|
Principles Of Islamic Jurisprudence
Principles of Islamic jurisprudence () are traditional methodological principles used in Islamic jurisprudence (''fiqh'') for deriving the rulings of Islamic law (''sharia''). Traditional theory of Islamic jurisprudence elaborates how the scriptures (Quran and hadith) should be interpreted from the standpoint of linguistics and rhetoric. It also comprises methods for establishing authenticity of hadith and for determining when the legal force of a scriptural passage is abrogated by a passage revealed at a later date. In addition to the Quran and hadith, the classical theory of Sunni jurisprudence recognizes secondary sources of law: juristic consensus ('' ijmaʿ'') and analogical reasoning ('' qiyas''). It therefore studies the application and limits of analogy, as well as the value and limits of consensus, along with other methodological principles, some of which are accepted by only certain legal schools ('' madhahib''). This interpretive apparatus is brought together under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the sharia; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the Quran and the sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions). Fiqh expands and develops Shariah through interpretation (''ijtihad'') of the Quran and ''Sunnah'' by Islamic jurists (''ulama'') and is implemented by the rulings (''fatwa'') of jurists on questions presented to them. Thus, whereas ''sharia'' is considered immutable and infallible by Muslims, ''fiqh'' is considered fallible and changeable. ''Fiqh'' deals with the observance of rituals, morals and social legislation in Islam as well as econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maslaha
''Maslaha'' or ''maslahah'' (, ) is a concept in Sharia (Islamic divine law) regarded as a basis of law.I. Doi, Abdul Rahman. (1995). "Mașlahah". In John L. Esposito. ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic World''. Oxford: Oxford University Press. It forms a part of extended methodological principles of Islamic jurisprudence (''uṣūl al-fiqh'') and denotes prohibition or permission of something, according to necessity and particular circumstances, on the basis of whether it serves the public interest of the Muslim community (''ummah''). In principle, ''maslaha'' is invoked particularly for issues that are not regulated by the Qur'an, the ''sunnah'' (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad), or ''qiyas'' (analogy). The concept is acknowledged and employed to varying degrees depending on the jurists and schools of Islamic jurisprudence (''madhhab''). The application of the concept has become more important in modern times because of its increasing rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111), archaically Latinized as Algazelus, was a Shafi'i Sunni Muslim scholar and polymath. He is known as one of the most prominent and influential jurisconsults, legal theoreticians, muftis, philosophers, theologians, logicians and mystics in Islamic history. He is considered to be the 11th century's '' mujaddid'',William Montgomery Watt, ''Al-Ghazali: The Muslim Intellectual'', p. 180. Edinburgh University Press, 1963. a renewer of the faith, who, according to the prophetic hadith, appears once every 100 years to restore the faith of the Islamic community.Dhahabi, Siyar, 4.566 Al-Ghazali's works were so highly acclaimed by his contemporaries that he was awarded the honorific title "Proof of Islam" ('' Ḥujjat al-Islām''). Al-Ghazali was a prominent mujtahid in the Shafi'i school of law. Much of Al-Ghazali's work stemmed around his spiritual crises following his appointment as the head of the Nizamiyya University in Baghdad - which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
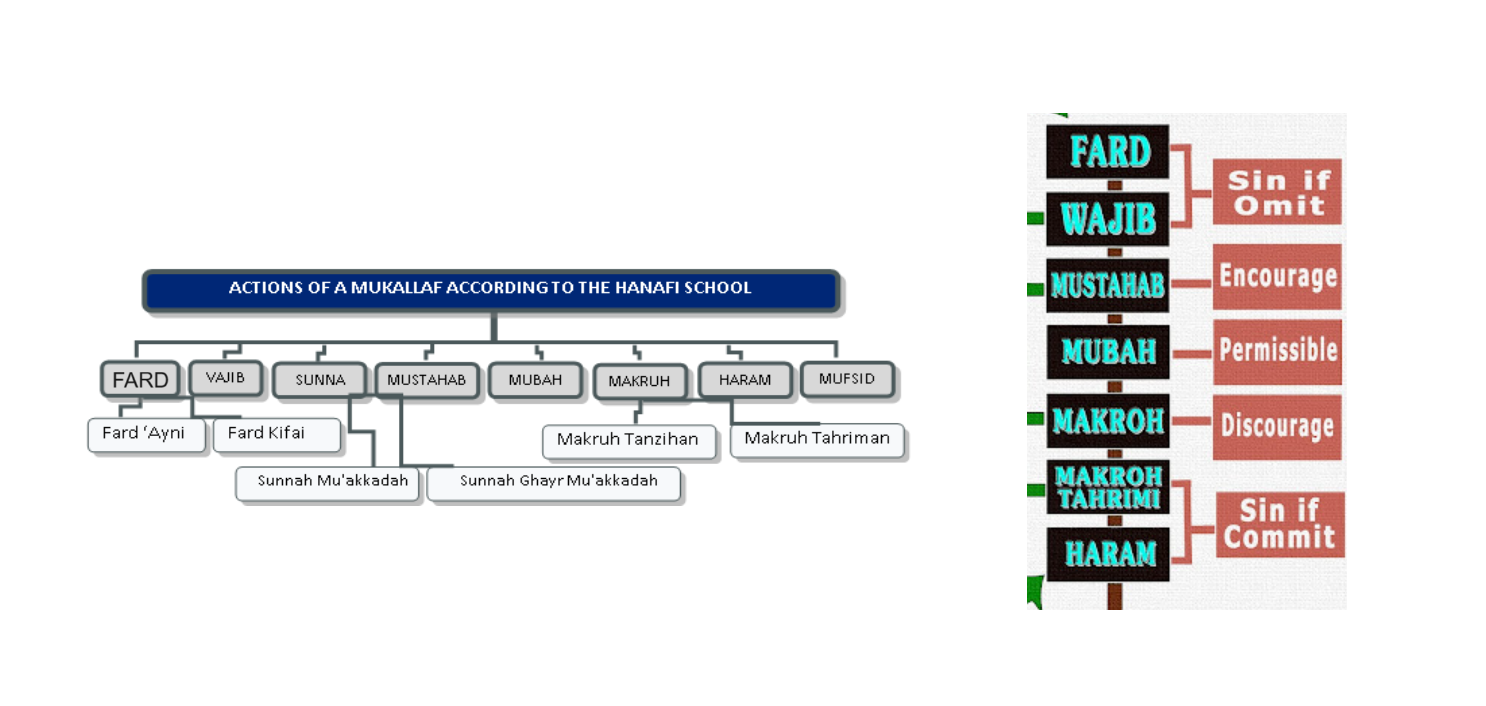
Halal
''Halal'' (; ) is an Arabic word that translates to in English. Although the term ''halal'' is often associated with Islamic dietary laws, particularly meat that is slaughtered according to Islamic guidelines, it also governs ethical practices in business, finance (such as the prohibition of interest or ''riba''), and daily living. It encompasses broader ethical considerations, including fairness, social justice, and the treatment of animals. The concept of ''halal'' is central to Islamic practices and is derived from the Quran and the Sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Prophet Muhammad). In the Quran, the term ''halal'' is contrasted with the term ''haram'' (). The guidelines for what is considered ''halal'' or ''haram'' are laid out in Islamic jurisprudence (''fiqh''), and scholars interpret these guidelines to ensure compliance with Islamic principles. This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification known as "Ahkam, the five decisions": Fard, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haram
''Haram'' (; ) is an Arabic term meaning 'taboo'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowledge; or, in direct contrast, to an evil and thus " sinful action that is forbidden to be done". The term also denotes something "set aside", thus being the Arabic equivalent of the Hebrew concept () and the concept of (cf. sacred) in Roman law and religion. In Islamic jurisprudence, ''haram'' is used to refer to any act that is forbidden by Allah and is one of the five Islamic commandments ( ) that define the morality of human action. Acts that are haram are typically prohibited in the religious texts of the Quran and the category of haram is the highest status of prohibition. Something that is considered haram remains prohibited no matter how good the intention is or how honorable the purpose is. Sins, good, and meritorious acts are placed on the (weighin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makruh
In Islamic terminology, something which is makruh or makrooh (, transliteration, transliterated: ''makrooh'' or ''makrūh'') is "disliked", literally "detestable" or "abominable". This is one of the Ahkam, five categories (''al-ahkam al-khamsa'') in Islamic law – ''wajib/fard'' (obligatory), ''Mustahabb/mandub'' (recommended), ''mubah'' (neutral), ''makruh'' (disapproved), ''haram'' (forbidden). Though a ''makruh'' act is not ''haraam, haram'' (forbidden) or subject to punishment, a person who abstains from this act will be rewarded. Muslims are encouraged to avoid such actions when or as possible. It is one of the degrees of approval (''ahkam'') in sharia, Islamic law. In the terminology of Islamic jurisprudence, "Makruh" refers to an action that is not forbidden to do, but had better to be abandoned. Acts considered ''makruh'' can vary between different Madhhab, madhhabs due to differing scholarly interpretations of the Quran and Hadith, with Hanafi scholars in particular dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mubah
''Mubāḥ'' (Arabic: مباح) is an Arabic word roughly meaning "permitted", which has technical uses in Islamic law. "Mubah" is an Islamic jurisprudential term that refers to an action for which a person has no specific obligation. Consequently, performing or abstaining from it is considered equally permissible, and neither action results in reward or punishment from the perspective of God in Islam. In uṣūl al-fiqh (), ''mubāḥ'' is one of the five degrees of approval (ahkam): # () - compulsory, obligatory # () - recommended # () - neutral, not involving God's judgment # () - disliked, reprehensible # () - forbidden Mubah is commonly translated as "neutral" or "permitted" in English., "indifferent" or "(merely) permitted". It refers to an action that is not mandatory, recommended, reprehensible or forbidden, and thus involves no judgement from God. Assigning acts to this legal category reflects a deliberate choice rather than an oversight on the part of jurists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustahabb
''Mustahabb'' () is an Islamic term referring to an action or thing that is recommended and favoured. ''Mustahabb'' actions are those whose ruling ('' ahkam'') in Islamic law falls between '' mubah'' (neutral; neither encouraged nor discouraged) and '' wajib'' (compulsory). One definition is "duties recommended, but not essential; fulfilment of which is rewarded, though they may be neglected without punishment". Synonyms of ''mustahabb'' include ''masnun'' and ''mandub''. The opposite of ''mustahabb'' is '' makruh'' (discouraged). Parallels have been drawn between the concept of ''mustahabb'' in Islamic law and the concept of supererogatory acts in the Western philosophical tradition. Examples There are possibly thousands of mustahabb acts, including: * As-Salamu Alaykum (a traditional Islamic greeting, though responding to the greeting is an obligation) * Sadaqah (charity outside of zakat) * Umrah (except in the Shafi'i and Hanbali madhhab A ''madhhab'' (, , pl. , ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fard
' () or ' () or fardh in Islam is a religious duty commanded by God in Islam, God. The word is also used in Turkish language, Turkish, Persian language, Persian, Pashto, Urdu, Hindi, Bengali language, Bangla (''spelled farz or faraz''), and Malay language, Malay (''spelled fardu or fardhu'') in the same meaning. Muslims who obey such commands or duties are said to receive ''hasanat'' (), ''ajr'' () or ''thawab'' () for each good deed. ''Fard'' or its synonym ''wājib'' () is one of the five types of ahkam () into which fiqh categorizes acts of every Muslim. The Hanafi fiqh, however, does not consider both terms to be synonymous, and makes a distinction between ''wajib'' and ''fard'', the latter being obligatory and the former slightly lesser degree than being obligatory. Individual duty and sufficiency The fiqh distinguishes two sorts of duties: * Individual duty or ''farḍ al-'ayn'' () is a personal requirement that each person is expected to fulfill on their own, such as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taqlid
''Taqlid'' (, " imitation") is an Islamic term denoting the conformity of one person to the teaching of another. The person who performs ''taqlid'' is termed ''muqallid''. The definite meaning of the term varies depending on context and age. Classical usage of the term differs between Sunni Islam and Shia Islam. Sunni Islamic usage designates the unjustified conformity of one person to the teaching of another, rather than the justified conformity of a layperson to the teaching of a ''mujtahid'' (a person who is qualified for independent reasoning). Shia Islamic usage designates general conformity to the teaching of a ''mujtahid'', and there is no negative connotation. The discrepancy corresponds to differing views on the Shia Imamate and Sunni imams. In contemporary usage, especially in the context of Salafism, ''taqlid'' is often portrayed in a negative light and translated as "blind imitation". This refers to the perceived stagnation of independent intellectual effort ('' ij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istishab
''Istiṣḥāb'' ( ) is an Islamic term used in the jurisprudence to denote the principle of the presumption of continuity. It is derived from an Arabic word ''suhbah'' meaning accompany. It is one of the fundamental principles of the legal deduction that presumes the continuation of a fact. It is based on probability and can be applied in the absence of other proofs. Istishab, an initiative of ash-Shafii, is the rationalistic principle of extracting a legal solution according to which changes are not considered to occur until clear signs of these changes are apparent. It serves as the basis for many legal rulings such as the presumption of innocence—the person is regarded as innocent unless proven guilty. Malik ibn Anas and ash-Shafii regarded it to be a proof until it is contradicted. Several classical jurists differed over this principle with some Hanafi jurists refusing to regard it as an evidence. It is now widely employed by the contemporary scholars. Definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |