|
Nyasa Languages
The Nyasa languages are an apparently valid genealogical group of Bantu languages The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, South .... With the reassignment of a couple of Guthrie Zone N languages to other branches, Nyasa is essentially synonymous with Zone N. The languages and their Guthrie identifications are: * '' Tumbuka'' (N21) * '' Tonga language (Malawi)'' (N15) * '' Chewa'' (''Nyanja'') (N31) * ''Sena'' group (N40): '' Chikunda''-'' Nyungwe'' (N42, N43), '' Sena'' (incl. ''Podzo'', ''Rue'') (N44) The poorly known Mwera (Nyasa) language spoken at Mbamba Bay on the east side of Lake Malawi is classified as N201 and presumably belongs here as well. References {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malawi
Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south, and southwest. Malawi spans over and has an estimated population of 21,240,689 (as of 2024). Lilongwe is its capital and largest city, while the next three largest cities are Blantyre, Mzuzu, and Zomba, the former capital. The part of Africa now known as Malawi was settled around the 10th century by the Akafula, also known as the Abathwa. Later, the Bantu groups came and drove out the Akafula and formed various kingdoms such as the Maravi and Nkhamanga kingdoms, among others that flourished from the 16th century. In 1891, the area was colonised by the British as the British Central African Protectorate, and it was renamed '' Nyasaland'' in 1907. In 1964, Nyasaland became an independent country as a Commonwealth realm under Prime Minister Hastings Banda, and was rena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
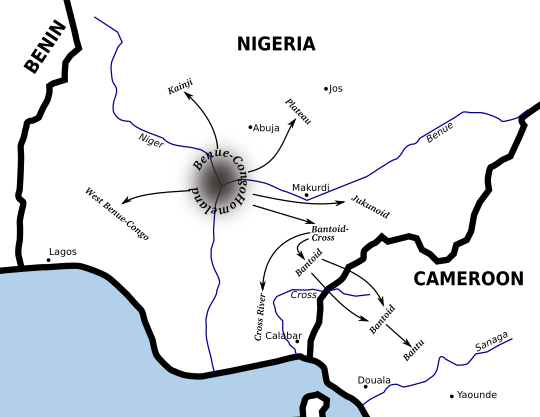
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantoid
Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named. History The term "Bantoid" was first used by Krause in 1895 for languages that showed resemblances in vocabulary to Bantu. Joseph Greenberg, in his 1963 ''The Languages of Africa'', defined Bantoid as the group to which Bantu belongs together with its closest relatives; this is the sense in which the term is still used today. However, according to Roger Blench, the Bantoid languages probably do not actually form a coherent group. Internal classification A proposal that divided Bantoid into North Bantoid and South Bantoid was introduced by Williamson. In this proposal, the Mambiloid and Dakoid languages (and later Tikar) are grouped together as North Bantoid, while everything else Bantoid is subsumed under So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bantoid Languages
Southern Bantoid (or South Bantoid) is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon (though the affiliation of some branches is uncertain). Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by ''Ethnologue'', though many of these are mutually intelligible. History Southern Bantoid was first introduced by Williamson in a proposal that divided Bantoid into North and South branches. The unity of the North Bantoid group was subsequently called into question, and Bantoid itself may be polyphyletic A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ..., but the work did establish Southern Banto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guthrie Classification Of Bantu Languages
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades (groups A10, A20, etc.); individual languages were assigned unit numbers (A11, A12, etc.), and dialects further subdivided (A11a, A11b, etc.). This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was a practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J (made of languages formerly classified in groups D and E) has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes. The list is first summarized, with links to articles on accepted groups of Bantu languages (bold decade headings). Following that is the complete 1948 list, as updated by Guthr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumbuka Language
Chitumbuka (also known as Senga) is a Bantu languages, Bantu language which is spoken primarily in Malawi, Zambia, Tanzania, and Zimbabwe.Michigan State University African Studies Center information page It is the native and primary language of at least 11 groups of Bantu peoples, namely, the Senga people, Senga, Tumbuka people, Tumbuka, Yombe people (Zambia), Yombe, Phoka people, Phoka, Henga people, Henga, Balowoka, Fungwe, Hewe, Northern Ngoni, Kamanga people, Kamanga and Tonga people (Malawi), with 12 known and studied dialects. The ''chi-'' prefix in front of ''Tumbuka'' means ''"the language of",'' so the language is usually called ''Chitumbuka'' even in English publications''.'' In Northern Region, Malawi, Northern Malawi, Chitumbuka is spoken in all 6 districts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonga Language (Malawi)
Tonga is a Tumbuka offshoot Bantu language that emerged in 18th Century when the Nkhamanga Kingdom started to decline and was split. Before the arrival of missionaries in what is now known as Malawi, Tonga was the Tumbuka dialect. It was after the missionaries established their churches when they treated the two as separate languages. Tonga is grouped in the Glottolog classification along with Tumbuka in a single group. The Tonga language as a legacy offshoot, has been described as "similar" to Tumbuka, and Turner's dictionary (1952) lists only those words which differ from the Tumbuka. Malawian Tonga is classified by Guthrie as being in Zone N15, whereas the Zambian Tonga is a different language classified as Zone M64. Therefore, the two languages are not the same but they only share a similar name. Similarities with Tumbuka as its dialect Almost all verbs found in Tumbuka are all available in Tonga. However, there are few slight differences that from an outsider, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chewa Language
Chewa ( ; also known as Nyanja ) is a Bantu languages, Bantu language spoken in Malawi and a recognised minority in Zambia and Mozambique. The noun class prefix ''chi-'' is used for languages, so the language is often called or Chinyanja. In Malawi, the name was officially changed from Chinyanja to Chichewa in 1968 at the insistence of President Hastings Banda, Hastings Kamuzu Banda (himself of the Chewa people), and this is still the name most commonly used in Malawi today. In Zambia, the language is generally known as Nyanja or '(language) of the lake' (referring to Lake Malawi). Chewa belongs to the same language group (Guthrie classification of Bantu languages#Zone N, Guthrie Zone N) as Tumbuka language, Tumbuka, Sena language, Sena and Nsenga language, Nsenga. Throughout the history of Malawi, only Chewa and Tumbuka language, Tumbuka have at one time been the primary dominant national languages used by government officials and in school curricula. However, the Tumbuka lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikunda Language
Kunda (''Chikunda'') is a Bantu language of Zimbabwe, with some thousands of speakers in Zambia and Mozambique. There is an extinct pidgin A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified form of contact language that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn f ... Chikunda once used for trade. References Further reading *Zemba, Mercy (2015)"A grammatical sketch of Kunda Language" University of Zambia MA dissertation.Description) {{Narrow Bantu languages (Zones N–S) Languages of Zambia Languages of Mozambique Languages of Zimbabwe Nyasa languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |