|
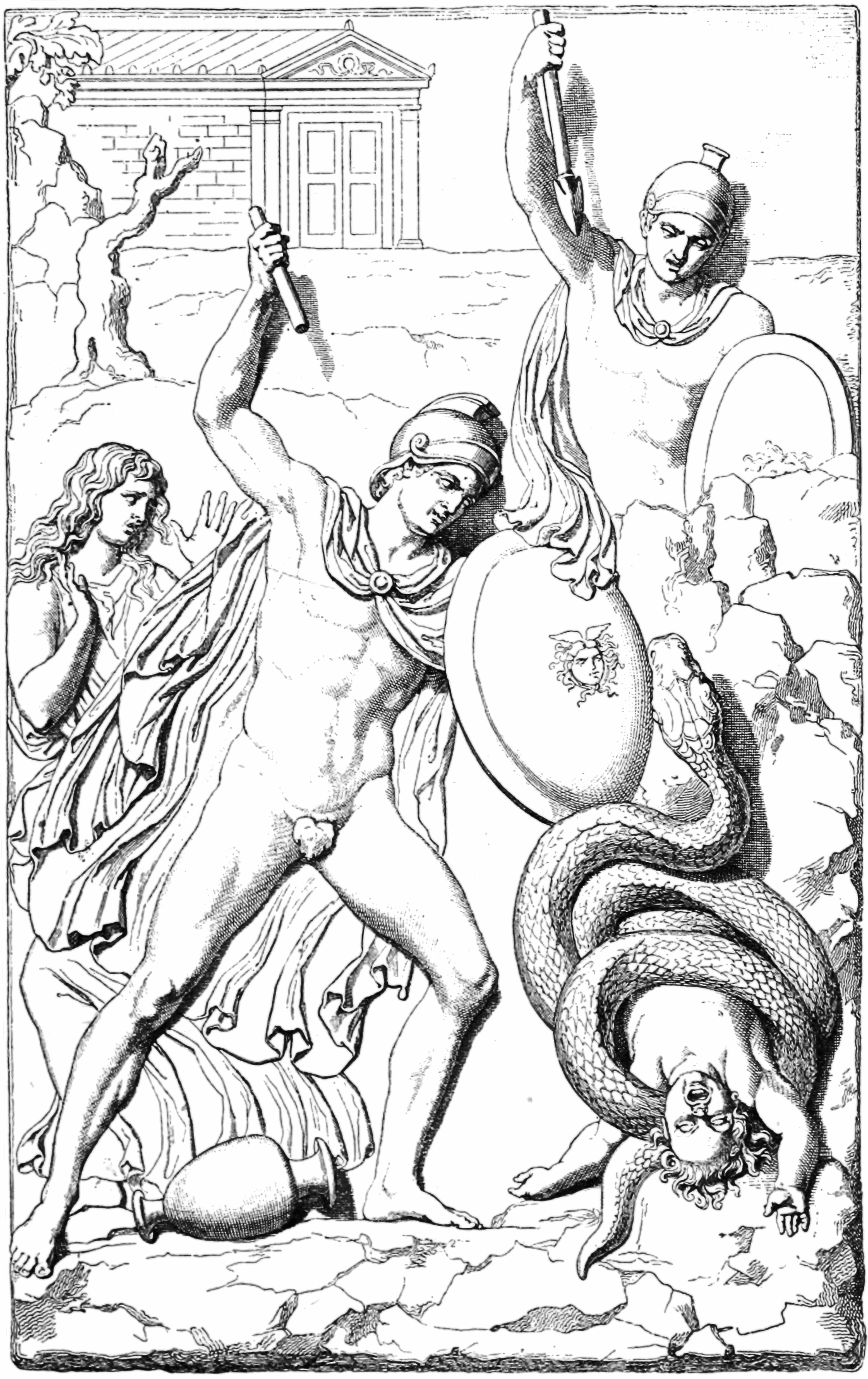
Niobids
In Greek mythology, the Niobids were the children of Amphion of Thebes and Niobe, slain by Apollo and Artemis because Niobe, born of the royal house of Phrygia, had boastfully compared the greater number of her own offspring with those of Leto, Apollo's and Artemis' mother: a classic example of '' hubris''. Names The number of Niobids mentioned most usually numbered twelve (Homer) or fourteen (Euripides and Apollodorus), but other sources mention twenty, four (Herodotus), or eighteen (Sappho). Generally half these children were sons, the other half daughters. The names of some of the children are mentioned; these lists vary by author: Other different names were also mentioned, including Amaleus, Amyclas and Meliboea (also in Apollodorus, see below). Manto, the seeress daughter of Tiresias, overheard Niobe's remark and bid the Theban women placate Leto, in vain. Apollo and Artemis slew all the children of Niobe with their arrows, Apollo shooting the sons, Artemis the daugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobe
Niobe (; : Nióbē) was in Greek mythology a daughter of Tantalus and of either Dione or of Eurythemista or Euryanassa. She was the wife of Amphion and the sister of Pelops and Broteas. Niobe is mentioned by Achilles in Homer's ''Iliad'', which relates her ''hubris'', for which she was punished by Leto, who sent Apollo and Artemis to slay all of her children, after which her children lay unburied for nine days while she abstained from food. Once the gods had interred the slain, Niobe retreated to her native Sipylus, "where Nymphs dance around the River Acheloos, and though turned to stone, she broods over the sorrows sent by the Gods". Later writers asserted that Niobe was wedded to Amphion, one of the twin founders of Thebes, where there was a single sanctuary where the twin founders were venerated, but no shrine to Niobe. Mythology Family Her father was the ruler of a city located near Manisa in today's Aegean Turkey that was called "Tantalis" or "the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leto
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Leto (; ) is a childhood goddess, the daughter of the Titans Coeus and Phoebe (Titaness), Phoebe, the sister of Asteria, and the mother of Apollo and Artemis.Hesiod, ''Theogony'404–409/ref> In the Olympian scheme, the king of gods Zeus is the father of her twins, Apollo and Artemis, whom Leto conceived after her hidden beauty accidentally caught the eye of Zeus. During her pregnancy, Leto sought for a place where she could give birth to Apollo and Artemis, since Hera, the wife of Zeus, in her jealousy, ordered all lands to shun her and deny her shelter. Hera is also the one to have sent the monstrous serpent Python (mythology), Python and the giant Tityos against Leto to pursue and harm her. Leto eventually found an island, Delos, that was not joined to the mainland or attached to the ocean floor, therefore it was not considered land or island and she could give birth. In some stories, Hera further tormented L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. He is considered to be the most beautiful god and is represented as the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth). Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracular god—the prophetic deity of the Pythia, Delphic Oracle and also the deity of ritual purification. His oracles were often consulted for guidance in various matters. He was in general seen as the god who affords help and wards off e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ismenus
In Greek mythology, the name Ismenus (Ancient Greek: Ἰσμηνός) or Ismenius may refer to: *Ismenus or Ismenius, son of Oceanus and Tethys, god of the river of the same name. He was mentioned as the father of several spring nymphs, including Dirce and Strophia, also Crocale and the musician Linus. In Statius' ''Thebaid'', the river god Ismenus gets involved in the war of the Seven against Thebes: he attempts to raise his waters against Hippomedon in revenge for the death of Crenaeus, son of his daughter Ismenis by Pan, but has to withdraw his attack at the request of Zeus. *Ismenus, son of Asopus and Metope, eponym of River Ismenus in Boeotia, on the banks of which he settled. *Ismenus, one of the Niobids. *Ismenus, also spelled Ismenius, son of Apollo and the Oceanid Melia, brother of the seer Tenerus, and an alternate eponym of River Ismenus, which is said to have previously been known as Ladon.Pausanias, 9.10.6 Notes References * Apollodorus, ''The Library ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphion
There are several characters named Amphion in Greek mythology: * Amphion, son of Zeus and Antiope, and twin brother of Zethus (see Amphion and Zethus). Together, they are famous for building Thebes. Pausanias recounts an Egyptian legend according to which Amphion employed magic to build the walls of the city. Amphion married Niobe, and killed himself after the loss of his wife and children (the Niobids) at the hands of Apollo and Artemis. Diodorus Siculus calls Chloris his daughter, but the other accounts of her parentage identify her father as another Amphion, the ruler of Minyan Orchomenus (see below). * Amphion, king of the Minyan Orchomenus and son of Iasus. By Persephone, daughter of Minyas, he became the father of Chloris, wife of Neleus and Phylomache, wife of Pelias; these husbands are sons of Tyro and Poseidon. * Amphion, son of Hyperasius, son of Pelles, son of Phorbas. From Achaean Pellene, he and his brother Asterius were counted among the Argonauts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later times, she was identified with Selene, the Lunar deity, personification of the Moon.Smiths.v. Artemis/ref> She was often said to roam the forests and mountains, attended by her entourage of nymphs. The goddess Diana (mythology), Diana is her Religion in ancient Rome, Roman equivalent. In Greek tradition, Artemis is the daughter of Zeus and Leto, and twin sister of Apollo. In most accounts, the twins are the products of an extramarital liaison. For this, Zeus' wife Hera forbade Leto from giving birth anywhere on solid land. Only the island of Delos gave refuge to Leto, allowing her to give birth to her children. In one account, Artemis is born first and then proceeds to assist Leto in the birth of the second twin, Apollo. Artemis was a kouro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholia
Scholia (: scholium or scholion, from , "comment", "interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of the manuscript of ancient authors, as glosses. One who writes scholia is a scholiast. The earliest attested use of the word dates to the 1st century BC. History Ancient scholia are important sources of information about many aspects of the ancient world, especially ancient literary history. The earliest scholia, usually anonymous, date to the 5th or 4th century BC (such as the ''scholia minora'' to the ''Iliad''). The practice of compiling scholia continued to late Byzantine times, outstanding examples being Archbishop Eustathius' massive commentaries to Homer in the 12th century and the ''scholia recentiora'' of Thomas Magister, Demetrius Triclinius and Manuel Moschopoulos in the 14th. Scholia were altered by successive copyists and owners of the manusc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactantius Placidus
Lactantius Placidus (c. 350 – c. 400 AD) was the presumed author of a commentary on Statius's poem ''Thebaid''. Wilhelm Siegmund Teuffel considered him to be the same person as Luctatius Placidus, the ostensible author of a medieval Latin glossary titled ''Glossae Luctatii Placidi grammatici'' ("Glosses of Luctatius Placidus the Grammarian"). Some authors also attribute an anonymous work titled ''Narrationes fabularum quae in Ov. Metam. occurrunt'' to Lactantius, though Franz Bretzigheimer argued against this view, on the basis that the commentator on Statius lacks evidence of Christian A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ... attitudes seen in the ''Narrationes''. The commentary on Statius has been edited by Robert Dale Sweeney, ''Lactantii Placidi in Statii Thebaid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek language, Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; , ; ) was a Latin poetry, Latin poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid (Latin poem), Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, the ''Silvae''; and an unfinished epic, the ''Achilleid''. He is also known for his appearance as a guide in the ''Purgatorio, Purgatory'' section of Dante Alighieri, Dante's epic poem, the ''Divine Comedy''. Life Family background The poet's father (whose name is unknown) was a native of Velia but later moved to Naples and spent time in Rome where he taught with marked success. From boyhood to adulthood, Statius's father proved himself a champion in the poetic contests at Naples in the Augustalia and in the Nemean, Pythian Games, Pythian, and Isthmian Games, Isthmian games, which served as important events to display poetic skill during the early empire. Statius declares in his lament for his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; ) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 9748 lines arranged in 12 books, and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes, Greece, Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of Seven against Thebes, seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Ancient Greek literature, Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Virgil's ''Aeneid'' and Senecan tragedy, the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid, Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatican Mythographers
The so-called Vatican Mythographers () are the anonymous authors of three Latin mythographical texts found together in a single medieval manuscript, Vatican Reg. lat. 1401. The name is that used by Angelo Mai when he published the first edition of the works in 1831. The text of the First Vatican Mythographer is found only in the Vatican manuscript; the second and third texts are found separately in other manuscripts, leading scholars to refer to a Second Vatican Mythographer and a Third Vatican Mythographer. Content Taken together, the works of the Vatican Mythographers provided a source-book of Greek and Roman myths and their iconography throughout the Middle Ages and the Renaissance. The texts, which were being copied in manuscripts as late as the 15th century, were parsed allegorically to provide Christianized moral and theological implications, "until in time the pagan divinities blossomed into full-fledged vices and virtues". Their '' testimonia'', sources, and parallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Painting - Death Of The Niobids - Pompeii (VII 15 2) - Napoli MAN 111479
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or serves a decorative purpose. There are various types of walls, including border barriers between countries, brick walls, defensive walls in fortifications, and retaining walls that hold back dirt, stone, water, or noise. Walls can also be found in buildings, where they support roofs, floors, and ceilings, enclose spaces, and provide shelter and security. The construction of walls can be categorized into framed walls and mass-walls. Framed walls transfer the load to the foundation through posts, columns, or studs and typically consist of structural elements, insulation, and finish elements. Mass-walls are made of solid materials such as masonry, concrete, adobe, or rammed earth. Walls may also house utilities like electrical wiring or plumbing and must conform to local building and fire codes. Walls have historically served defensive purposes, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |