|
Osco-Umbrian Languages
The Osco-Umbrian, Sabellic or Sabellian languages are an extinct group of Italic languages, the Indo-European languages that were spoken in central and southern Italy by the Osco-Umbrians before being replaced by Latin, as the power of ancient Rome expanded. Their written attestations developed from the middle of the 1st millennium BC to the early centuries of the 1st millennium AD. There is one text of about 4,000 words in Umbrian, but otherwise the languages are known almost exclusively from inscriptions, principally of Oscan and Umbrian, but there are also some Osco-Umbrian loanwords in Latin. Besides the two major branches of Oscan and Umbrian (and their dialects), South Picene may represent a third branch of Sabellic. The whole linguistic Sabellic area, however, might be considered a dialect continuum. Paucity of evidence from most of the "minor dialects" contributes to the difficulty of making these determinations. Relationship with the Italic languages Following an ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as List of islands of Italy, nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the List of European countries by area, tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and List of cities in Italy, largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous List of ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aequian Language
Aequian is an extinct Italic language presumed spoken by the people the Romans termed Aequi and Aequicoli living in the Alban hills of northeast Latium and the central Apennines east of them during the early and middle Roman Republic; that is, approximately from the 5th to the 3rd century BC, when they were defeated by the armies of Rome and were subsequently Romanized. As the area was heavily colonized by Latin speakers from Rome, most of the inscriptions from there are in Latin. Two undated inscriptions appear to be in a different dialect, termed Aequian by the scholars with the presumption that in fact they represent the language of the entire pre-Roman tribe. Not enough text survives to deduce any more than that it belonged to the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family. Corpus Aequian is scantily documented by two inscriptions. Conway's publication of Italic inscriptions adds a gloss, several place names and several dozen personal names, but it does not distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
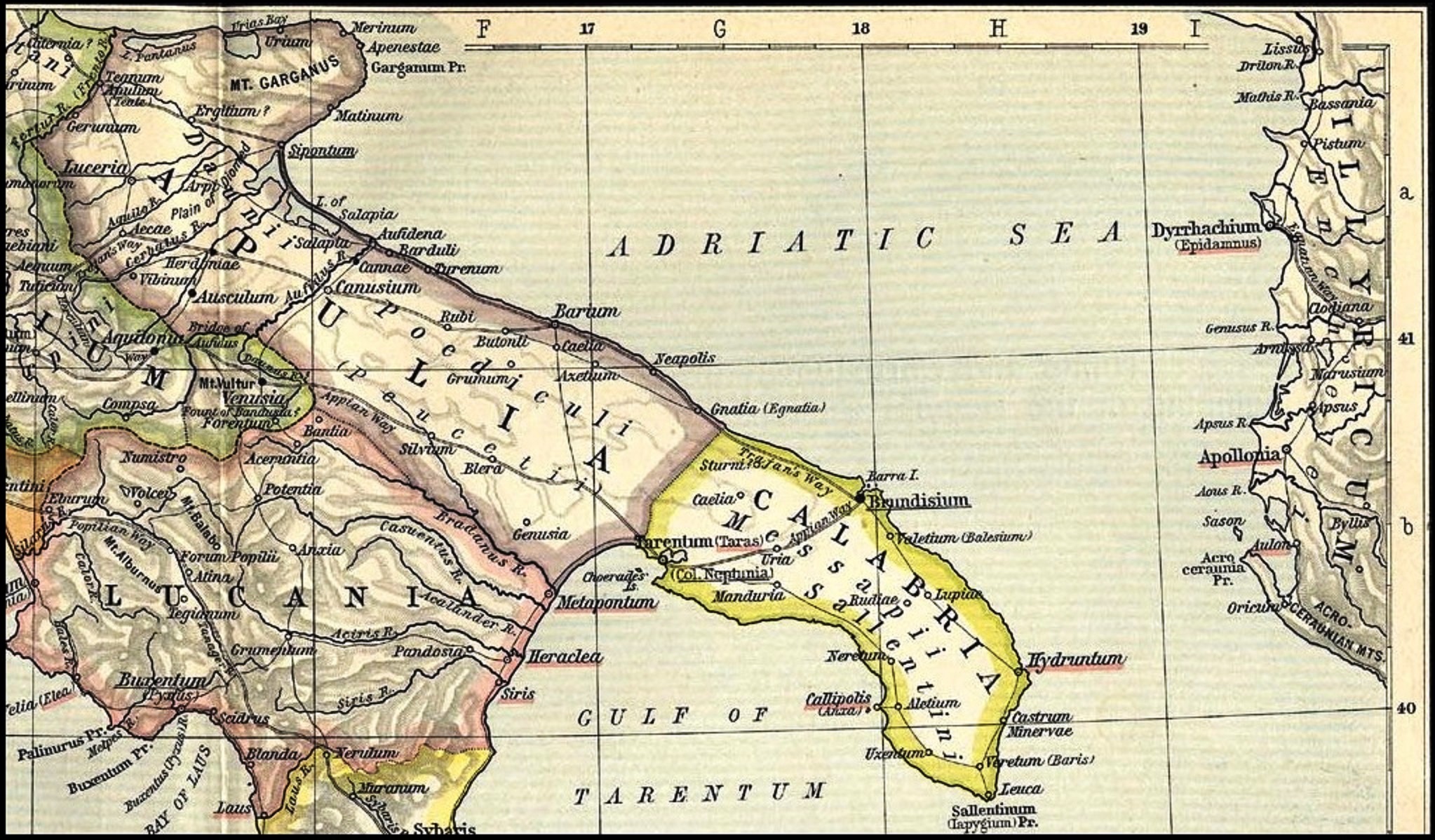
Messapians
The Messapians were an Iapygian tribe who inhabited Salento in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Daunians, inhabited central and northern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC. The Messapians lived in the eponymous region Messapia, which extended from Leuca in the southeast to Kailia and Egnatia in the northwest, covering most of the Salento peninsula. This region includes the Province of Lecce and parts of the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto today. Starting in the third century BC, Greek and Roman writers distinguished the indigenous population of the Salento peninsula differently. According to Strabo, the names ''Iapygians'', ''Daunians'', ''Peucetians'' and ''Messapians'' were exclusively Greek and not used by the natives, who divided the Salento in two parts. The southern and Ionian part of the peninsula was the territory of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapygians
The Iapygians or Apulians () were an Indo-European-speaking people, dwelling in an eponymous region of the southeastern Italian Peninsula named Iapygia (modern Apulia) between the beginning of the first millennium BC and the first century BC. They were divided into three tribal groups: the Daunians, Peucetians and Messapians. They spoke Messapic, a language of Paleo-Balkan provenance. After their lands were gradually colonized by the Romans from the late 4th century onward and eventually annexed to the Roman Republic by the early 1st century BC, Iapygians were fully Latinized and assimilated into Roman culture. Name The region was known to the Greeks of the 5th century BC as ''Iapygía'' (), and its inhabitants as the ''Iápyges'' (Ἰάπυγες). It was probably the term used by the indigenous peoples to designate themselves. The name ''Iapyges'' has also been compared to that of the '' Iapydes'', an Illyrian tribe of northern Dalmatia. Some ancient sources treat Iapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falisci
The Falisci were an Italic peoples, Italic tribe who lived in what is now northern Lazio, on the Etruscan side of the Tiber River. They spoke an Italic languages, Italic language, Faliscan language, Faliscan, closely related to Latin. Originally a sovereign state, politically and socially they supported the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, joining the Etruscan League. This conviction and affiliation led to their ultimate near destruction and total subjugation by Rome. Only one instance of their own endonym has been found to date: an inscription from Falerii Novi from the late 2nd century AD refers to the ', "the Faliscans who are in Sardinia", where ' is the nominative plural case. An Etruscan inscription calls them the '. The Latin cannot be far different from the original name. The -sc- suffix is "distinctive of the Italic ethnonyms". Geography The Falisci resided in a region called by the Romans the ', "Faliscan Country", located on the right bank of the Tiber River betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latins (Italic Tribe)
The Latins (), sometimes known as the Latials or Latians, were an Italic peoples, Italic tribe that included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome (see Roman people). From about 1000 BC, the Latins inhabited the small region known to the Romans as Old Latium (in Latin ''Latium vetus''), the area in the Italian Peninsula between the river Tiber and the promontory of Mount Circeo southeast of Rome. Following the Roman expansion, the Latins spread into the Latium adiectum, inhabited by Osco-Umbrian languages, Osco-Umbrian peoples. Their language, Latin, belonged to the Italic languages, Italic branch of Indo-European. Speakers of Italic languages are assumed to have migrated into the Italian Peninsula during the late Bronze Age (1200–900 BC). The material culture of the Latins, known as the Latial culture, was a distinctive subset of the proto-Villanovan culture that appeared in parts of the Italian peninsula in the first half of the 12th century BC. The Latins mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbri
The Umbri were an Italic peoples, Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the Regio VI Umbria, ancient Umbria. Most ancient Umbrian cities were settled in the 9th-4th centuries BC on easily defensible hilltops. Regio VI Umbria, Umbria was bordered by the Tiber and Nar rivers and included the Apennine slopes on the Adriatic. The ancient Umbrian language is a branch of a group called Osco-Umbrian languages, Oscan-Umbrian, which is related to the Latino-Faliscan languages. Origins They are also called ''Ombrii'' in some Roman Empire, Roman sources. Ancient Roman writers thought the Umbri to be of Gauls, Gaulish origin; Cornelius Bocchus wrote that they were descended from an ancient Gaulish tribe. Plutarch wrote that the name might be a different way of writing the name of a northern European tribe, the Ambrones, and that both ethnonyms were cognate with "King of the Boii". However, both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osci
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language of the Samnites was called Oscan, the Samnites were never referred to as Osci, nor were the Osci called Samnites. Traditions of the Opici fall into the legendary period of Italian history, roughly from the beginning of the first millennium BC until the foundation of the Roman Republic. No consensus can be reached concerning their location and language. By the end of this period, the Oscan language had evolved and was spoken by a number of sovereign tribal states. By far the most important of these in terms of military prowess and wealth was the Samnites, who rivalled Rome for about 50 years in the second half of the 4th century BC, sometimes being allies, and sometimes at war with the city, until they were finally subdued with consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giacomo Devoto
Giacomo Devoto (19 July 1897 – 25 December 1974) was an Italian historical linguist and one of the greatest exponents of the twentieth century of the discipline. He was born in Genoa and died in Florence. Biography He was the son of clinician and pathologist Luigi Devoto (1864–1936) and brother of industrialist Giovanni (1903–1944). In 1939 he founded with Bruno Migliorini the journal Lingua Nostra. In 1931 he took the oath of allegiance to fascism with quiet cynicism (the expression is Gennaro Sasso's): the oath had for him "the value of a glass of cold water.". In January 1945, immediately after the Liberation, he founded in Florence together with Piero Calamandrei, Corrado Tumiati, Enzo Enriques Agnoletti and Paride Baccarini the AFE, the Association of European Federalists, later merging into the European Federalist Movement founded by Altiero Spinelli, in which he played a leading role in the years 1947–1948. Assessor in the council of the City of Florence chaire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alois Walde
Alois Walde (November 30, 1869 – October 3, 1924) was an Austrian linguist. Alois Walde studied classical philology and comparative linguistics at the University of Innsbruck where he was awarded a PhD in 1894. The year after, he became a state employee at the university library. In 1895, he was awarded his ''habilitation'' and became a professor in 1904 at the University of Innsbruck. 1909-1912, Walde was Professor of comparative linguistics at the University of Giessen, but returned in 1912 to Innsbruck where he became the dean of faculty in 1914 and rector of the university in 1916. The year after, he became a corresponding member of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. In 1922, he took up a professorship at Albertina University Königsberg. In the same year, Walde accepted a professorship at Breslau University for 1924, but he died before he could take the new position.Walter Porzig: ''Alois Walde.'' In: ''Indogermanisches Jahrbuch.'' Volume 10, 1926, , pp. 421–428 (with p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faliscan Language
The Faliscan language is the extinct Italic language of the ancient Falisci, who lived in southern Etruria at Tiber Valley. Together with Latin, it formed the Latino-Faliscan languages group of the Italic languages. It seems probable that the language persisted, being gradually permeated with Latin, until at least 150 BC. Corpus An estimated 355 inscriptions survive, mostly short and dating from the 7th to the 2nd centuries BC. Some are written from right to left in a variety of the Old Italic alphabet, derived from the Etruscan alphabet, but they show some traces of the influence of the Latin alphabet. An inscription to Ceres of c. 600 BC, found in Falerii, usually taken to be the oldest example, is written left to right. A specimen of the language appears written around the edge of a picture on a patera, the genuineness of which is established by the fact that the words were written before the glaze was put on: ', . That sample indicates that Faliscan was less conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |