Mubah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mubāḥ'' (
Mubah
Mubah definition
Halal, Mustahabb, Mubah, Makrooh & Haram
The Permissible (Mubah, Also Halal, Ja'iz)
Arabic words and phrases Arabic words and phrases in Sharia Sharia legal terminology {{arabic-lang-stub
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
: مباح) is an Arabic word roughly meaning "permitted", which has technical uses in Islamic law
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on scriptures of Islam, particularly the Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intan ...
. "Mubah" is an Islamic jurisprudential term that refers to an action for which a person has no specific obligation. Consequently, performing or abstaining from it is considered equally permissible, and neither action results in reward or punishment from the perspective of God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
in Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
.
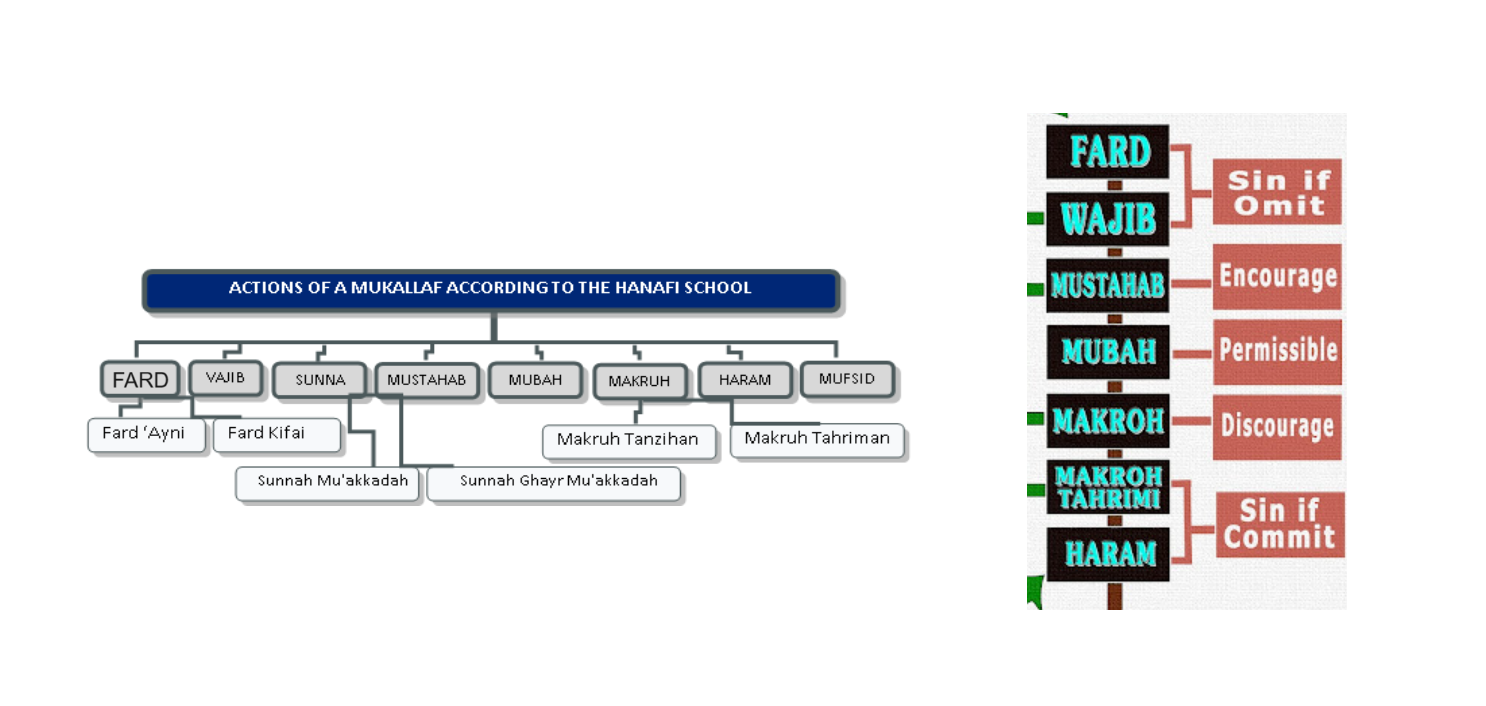
In uṣūl al-fiqh (), ''mubāḥ'' is one of the five degrees of approval (ahkam
''Ahkam'' (, plural of , ) is an Islamic term with several meanings. In the Quran, the word ''hukm'' is variously used to mean arbitration, judgement, authority, or God's will. In the early Islamic period, the Kharijites gave it political conn ...
):
# () - compulsory, obligatory
# () - recommended
# () - neutral, not involving God's judgment
# () - disliked, reprehensible
# () - forbidden
Mubah is commonly translated as "neutral" or "permitted" in English., "indifferent" or "(merely) permitted". It refers to an action that is not mandatory, recommended, reprehensible or forbidden, and thus involves no judgement from God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
. Assigning acts to this legal category reflects a deliberate choice rather than an oversight on the part of jurists.
In Islamic property law, the term ''mubāḥ'' refers to things which have no owner. It is similar to the concept '' res nullius'' used in Roman law and common law.
Categorization

See also
* , a similar concept in Stoicism * *Ahkam
''Ahkam'' (, plural of , ) is an Islamic term with several meanings. In the Quran, the word ''hukm'' is variously used to mean arbitration, judgement, authority, or God's will. In the early Islamic period, the Kharijites gave it political conn ...
* Baligh
* Batil
* Ghanimah
* Hirabah
* Ibadah
''Ibadah'' (, ''‘ibādah'', also spelled ''ibada'') is an Arabic word meaning service or servitude. In Islam, ''ibadah'' is usually translated as “worship”, and ''ibadat''—the plural of ''ibadah''—refers to Islamic jurisprudence ( ...
* Khums
* Zakat
Zakat (or Zakāh زكاة) is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. Zakat is the Arabic word for "Giving to Charity" or "Giving to the Needy". Zakat is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam a relig ...
* Taqiyya
* Thawab
* Ulu'l-amr
* Wakil
* Makruh
In Islamic terminology, something which is makruh or makrooh (, transliteration, transliterated: ''makrooh'' or ''makrūh'') is "disliked", literally "detestable" or "abominable". This is one of the Ahkam, five categories (''al-ahkam al-khamsa'') ...
* Haram
''Haram'' (; ) is an Arabic term meaning 'taboo'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowledge; or, in direct cont ...
* Ghibah
* Gunah
* Islah
* Istighfar
* Qasd
* Taghut
* Tawbah
* Tazkiah
* Wasat
* Maslaha
''Maslaha'' or ''maslahah'' (, ) is a concept in Sharia (Islamic divine law) regarded as a basis of law.I. Doi, Abdul Rahman. (1995). "Mașlahah". In John L. Esposito. ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic World''. Oxford: Oxford Univer ...
* Qiyas
Qiyas (, , ) is the process of deductive analogy in which the teachings of the hadith are compared and contrasted with those of the Quran in Islamic jurisprudence, in order to apply a known injunction ('' nass'') to a new circumstance and cre ...
* Ijazah
An ''ijazah'' (, "permission", "authorization", "license"; plural: ''ijazahs'' or ''ijazat'') is a license authorizing its holder to transmit a certain text or subject, which is issued by someone already possessing such authority. It is particul ...
* Ijma
Ijma (, ) is an Arabic term referring to the consensus or agreement of the Islamic community on a point of Islamic law. Sunni Muslims regard it as one of the secondary sources of Sharia law, after the Qur'an, and the Sunnah.
Exactly what group s ...
References
External links
Mubah
Mubah definition
Halal, Mustahabb, Mubah, Makrooh & Haram
The Permissible (Mubah, Also Halal, Ja'iz)
Arabic words and phrases Arabic words and phrases in Sharia Sharia legal terminology {{arabic-lang-stub