|
Pyrenula
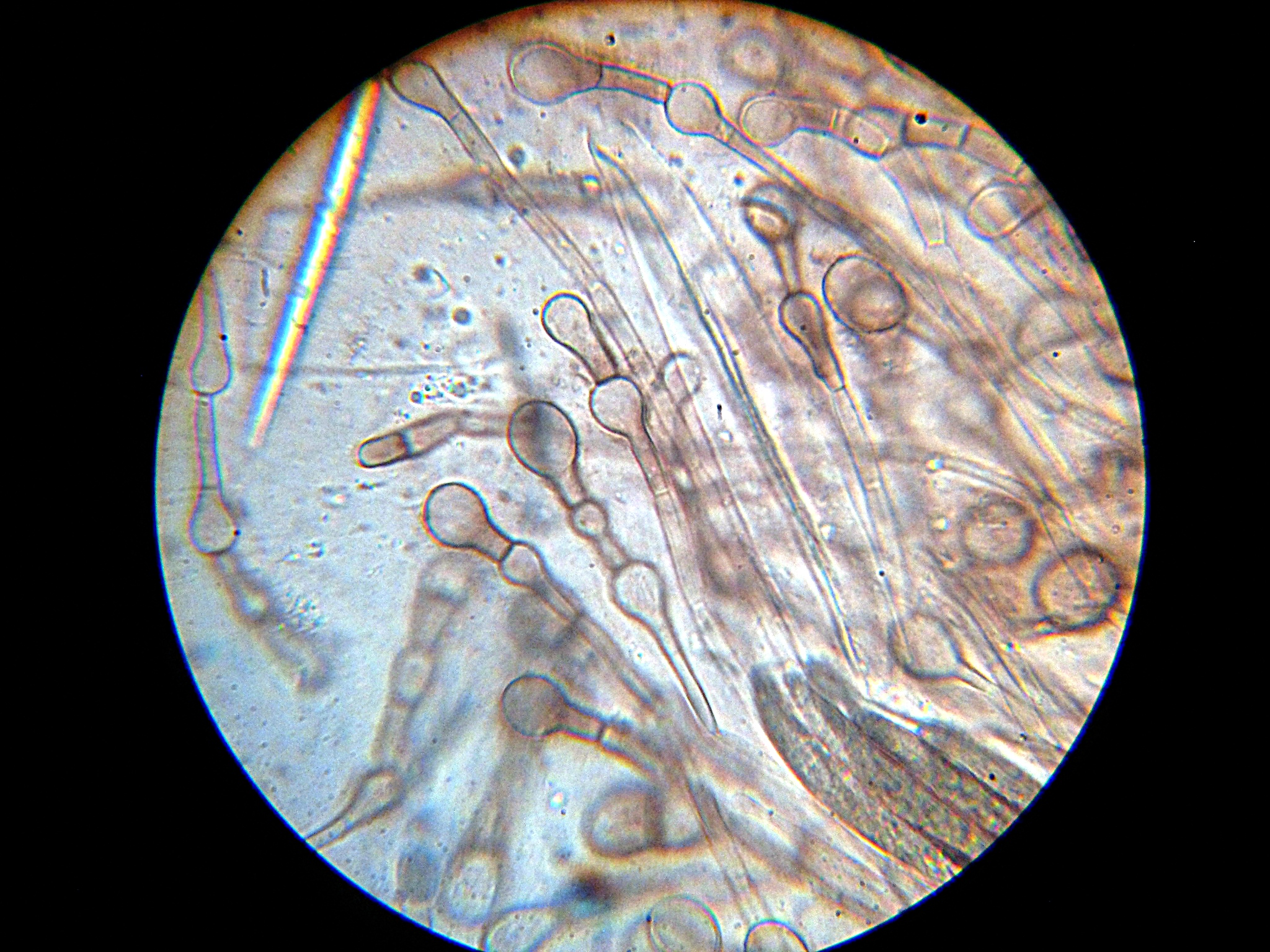
''Pyrenula'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Pyrenulaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, especially in tropical regions, and contains about 200 species. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed in 1814 by Erik Acharius. Acharius distinguished ''Pyrenula'' by its crustose thallus that forms a flat, closely attached, uniform crust, and its characteristic wart-like structures that either protrude from or encircle the fruiting bodies. The genus is characterized by simple, thick-walled, black perithecia with papillate ostioles, and spherical chambers containing a cellular mass that becomes powdery at maturity. Description ''Pyrenula'' is a genus of crustose lichens, which form thin, crust-like growths that are usually embedded in the surface of bark, though occasionally they develop more visibly on the surface. The thallus (the main body of the lichen) is generally smooth and continuous, but in some species it may be cracked into small, plate-like sections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenula Nitida
''Pyrenula nitida'' is a species of crustose lichen belonging to the family Pyrenulaceae. It has a cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and en .... See also * List of ''Pyrenula'' species References nitida Lichen species Lichens described in 1772 Cosmopolitan lichens {{Eurotiomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenulaceae
The Pyrenulaceae are a family of mostly lichenized fungi in the order Pyrenulales. The family was circumscribed by the German botanist Gottlob Ludwig Rabenhorst in 1870. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, but are especially prevalent in the tropics, where they grow with green algae on bark. Genera , the following genera are assigned to the family. * '' Acrocordiella'' * '' Anthracothecium'' * '' Blastodesmia'' * '' Clypeopyrenis'' * '' Daruvedia'' * '' Distopyrenis'' * ''Granulopyrenis'' * '' Lacrymospora'' * '' Lithothelium'' * '' Mazaediothecium'' * '' Micromma'' * '' Parapyrenis'' * ''Pyrenographa ''Pyrenographa'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pyrenulaceae. References External links *Pyrenographa' at Index Fungorum ''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingd ...'' * '' Pyrenowilmsia'' * '' Pyrenula'' * '' Pyrgillus'' * '' Serusiauxia'' * '' Sulcopyrenula'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erik Acharius
Erik Acharius (10 October 1757 – 14 August 1819) was a Swedish botanist who pioneered the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of lichens and is known as the "father of lichenology". Acharius was famously the last pupil of Carl Linnaeus. Life Acharius was born in 1757 to Johan Eric Acharius and Catharina Margaretha Hagtorn in Gävle.Sernander., K. “Erik Acharius - Svenskt Biografiskt Lexikon.” Fredrik Teodor Borg - Svenskt Biografiskt Lexikon, sok.riksarkivet.se/sbl/Presentation.aspx?id=5503. He received a private education until he was admitted to Gävle Gymnasium in 1770. Later he matriculated at Uppsala University in 1773 where he studied natural history and medicine under Linnaeus and was the last student to defend a dissertation before him.Thell, A., Kärnefelt, I., Seaward, M., & Westberg, M. (Eds.) (2013). In the footsteps of Erik Acharius. 20th biennial meeting of the Nordic Lichen Society. Vadstena 11–15 August 2013. Programme and Abstracts. Nordic Lichen Society. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathematics), surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar Cross section (geometry), cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is Bounded set, bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular Rotational symmetry, axes of symmetry which intersect at a Central symmetry, center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascospore
In fungi, an ascospore is the sexual spore formed inside an ascus—the sac-like cell that defines the division Ascomycota, the largest and most diverse Division (botany), division of fungi. After two parental cell nucleus, nuclei fuse, the ascus undergoes meiosis (halving of genetic material) followed by a mitosis (cell division), ordinarily producing eight genetically distinct haploid spores; most yeasts stop at four ascospores, whereas some moulds carry out extra post-meiotic divisions to yield dozens. Many asci build turgor, internal pressure and shoot their spores clear of the calm boundary layer, thin layer of still air enveloping the fruit body, whereas subterranean truffles depend on animals for biological dispersal, dispersal. Ontogeny, Development shapes both form and endurance of ascospores. A hook-shaped crozier aligns the paired nuclei; a double-biological membrane, membrane system then parcels each daughter nucleus, and successive wall layers of β-glucan, chitosan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascus
An ascus (; : asci) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. '' Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. '' Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some '' Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are o ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the ketone, keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to Pulp (paper), wood pulp for papermaking. Many Anthraquinones, anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as Anthraquinone dyes, dyes, pharmaceuticals, and Catalysis, catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly solubility, soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite. Synthesis There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-anthraquinone: # The oxidation of anthracene. Chromium(VI) is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cell (biology), cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell (biology), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia ( basidiomycetes) or paraphyses ( ascomycetes). Cystidia are often important for microscopic identification. The subhymenium consists of the supportive hyphae from which the cells of the hymenium grow, beneath which is the hymenophoral trama, the hyphae that make up the mass of the hymenophore. The position of the hymenium is traditionally the first characteristic used in the classification and identification of mushrooms. Below are some examples of the diverse types which exist among the macroscopic Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. * In agarics, the hymenium is on the vertical faces of the gills. * In boletes and polypores, it is in a spongy mass of downward-pointing tubes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. Etymology Because it was produced from halite, rock salt according to the methods of Johann Rudolph Glauber, hydrochloric acid was historically called by European alchemists ''spirits of salt'' or ''acidum salis'' (salt acid). Both names are still used, especially in other languages, such as , , , , , , , , , , (''ensan''), zh, 盐酸 (''yánsuān''), and (''yeomsan''). Gaseous HCl was called ''marine acid air''. The name ''muriatic acid'' has the same origin (''muriatic'' means "pertaining to brine or salt", hence ''muriate'' means hydrochloride), and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
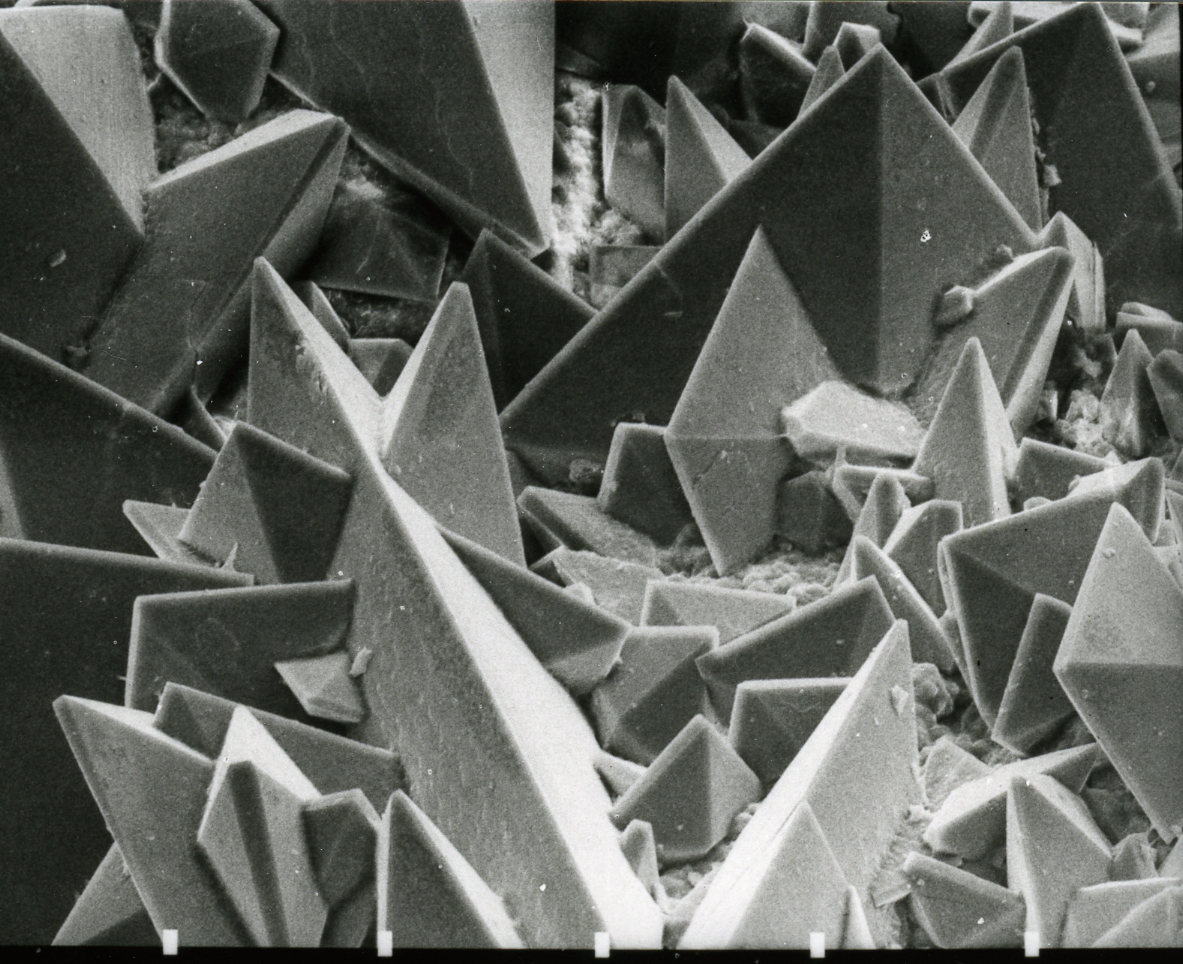
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula or . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |