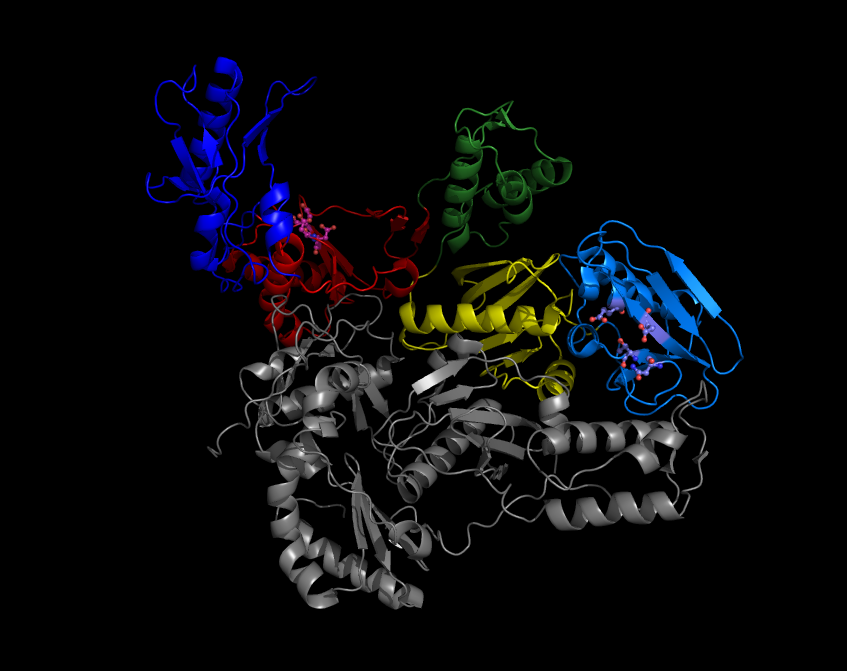
|
Ortervirales
''Ortervirales'' is an order that contains all accepted species of single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate (Group VI) and all accepted species of double-stranded DNA viruses (except ''Hepadnaviridae'') that replicate through an RNA intermediate (Group VII). The name is derived from the reverse of retro. All reverse-transcribing viruses possess significant similarities to each other. Their reverse transcriptase proteins share a common origin. Moreover, belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses, and retroviruses have other features in common. Their polymerase proteins are similar in structure and include aspartic protease (retroviral aspartyl protease) and an integrase belonging to the DDE recombinase superfamily (see Recombination-activating gene#Structure, Recombination-activating gene [structure]). They also share similar capsid and nucleocapsid proteins/domains. Caulimoviruses also share some features with belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus ''retro'' (backward). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, transcribing and translating the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus. Many retroviruses cause serious diseases in humans, other mammals, and birds. Retroviruses have many subfamilies in three basic groups. * Oncoretroviruses (cancer-causing retroviruses) include human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) causing a type of leukemia in humans, and murine le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belpaoviridae
''Semotivirus'' is the only genus of viruses in the family ''Belpaoviridae'' (formerly included in the family ''Metaviridae''). Species exist as retrotransposons in a Eukaryote, eukaryotic host's genome. BEL/pao transposons are only found in animals. ''Semotivirus'' is the only genus currently recognized, the genus description corresponds to the family, ''Belpaoviridae'' description. Classification The lone genus in the family, ''Semotivirus'', was formerly included in the ''Metaviridae'' family but was removed due to its paraphyletic relationship to other ''Metaviridae'' genera. There is a good chance that more species and genera will be added to the family ''Belpaoviridae'' in the future, given the diversity of belpaovirids that is already recognized. The Pol domain order of the families ''Belpaoviridae'', ''Metaviridae'', and ''Retrovirus, Retroviridae'' is the same within the order ''Ortervirales'', however the integrase is either lacking in the case of the ''Caulimoviridae'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoviridae
''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of viruses, which includes three genera. Viruses of the family are actually LTR retrotransposons of the Ty1-copia family. They replicate via structures called virus-like particles (VLPs). VLPs are not infectious like normal virions, but they nevertheless make up an essential part of the pseudoviral lifecycle. Taxonomy ''Pseudoviridae'' is unofficially classified under group VI RNA Reverse Transcribing Viruses and infect fungi and invertebrates. ''Pseudoviridae'' comprises highly divergent members and most ''Pseudoviridae'' encode Gag and Pol on a single open reading frame. ''Pseudoviridae'' is included in the order ''Ortervirales'' along with families ''Belpaoviridae'', ''Metaviridae'', ''Retroviridae'', and ''Caulimoviridae''. The family includes the following genera: * ''Hemivirus'' * ''Pseudovirus (genus), Pseudovirus'' * ''Sirevirus'' Further ''Pseudoviridae'' species not classified into a genus are: * Penicillium camemberti virus – GP1NCB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaviridae
''Metaviridae'' is a family of viruses which exist as Ty3-gypsy LTR retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. They are closely related to retroviruses: members of the family ''Metaviridae'' share many genomic elements with retroviruses, including length, organization, and genes themselves. This includes genes that encode reverse transcriptase, integrase, and capsid proteins. The reverse transcriptase and integrase proteins are needed for the retrotransposon activity of the virus. In some cases, virus-like particles can be formed from capsid proteins. Some assembled virus-like particles of members of the family ''Metaviridae'' can penetrate and infect previously uninfected cells. An example of this is the gypsy, a retroelement found in the ''Drosophila melanogaster'' genome. The ability to infect other cells is determined by the presence of the retroviral ''env'' genes which encode coat proteins. Metaviridae retrotransposons are found in all eukaryotes known and studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulimoviridae
''Caulimoviridae'' is a family of viruses infecting plants. The family contains 11 genera. Viruses belonging to the family ''Caulimoviridae'' are termed double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) reverse-transcribing viruses (or pararetroviruses) i.e. viruses that contain a reverse transcription stage in their replication cycle. This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle. Taxonomy The following genera are recognized: *''Badnavirus'' *''Caulimovirus'' *''Cavemovirus'' *''Dioscovirus'' *''Petuvirus'' *''Rosadnavirus'' *''Ruflodivirus'' *''Solendovirus'' *''Soymovirus'' *''Tungrovirus'' *''Vaccinivirus'' Virus particle structure All viruses of this family are non-enveloped. Virus particles are either bacilliform or isometric. The type of nucleocapsid incorporated into the virus structure determines the size of the viral particles. Bacilliform particles are approximately 35–50 nm in diameter and up to 900 nm in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTR Retrotransposon
LTR retrotransposons are class I transposable elements (TEs) characterized by the presence of long terminal repeats (LTRs) directly flanking an internal coding region. As retrotransposons, they mobilize through reverse transcription of their mRNA and integration of the newly created cDNA into another genomic location. Their mechanism of retrotransposition is shared with retroviruses, with the difference that the rate of horizontal transfer in LTR-retrotransposons is much lower than the vertical transfer by passing active TE insertions to the progeny. LTR retrotransposons that form virus-like particles are classified under ''Ortervirales''. Their size ranges from a few hundred base pairs to 30 kb, the largest species reported to date are members of the Burro retrotransposon family in '' Schmidtea mediterranea''. In plant genomes, LTR retrotransposons are the major repetitive sequence class constituting more than 75% of the maize genome. LTR retrotransposons make up about 8% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepadnaviridae
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. The family contains five genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family include: liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas (chronic infections), and cirrhosis. It is the sole accepted family in the order ''Blubervirales''. Taxonomy The following genera are recognized: * '' Avihepadnavirus'' * '' Orthohepadnavirus'' * '' Herpetohepadnavirus'' * '' Metahepadnavirus'' * '' Parahepadnavirus'' History and discovery Although liver diseases transmissible among human populations were identified early in the history of medicine, the first known hepatitis with a viral etiological agent was Hepatitis A, in the picornaviridae family. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) was identified as an infection distinct from Hepatitis A through its contamination of yellow fever vaccine. The vaccine contained human serum as a stabilizing agent which was HBV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of virus taxa. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. The process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, but rather expands it to include transfers of information from RNA to DNA. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genome, from which new RNA copies can be made via host-cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme (Enzyme Commission number, EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by copying a DNA template strand using Base pair, base-pairing interactions or RNA by half ladder replication. A DNA polymerase from the thermophile, thermophilic bacterium, ''Thermus aquaticus'' (''Taq'') (Protein Data Bank, PDB]1BGX EC 2.7.7.7) is used in the polymerase chain reaction, an important technique of molecular biology. A polymerase may be template-dependent or template-independent. Polynucleotide adenylyltransferase, Poly-A-polymerase is an example of template independent polymerase. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase also known to have template independent and template dependent activities. By function *DNA polymerase (DNA-directed DNA polymerase, DdDP) **Family A: DNA polymerase I; Pol POLG, γ, POLQ, θ, DNA polymer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroviral Aspartyl Protease
Retroviral aspartyl proteases or retropepsins are single domain aspartyl proteases from retroviruses, retrotransposons, and badnaviruses (plant dsDNA viruses). These proteases are generally part of a larger pol or gag polyprotein. Retroviral proteases are homologous to a single domain of the two-domain eukaryotic aspartyl proteases such as pepsins, cathepsins, and renins (; MEROPS A1). Retropepsins are members of MEROPS A2, clan AA. All known members are endopeptidases. The enzyme is only active as a homodimer, as each one corresponds to half of the eukaryotic two-lobe enzyme. The two parts each contribute one catalytic aspartyl residue. Retroviral aspartyl protease is synthesised as part of the pol polyprotein that contains an aspartyl protease, a reverse transcriptase, RNase H and integrase. pol polyprotein undergoes specific enzymatic cleavage to yield the mature proteins. Not all retroviral aspartyl proteases generated from ''pol'' are retropepsins in the stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |