecular analysis also supports moving the species out from the drongo family, instead placing it as a sister species to the silktail of Fiji, and both those species in the fantail Fantails are small insectivorous songbirds of the genus ''Rhipidura'' in the family Rhipiduridae, native to Australasia, Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Most of the species are about long, specialist aerial feeders, and named as "f ... family Rhipiduridae. References External linksImage at ADW Rhipiduridae Endemic birds of New Guinea Birds described in 1874 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Rhipiduridae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Fantail
The grey fantail (''Rhipidura albiscapa'') is a small insectivorous bird. There is no sexual dimorphism. It is a common fantail found in Australia, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and New Caledonia. The species is considered by many to be conspecific with the New Zealand fantail (''Rhipidura fuliginosa'');Bird Life International, Grey Fantail grey fantail entry on the Birdlife International Database including explanation as to why grey and New Zealand fantails are not considered to be separate species. however, differences in its calls lead some authorities to treat it as a separate species. The studies of grey fantail in 1999 by Richard Schodde and Ian Mason recommen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhipidura
Fantails are small insectivorous songbirds of the genus ''Rhipidura'' in the family (biology), family Rhipiduridae, native to Australasia, Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Most of the species are about long, specialist aerial feeders, and named as "fantails", but the Australian willie wagtail is a little larger, and, though still an expert hunter of insects on the wing, concentrates equally on terrestrial prey. The true wagtails are part of the genus ''Motacilla'' in the family Motacillidae and are not close relatives of the fantails. Taxonomy The genus '' Rhipidura '' was introduced in 1827 by the naturalists Nicholas Aylward Vigors, Nicholas Vigors and Thomas Horsfield. The type species was subsequently designated as ''Muscicapa flabellifera'' Johann Friedrich Gmelin, Gmelin, JF, 1788 by the English zoologist George Robert Gray, George Gray in 1840. This is a junior synonym of ''Muscicapa fuliginosa'' Anders Erikson Sparrman , Sparrman, 1787, the New Zealand fanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprolia
The silktails are a group of birds endemic to Fiji. The two species ( Taveuni silktail and Natewa silktail) are placed in the genus ''Lamprolia''. They look superficially like a diminutive bird-of-paradise but are actually closely related to the fantails. Species * Taveuni silktail (''Lamprolia victoriae'') Finsch, 1874 — Taveuni ; * Natewa silktail (''Lamprolia klinesmithi'') Ramsay, EP, 1876 — Vanua Levu. Taxonomy and systematics The systematic position of the silktails have been a long-standing mystery. When describing the Taveuni silktail, Otto Finsch wrote "I scarcely remember a bird which has puzzled me in respect of its generic position so much as this curious little creature". They have variously been placed with the birds-of-paradise (Paradisaeidae), the Australasian robins (Petroicidae) and the fairy-wrens (Maluridae). Since 1980, the genus has generally been considered to be an ancient and aberrant monarch flycatcher. A 2009 molecular study placed them as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Families
This article lists living orders and families of birds. In total there are about 11,000 species of birds described as of 2024, though one estimate of the real number places it at almost 20,000. The order passerines (perching birds) alone accounts for well over 5,000 species. Taxonomy is very fluid in the age of DNA analysis, so comments are made where appropriate, and all numbers are approximate. In particular see Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy for a very different classification. Phylogeny Cladogram of modern bird relationships based on Stiller ''et al'' (2024)., showing the 44 orders recognised by the IOC. Subclass Palaeognathae The Palaeognathae or "old jaws" is one of the two superorders recognized within the taxonomic class Aves and consist of the ratites and tinamous. The ratites are mostly large and long-legged, flightless birds, lacking a keeled sternum. Traditionally, all the ratites were place in the order Struthioniformes. However, recent genetic analysis has found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jakob Sundevall
Carl Jakob Sundevall (22 October 1801 in Högestad – 2 February 1875) was a Sweden, Swedish zoologist. Sundevall studied at Lund University, where he received a Ph.D. in 1823. After traveling to East Asia, he studied medicine, graduating as a Doctor of Medicine in 1830. He was employed at the Swedish Museum of Natural History, Stockholm, from 1833, and was professor and keeper of the vertebrate section from 1839 to 1871. He wrote ''Svenska Foglarna'' (1856–87), which described 238 species of birds observed in Sweden. He classified a number of birds collected in southern Africa by Johan August Wahlberg. In 1835, he developed a phylogeny for the birds based on the muscles of the hip and leg that contributed to later work by Thomas Huxley. He then went on to examine the arrangement of the deep plantar tendons in the bird's foot. This latter information is still used by avian taxonomists. Sundevall was also an entomologist and arachnologist, for which (for the latter field) in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insectivorous
A robber fly eating a hoverfly An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant which eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects. The first vertebrate insectivores were amphibians. When they evolved 400 million years ago, the first amphibians were piscivores, with numerous sharp conical teeth, much like a modern crocodile. The same tooth arrangement is however also suited for eating animals with exoskeletons, thus the ability to eat insects can stem from piscivory. At one time, insectivorous mammals were scientifically classified in an order called Insectivora. This order is now abandoned, as not all insectivorous mammals are closely related. Most of the Insectivora taxa have been reclassified; those that have not yet been reclassified and found to be truly related to each other remain in the order Eulipotyphla. Although individually small, insects exist in enormous numbers. Insects make up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
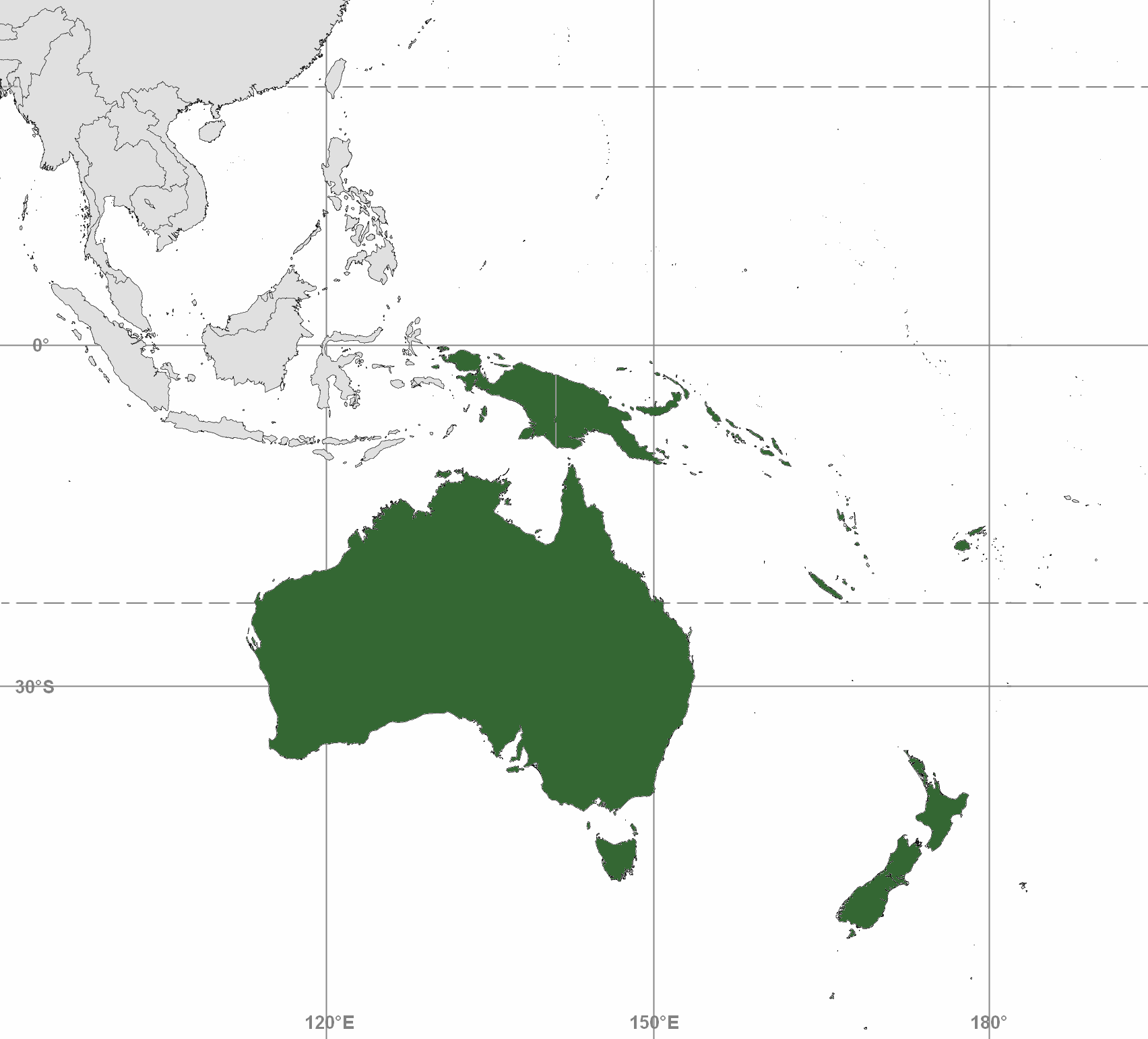
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |