|
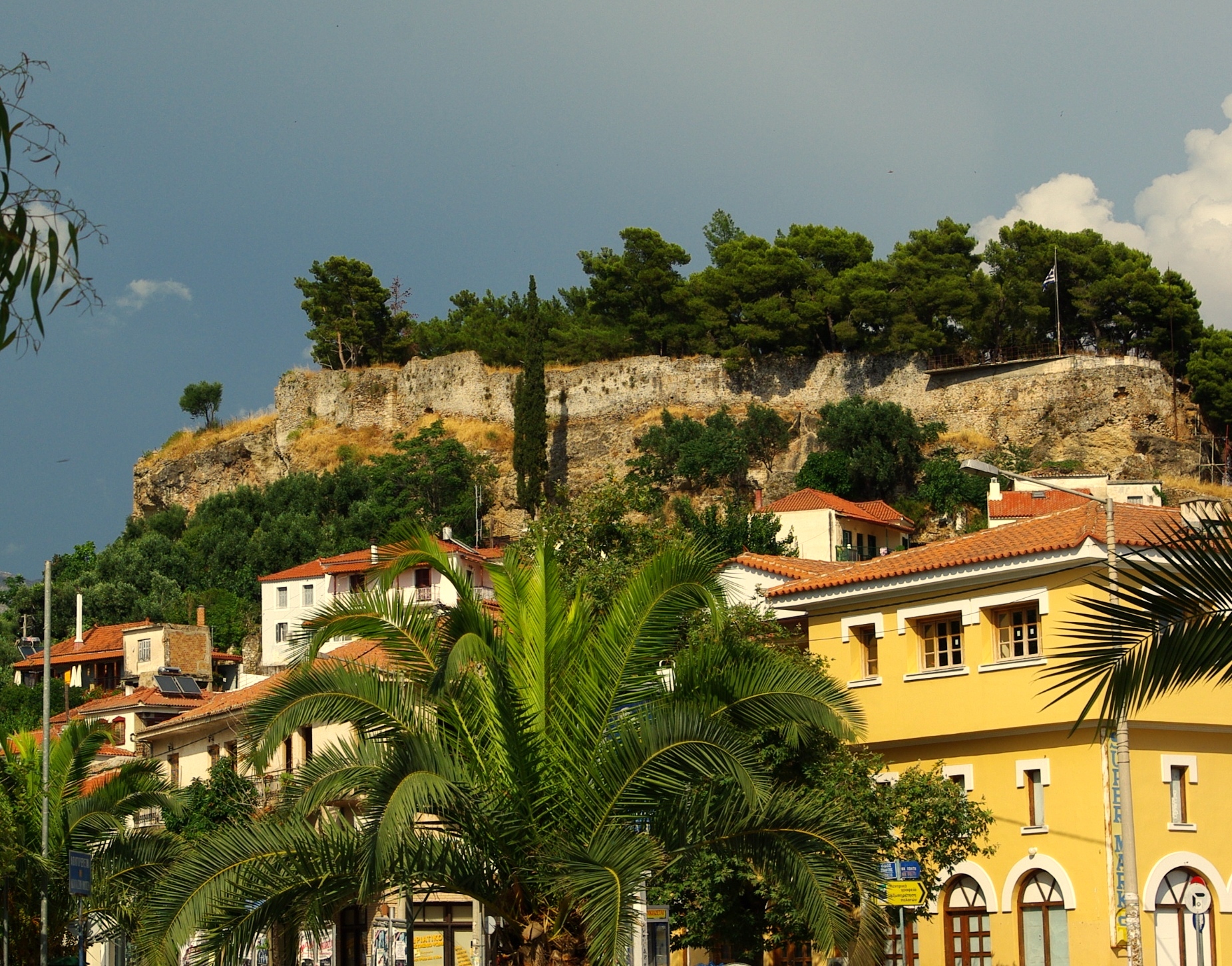
Pylos
Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It was the capital of the former Pylia Province. It is the main harbour on the Bay of Navarino. Nearby villages include Gialova, Pyla, Elaiofyto, Schinolakka, and Palaionero. The town of Pylos has 2,568 inhabitants, the municipal unit of Pylos 4,559 (2021). The municipal unit has an area of 143.911 km2. Pylos has been inhabited since Neolithic times. It was a significant kingdom in Mycenaean Greece, with the remains of the so-called "Palace of Nestor" excavated nearby, named after Nestor (mythology), Nestor, the king of Pylos in Homer's ''Iliad''. In Classical Greece, Classical times, the site was uninhabited, but became the site of the Battle of Pylos in 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pylos
The naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Navarino Bay, Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athens, Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos by a storm, and, at the instigation of Demosthenes (general), Demosthenes, the Athenian soldiers fortified the peninsula, and a small force was left there when the fleet departed again. The establishment of an Athenian garrison in Spartan territory frightened the Spartan leadership, and the Spartan army, which had been ravaging Attica under the command of Agis II, Agis, ended their expedition (the expedition only lasted 15 days) and marched home, while the Spartan fleet at Corcyra sailed to Pylos. Demosthenes had five triremes and their complements of soldiers as a garrison, and was reinforced by 40 hoplites from a Messenian ship that happened to stop at Pylos. In total, Demosthenes probably had about 600 men, only 90 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The most prominent site was Mycenae, after which the culture of this era is named. Other centers of power that emerged included Pylos, Tiryns, and Midea in the Peloponnese, Orchomenos, Thebes, and Athens in Central Greece, and Iolcos in Thessaly. Mycenaean settlements also appeared in Epirus, Macedonia, on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the south-west coast of Asia Minor, and on Cyprus, while Mycenaean-influenced settlements appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
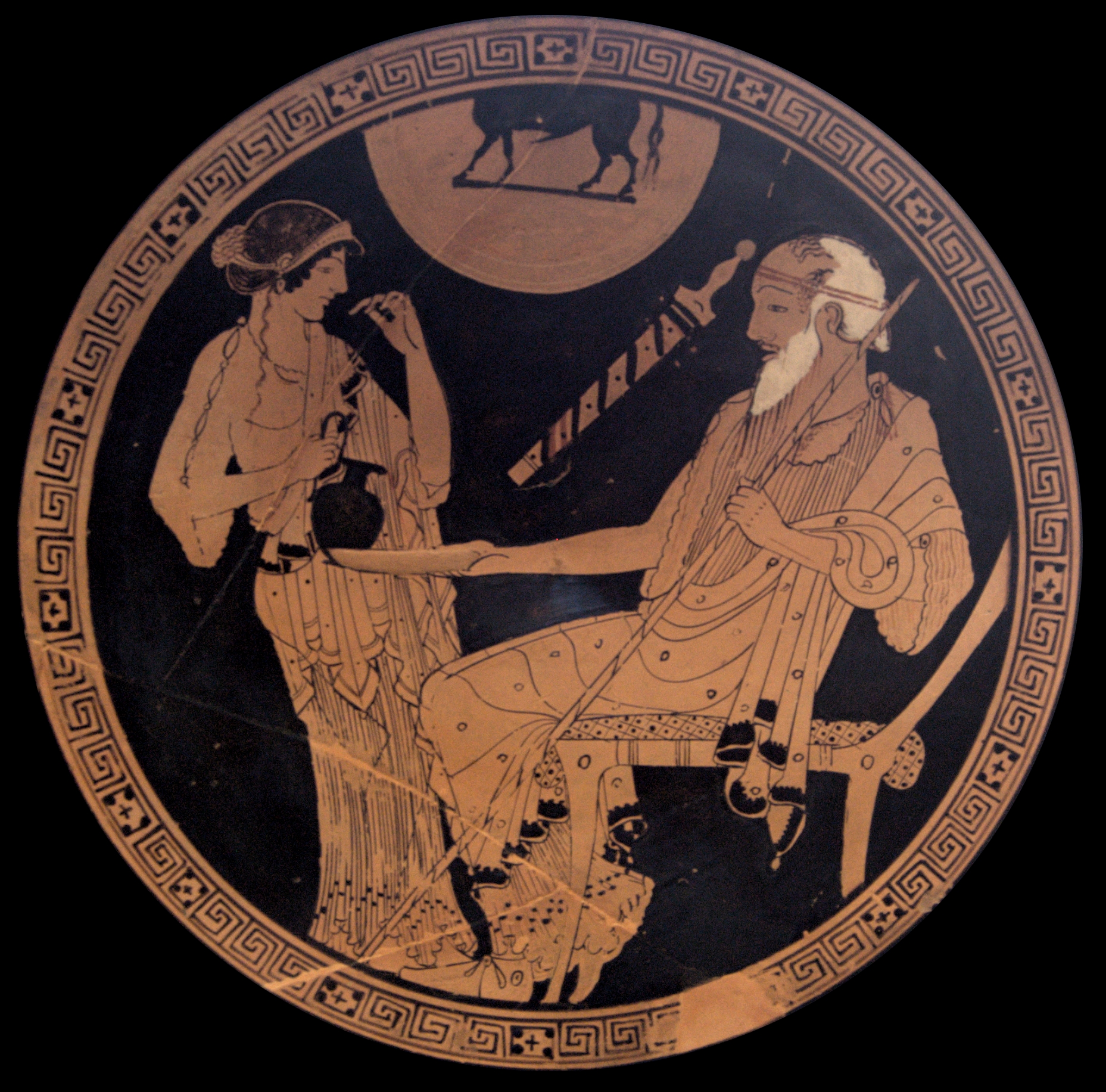
Nestor (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Nestor of Gerenia (, ''Nestōr Gerēnios'') was a legendary king of Pylos. He is a prominent secondary character in Homer's ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', where he appears as an elderly warrior who frequently offers advice to the other characters. The Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean-era palace at Pylos is known as the ''Palace of Nestor'', though there is no evidence that he was an actual person. Description In the account of Dares Phrygius, Dares the Phrygian, Nestor was illustrated as "... large, broad and fair. His nose was long and hooked. He was a wise adviser." Family Nestor was the son of King Neleus of Pylos and Chloris of Pylos, Chloris, daughter of King AmphionBibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Apollodorus, 1.9.9; Scholia on Homer, ''Odyssey'' 11.281 citing Pherecydes of Athens, Pherecydes of Orchomenus (Boeotia), Orchomenus. Otherwise, Nestor's mother was called Polymede. His wife was either Eurydice of Pylos, Eurydice or Anaxibia; their children inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morea Expedition
The Morea expedition () is the name given to the land intervention of the French Army in the Peloponnese between 1828 and 1833, at the time of the Greek War of Independence, with the aim of expelling the Ottoman-Egyptian occupation forces from the region. It was also accompanied by a scientific expedition mandated by the French Academy. After the fall of Messolonghi in 1826, the Western European powers decided to intervene in favour of revolutionary Greece. Their primary objective was to force Ibrahim Pasha, the Ottoman Empire's Egyptian ally, to evacuate the occupied regions and the Peloponnese. The intervention began when a Franco-Russo-British fleet was sent to the region and won the Battle of Navarino in October 1827, destroying the entire Turkish-Egyptian fleet. In August 1828, a French expeditionary corps of 15,000 men led by General Nicolas-Joseph Maison landed in the southwestern Peloponnese. During October, soldiers took control of the principal strongholds still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a prefecture (''nomos'') covering the same territory. The capital and largest city of Messenia is Kalamata. Geography Physical Messenia borders on Elis to the north, Arcadia to the northeast, and Laconia to the southeast. The Ionian Sea lies to the west, and the Gulf of Messinia to the south. The most important mountain ranges are the Taygetus in the east, the Kyparissia mountains in the northwest and the Lykodimo in the southwest. The main rivers are the Neda in the north and the Pamisos in central Messenia. Off the south coast of the southwesternmost point of Messenia lie the Messinian Oinousses islands. The largest of these are Sapientza, Schiza and Venetiko. The small island Sphacteria closes off the bay of Pylos. All these islands are virtua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Nestor
The Palace of Nestor (Modern Greek: Ανάκτορο του Νέστορα) was an important centre in Mycenaean times, and described in Homer's ''Odyssey'' and ''Iliad'' as Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos". The palace featured in the story of the Trojan War, as Homer tells us that Telemachus: went to Pylos and to Nestor, the shepherd of the people, and he received me in his lofty house and gave me kindly welcome, as a father might his own son who after a long time had newly come from afar: even so kindly he tended me with his glorious sons. The site is the best preserved Mycenaean Greek palace discovered. The palace is the primary structure within a larger Late Helladic era settlement, once probably surrounded by a fortified wall. The palace was a two-storey building with store rooms, workshops, baths, light wells, reception rooms and a sewage system. The settlement had been long occupied with most artifacts discovered dating from 1300 BC. The palace complex was destroyed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
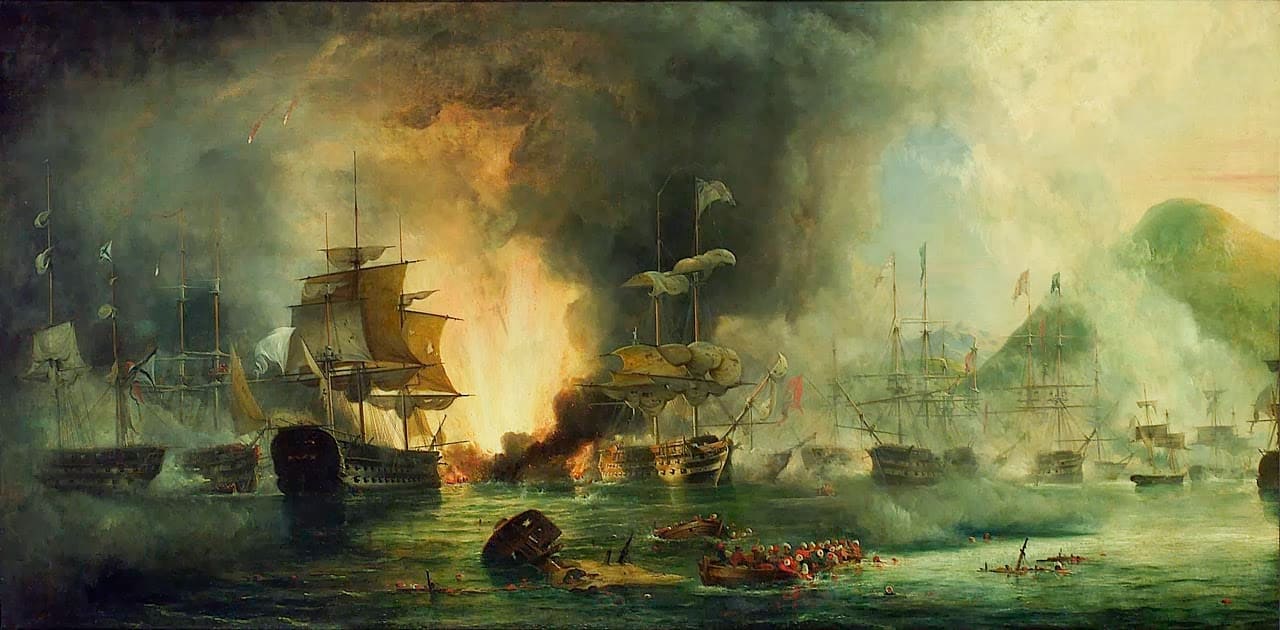
Battle Of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O.S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied forces from Britain, France, and Russia decisively defeated Ottoman and Egyptian forces which were trying to suppress the Greeks, thereby making Greek independence much more likely. An Ottoman armada which, in addition to Imperial warships, included squadrons from the ''eyalets'' of Egypt and Regency of Algiers and Tunis, was destroyed by an Allied force of British, French and Russian warships. It was the last major naval battle in history to be fought entirely with sailing ships, although most ships fought at anchor. The Allies' victory was achieved through superior firepower and gunnery. The context of the three Great Powers' intervention in the Greek conflict was the Russian Empire's long-running expansion at the expense of the deca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylos-Nestoras
Pylos-Nestoras () is a municipality in the Messenia regional unit, Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Pylos. The municipality has an area of 554.265 km2. Municipality The municipality Pylos-Nestoras was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 6 former municipalities, that became municipal units: * Chiliochoria *Koroni * Methoni * Nestoras * Papaflessas *Pylos Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of ... References Municipalities of Peloponnese (region) Populated places in Messenia {{Peloponnese-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gialova
Gialova (Greek: Γιάλοβα) is a village on Navarino Bay in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor in the regional unit of Messenia in the south-west Peloponnese, Greece, about six kilometres north of Pylos. The name derives from Greek γιαλός (shore) and Turkish ova (lowland), i.e. "lowland shore". Topography The village is in two parts. The beach/port part of the village consists of two short streets, one fronting the Bay and the other at right angles to it, leading to the main Pylos-Kiparissia road. This part is largely touristic - bars and restaurants, shops, and the one hotel. Where the two streets meet there is a mole used by local fishing boats (and for car parking). The other, residential and commercial part of the village is about 1km further north along the Pylos-Kiparissia road. The modern development of Gialova also includes several houses and holiday villas on the hill behind Gialova, called Dapia (Greek: Ντάπια). Population The area of Gialova was firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
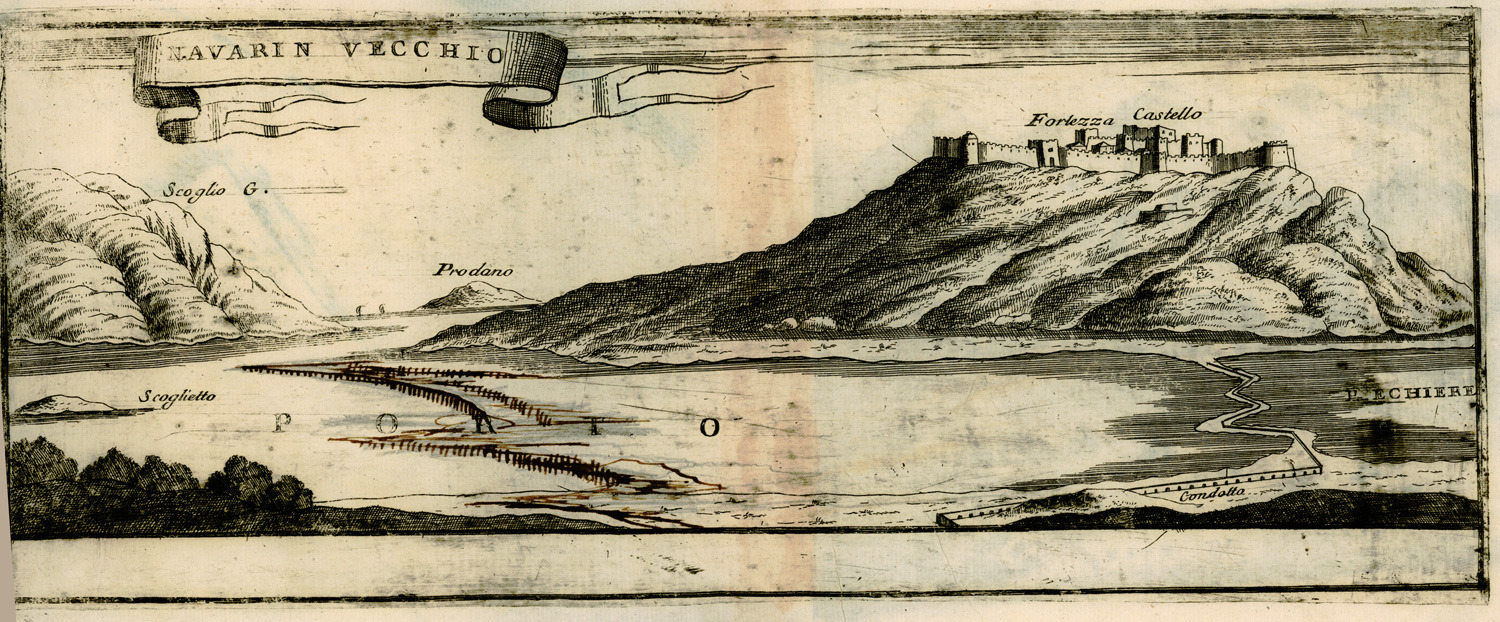
Old Navarino Castle
The Old Navarino castle () is a 13th-century Frankish fortress near Pylos, Greece. It is one of two castles guarding the bay on which it sits; the other is the Ottoman-built New Navarino. It is frequently known simply as Palaiokastro or Paliokastro (, "old castle"). It occupies the site of the Athenian fort at the 425 BC Battle of Pylos. Name In Frankish times, under the Principality of Achaea, it was known as ("Cane Harbour") or in French, with some variants and derivatives: in Italian , or , in medieval Catalan , in Latin , / ( or ) in Greek, etc. In the late 14th/early 15th centuries, when it was held by the Navarrese Company, it was also known as , and called (, "village of the Spaniards") by the local Greeks. History The castle sits atop an imposing rock formation on the northern edge of the bay, flanked by sheer cliffs; the naturally defensible site has probably been occupied since classical times. Although there are no physical barriers to access, the castle ruins h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Navarino Fortress
The fortress of New Navarino (; Ottoman Turkish: ''Anavarin-i cedid'') is an Ottoman fortification near Pylos, Greece. It is one of two castles guarding the strategic Bay of Pylos, on which it sits; New Navarino is located in the southern entrance of the bay, while the northern entrance is guarded by the 13th-century Old Navarino castle, built by the Crusaders of the Principality of Achaea. In juxtaposition with the latter, New Navarino is often known simply as Neokastro or Niokastro (, "new castle").. History The fortress was built by the Ottoman Kapudan Pasha, Uluç Ali Reis, in 1572/3, shortly after the Battle of Lepanto. In 1645, Navarino was used as a base for the Ottoman invasion of Crete during the opening stages of the Cretan War. During the Morean War, the Republic of Venice under Francesco Morosini captured both fortresses at Navarino in 1686, defended by Mustafa Pasha and Djafer Pasha respectively. Along with the rest of the Peloponnese, the fortresses remained i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet (built with Persian subsidies) finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. The first phase (431–421 BC) was named the Ten Years War, or the Archidamian War, after the Spartan king Archidamus II, who invaded Attica several times with the full hoplite army of the Peloponnesian League, the alliance network dominated by Sparta (then known as Lacedaemon). The Long Walls of Athens rendered this strategy ineffective, while the superior navy of the Delian League (Athens' all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |