|
Parker Solar Probe
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 to make observations of the Stellar corona, Sun's outer corona. It used repeated Gravity assist, gravity assists from Venus to develop an eccentric orbit, approaching within 9.86 solar radius, solar radii (6.9 million km or 4.3 million miles) from the center of the Sun. At its closest approach in 2024, its speed relative to the Sun was or 191 km/s (118.7 mi/s), which is 0.064% the speed of light. It is the fastest object ever built on Earth. The project was announced in the fiscal 2009 budget year. Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory designed and built the spacecraft, which was launched on 12 August 2018. It became the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person, honoring physicist Eugene Parker, Eugene Newman Parker, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago. On 29 October 2018, at about 18:04 UTC, the spacecraft became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix "wikt:helio-, helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA defines heliophysics as "(1) the comprehensive new term for the science of the Sun - Solar System Connection, (2) the exploration, discovery, and understanding of Earth's space environment, and (3) the system science that unites all of the linked phenomena in the region of the cosmos influenced by a star like Sun, our Sun." Heliophysics is broader than Solar physics, that studies the Sun itself, including its interior, atmosphere, and magnetic fields. It concentrates on the Sun's effects on Earth and other bodies within the Solar System, as well as the changing conditions in space. It is primarily concerned with the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, and upper atmosphere of the Earth and other planets. Heliophysics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Strategic Science Missions
NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions. "Large" refers to the budget of each mission, typically the most expensive mission in the scientific discipline. Within the Astrophysics Division and the Planetary Science Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$1 billion. Within Earth Science Division and Heliophysics Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$500 million.Powering Science: NASA's Large Strategic Science Missions (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Parker
Eugene Newman Parker (June 10, 1927 – March 15, 2022) was an American solar and plasma physicist. In the 1950s he proposed the existence of the solar wind and that the magnetic field in the outer Solar System would be in the shape of a Parker spiral, predictions that were later confirmed by spacecraft measurements. In 1987, Parker proposed the existence of nanoflares, a leading candidate to explain the coronal heating problem. Parker obtained his PhD from Caltech and spent four years as a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Utah. He joined University of Chicago in 1955 and spent the rest of his career there, holding positions in the physics department, the astronomy and astrophysics department, and the Enrico Fermi Institute. Parker was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1967. In 2017, NASA named its Parker Solar Probe in his honor, the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person. Biography Parker was born in Houghton, Michigan to Glenn and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local, regional, national, and international news. Founded in 1837, the newspaper was owned by Tribune Publishing until May 2021, when it was acquired by Alden Global Capital, which operates its media properties through Digital First Media. David D. Smith, the executive chairman of Sinclair Broadcast Group, closed a deal to buy the paper on January 15, 2024. History 19th century ''The Sun'' was founded on May 17, 1837, by Arunah Shepherdson Abell and two associates, William Moseley Swain from Rhode Island, and Azariah H. Simmons from Philadelphia, where they had started and published the '' Public Ledger'' the year before. Abell became a journalist with the ''Providence Patriot'' and later worked with newspapers in New York City and Boston.Van Doren, Charles and Robert McKendry, ed., ''Webster's American Biographies''. (Springfield, Massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Radius
Solar radius is a unit of distance used to express the size of objects in astronomy relative to the Sun. The solar radius is usually defined as the radius to the layer in the Sun's photosphere where the optical depth equals 2/3: 1\,R_ = 6.957\times 10^8 \hbox is approximately 10 times the average radius of Jupiter, 109 times the radius of the Earth, and 1/215 of an astronomical unit, the approximate distance between Earth and the Sun. The solar radius to either pole and that to the equator differ slightly due to the Sun's rotation, which induces an oblateness in the order of 10 parts per million. Measurements The uncrewed SOHO spacecraft was used to measure the radius of the Sun by timing transits of Mercury across the surface during 2003 and 2006. The result was a measured radius of . Haberreiter, Schmutz & Kosovichev (2008) determined the radius corresponding to the solar photosphere to be . This new value is consistent with helioseismic estimates; the same study sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
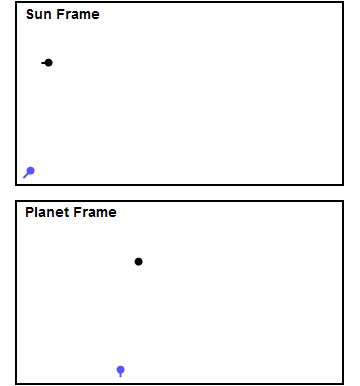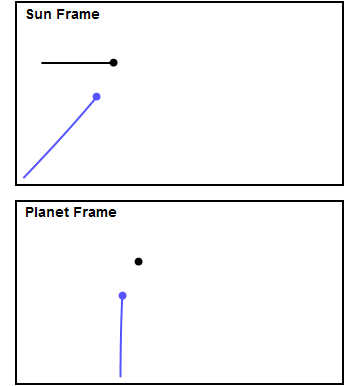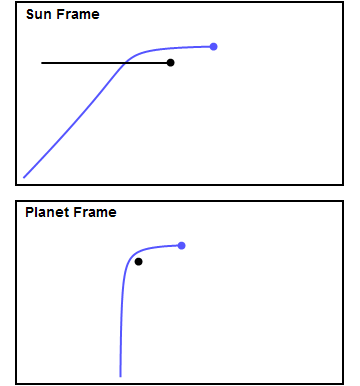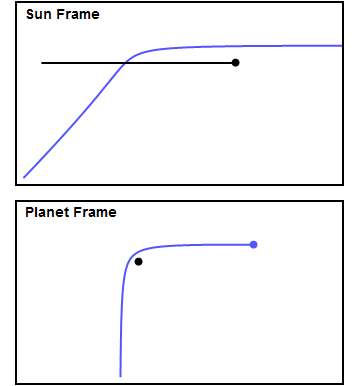
Gravity Assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the Course (navigation), path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and linear momentum by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's laws of motion#Newton's third law, Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Corona
In astronomy, a corona (: coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively luminosity, dim region of Plasma (physics), plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures such as solar prominence, prominences, coronal loops, and helmet streamers. The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. Coronal light is typically obscured by diffuse sky radiation and Glare (vision), glare from the solar disk, but can be easily seen by the naked eye during a total solar eclipse or with a specialized coronagraph. Spectroscopic measurements indicate strong ionization in the corona and a plasma temperature in excess of , much hotter than the surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere. is, in turn, derived . History In 1724, French-Italian astronomer Giacomo F. Maraldi recognized that the aura visible during a solar eclipse belongs to the Sun, not to the Moon. In 1809, Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Probe
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which they have a pre-programmed list of operations that will be executed unless otherwise instructed. A robotic spacecraft for scientific measurements is often called a space probe or space observatory. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to lower cost and risk factors. In addition, some planetary destinations such as Venus or the vicinity of Jupiter are too hostile for human survival, given current technology. Outer planets such as Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are too distant to reach with current crewed spaceflight technology, so telerobotic probes are the only way to explore them. Telerobotics also allows exploration of regions that are vulnerable to contamination by Earth micro-organisms sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Orbiter
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing probe developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) with a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) contribution. Solar Orbiter, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of the polar regions of the Sun which is difficult to do from Earth. These observations are important in investigating how the Sun creates and controls its heliosphere. SolO makes observations of the Sun from an eccentric orbit moving as close as ≈60 solar radii (RS), or 0.284 astronomical units (au), placing it inside Mercury's perihelion of 0.3075 au. During the mission the orbital inclination will be raised to about 24°. The total mission cost is US$1.5 billion, counting both ESA and NASA contributions. SolO was launched on 10 February 2020 from Cape Canaveral, Florida (USA). The nominal mission is planned until the end of 2026, with a potential extension unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |