Heliophysics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from
this youtube movie
/ref> He proposed " Heliophysics Science Division", which has been in use since then. The Heliophysics Science Division uses the term "heliophysics" to denote the study of the heliosphere and the objects that interact with it – most notably planetary atmospheres and magnetospheres, the solar corona, and the
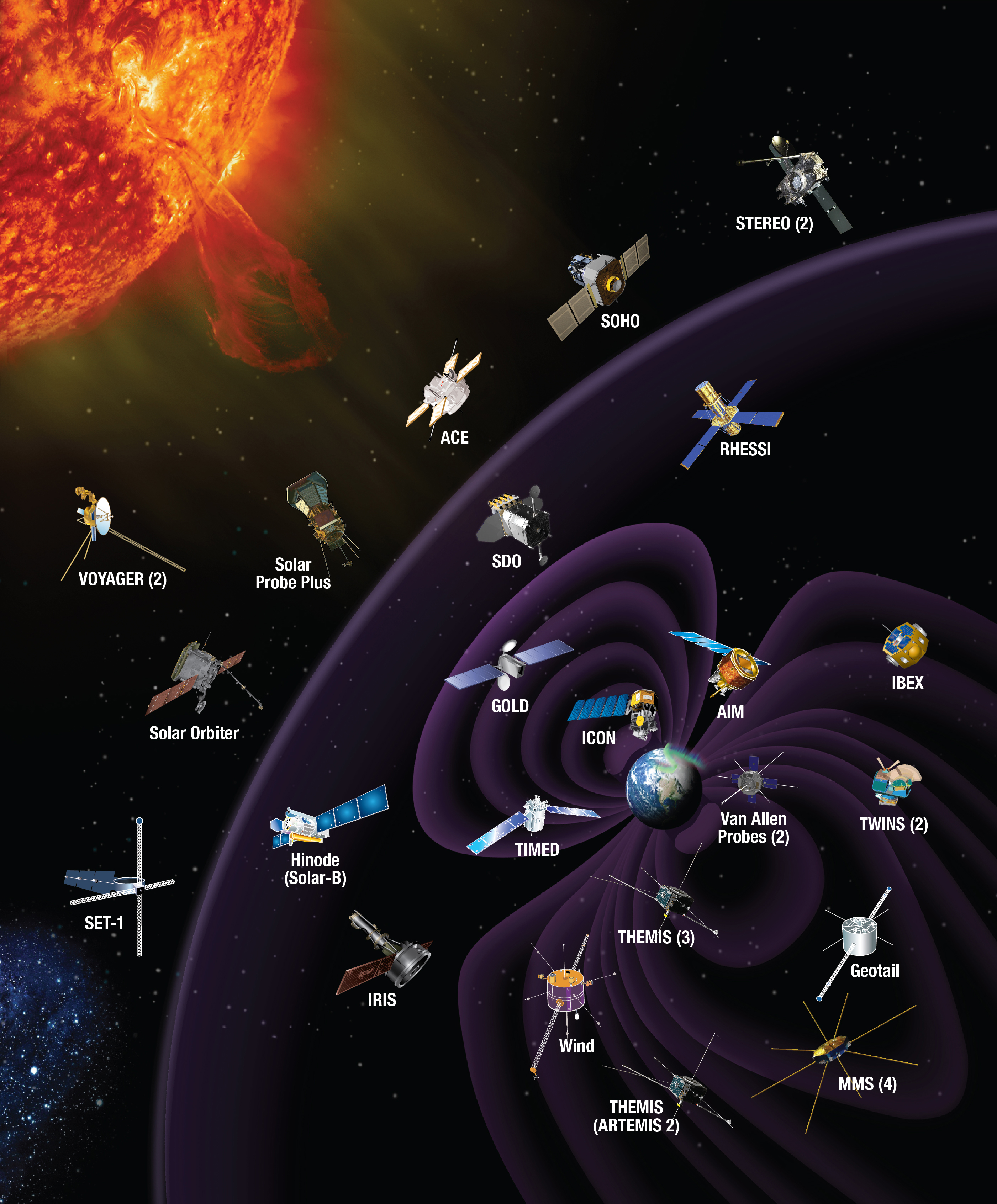 Methods have been developed to see into the internal workings of the Sun and understand how the
Methods have been developed to see into the internal workings of the Sun and understand how the
NASA HeliophysicsHeliophysics Integrated Observatory
*NASA video
Understanding The Sun – The Heliophysics Program
*NASA video
Introduction to Heliophysics
*American Geophysical Union video
Heliophysics and the Weather in Space''Principles Of Heliophysics: a textbook on the universal processes behind planetary habitability'' by Karel Schrijver et alNASA Heliophysics textbooksNASA-funded Summer Schools
{{Authority control Sun Space science Space weather Astrophysics Space plasmas
 Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek
Attic Greek is the Greek language, Greek dialect of the regions of ancient Greece, ancient region of Attica, including the ''polis'' of classical Athens, Athens. Often called Classical Greek, it was the prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige diale ...
''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
defines heliophysics as "(1) the comprehensive new term for the science of the Sun - Solar System Connection, (2) the exploration, discovery, and understanding of Earth's space environment, and (3) the system science that unites all of the linked phenomena in the region of the cosmos influenced by a star like our Sun."
Heliophysics is broader than Solar physics, that studies the Sun itself, including its interior, atmosphere, and magnetic fields. It concentrates on the Sun's effects on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
and other bodies within the Solar System, as well as the changing conditions in space. It is primarily concerned with the magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
, ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
, thermosphere, mesosphere, and upper atmosphere of the Earth and other planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s. Heliophysics combines the science of the Sun, corona, heliosphere and geospace, and encompasses a wide variety of astronomical phenomena, including "cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
and particle acceleration, space weather and radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcan ...
and magnetic reconnection, nuclear energy generation and internal solar dynamics, solar activity
Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere of the Sun. They take many forms, including solar wind, Solar radio emission, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, Stellar corona#Coron ...
and stellar magnetic fields, aeronomy and space plasmas, magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s and global change", and the interactions of the Solar System with the Milky Way Galaxy.
History and etymology
Term "heliophysics" () was widely used in Russian-languagescientific literature
Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical ...
. The Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
third edition (1969–1978) defines "Heliophysics" as " ��a division of astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the ...
that studies physics of the Sun". In 1990, the Higher Attestation Commission, responsible for the advanced academic degrees in Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and later in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and the Former Soviet Union, established a new specialty “Heliophysics and physics of solar system”. In English-language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
scientific literature prior to about 2001, the term heliophysics was sporadically used to describe the study of the "physics of the Sun". As such it was a direct translation from the French "héliophysique" and the Russian "гелиофизика". In 2001, Joseph M. Davila, Nat Gopalswamy and Barbara J. Thompson at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center adopted the term in their preparations of what became known as the International Heliophysical Year (2007–2008), following 50 years after the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; ), also referred to as the third International Polar Year, was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War w ...
; in adopting the term for this purpose, they expanded its meaning to encompass the entire domain of influence of the Sun (the heliosphere). As an early advocate of the newly expanded meaning, George Siscoe offered the following characterization:
"Heliophysics ncompassesenvironmental science, a unique hybrid betweenAround mid-2006, Richard R. Fisher, then Director of the Sun-Earth Connections Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, was challenged by the NASA administrator to come up with a concise new name for his division that "had better end on 'physics'".Richard Fisher speaking just after the 1h30m mark imeteorology Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...andastrophysics Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the ..., comprising a body of data and a set of paradigms (general laws—perhaps mostly still undiscovered) specific to magnetized plasmas and neutrals in the heliosphere interacting with themselves and with gravitating bodies and their atmospheres."
this youtube movie
/ref> He proposed " Heliophysics Science Division", which has been in use since then. The Heliophysics Science Division uses the term "heliophysics" to denote the study of the heliosphere and the objects that interact with it – most notably planetary atmospheres and magnetospheres, the solar corona, and the
interstellar medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the outer space, space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as cosmic dust, dust and cosmic rays. It f ...
.
Heliophysical research connects directly to a broader web of physical processes that naturally expand its reach beyond NASA's narrower view that limits it to the Solar System: heliophysics reaches from solar physics out to stellar physics in general, and involves several branches of nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies th ...
, plasma physics
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including th ...
, space physics and magnetospheric physics. The science of heliophysics lies at the foundation of the study of space weather, and is also directly involved in understanding planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to Abiogenesis, develop and sustain an environment hospitable to life. Life may be abiogenesis, generated directly on a planet or satellite endogenously. Res ...
.
Background
The Sun is an activestar
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
, and Earth is located within its atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, so there is a dynamic interaction. The Sun' light influences all life and processes on Earth; it is an energy provider that allows and sustains life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
on Earth. However, the Sun also produces streams of high energy particles known as the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
, and radiation that can harm life or alter its evolution. Under the protective shield of Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from structure of Earth, Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from ...
and its atmosphere, Earth can be seen as an island in the universe where life has developed and flourished.
The intertwined response of the Earth and heliosphere are studied because the planet is immersed in this unseen environment. Above the protective cocoon of Earth's lower atmosphere is a plasma soup composed of electrified and magnetized matter entwined with penetrating radiation and energetic particles. Modern technologies are susceptible to the extremes of space weather — severe disturbances of the upper atmosphere and of the near-Earth space environment that are driven by the magnetic activity of the Sun. Strong electrical currents driven in the Earth's surface during auroral events can disrupt and damage modern electric power grids and may contribute to the corrosion of oil and gas pipelines.
Heliophysics research program
 Methods have been developed to see into the internal workings of the Sun and understand how the
Methods have been developed to see into the internal workings of the Sun and understand how the Earth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
responds to solar activity
Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere of the Sun. They take many forms, including solar wind, Solar radio emission, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, Stellar corona#Coron ...
. Further studies are concerned with exploring the full system of complex interactions that characterize the relationship of the Sun with the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
.
There are three primary objectives that define the multi-decadal studies:
* To understand the changing flow of energy and matter throughout the Sun, heliosphere, and planetary environments.
* To explore the fundamental physical processes of space plasma systems.
* To define the origins and societal impacts of variability in the Earth-Sun system.
Heliosphere
Plasmas and their embedded magnetic fields affect the formation and evolution of planets and planetary systems. The heliosphere shields the Solar System from galactic cosmic radiation. Earth is shielded by itsmagnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
, protecting it from solar and cosmic particle radiation and from erosion of the atmosphere by the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
. Planets without a shielding magnetic field, such as Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, are exposed to those processes and evolve differently. On Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, the magnetic field changes strength and configuration during its occasional polarity reversals, altering the shielding of the planet from external radiation sources.
Magnetospheres
Determine changes in theEarth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
, ionosphere, and upper atmosphere in order to enable specification, prediction, and mitigation of their effects. Heliophysics seeks to develop an understanding of the response of the near-Earth plasma regions to space weather. This complex, highly coupled system protects Earth from the worst solar disturbances while redistributing energy and mass throughout.
See also
* NASA's Heliophysics Science Division * List of heliophysics missions ** Parker Solar Probe ** Solar Orbiter ** Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) ** Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) **STEREO
Stereophonic sound, commonly shortened to stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configurat ...
** Ulysses (spacecraft)
''Ulysses'' ( , ) was a Uncrewed spacecraft, robotic space probe whose primary mission was to orbit the Sun and study it at all latitudes. It was launched in 1990 and made three "fast latitude scans" of the Sun in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2 ...
* Aeronomy
* Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE)
* WIND (spacecraft)
* Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission (MMS)
* Cluster II (spacecraft) (Cluster II)
References
External links
NASA Heliophysics
*NASA video
Understanding The Sun – The Heliophysics Program
*NASA video
Introduction to Heliophysics
*American Geophysical Union video
Heliophysics and the Weather in Space
{{Authority control Sun Space science Space weather Astrophysics Space plasmas