|
Military Of Zambia
The Zambian Defence Force is the military of Zambia. It consists of the Zambian Army, the Zambian Air Force, and the Zambia National Service. The defence forces were formed at Zambian independence on 24 October 1964, from constituent units of the dissolved Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland Armed Forces. During the 1970s and 1980s, it played a key role in a number of regional conflicts, namely the South African Border War and Rhodesian Bush War. Being a landlocked country Zambia has no navy, although the Zambian Army maintains a maritime patrol unit for maintaining security on inland bodies of water.'Zambia Army Commando Unit splits, forms Marine Unit', ''Lusaka Voice'', 18 February 2015, accessed 5 February 2017, History Background and independence The Zambian Defence Force had its roots in the Northern Rhodesia Regiment, a multi-ethnic military unit which was raised by the British colonial government and had served with distinction during World War II. In 1960, the constituen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambia National Service
The Zambia National Service, abbreviated ZNS, is part of the Zambian Defence Force, has been a cornerstone of national development since its establishment in 1971 through an Act of Parliament. Committed to the twin objectives of training civilian and safeguarding the territorial integrity of Zambia, the ZNS Act empowers them to prepare individuals to dutifully serve and protect the nation. However, it's not only about defense; ZNS also plays a vital role in imparting agricultural and craft skills to Zambians, promoting self-sufficiency and national prosperity. Originating in 1963 as the ''Land Army'', ZNS has evolved into a dynamic force for national progress, underlining its multifaceted contribution to Zambia. Additionally, ZNS is also a major sponsor of Green Eagles football club, further exemplifying its commitment to the nation's well-being. History The history of the Zambia National Service (ZNS) evolves from a politically charged origin to a pivotal institution in Zambia's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Patrol
Maritime patrol or maritime reconnaissance is the task of monitoring areas of water. Generally conducted by military and law enforcement agencies, maritime patrol is usually aimed at identifying human activities. Maritime patrol refers to active patrol of an area, as opposed to passive monitoring systems such as sound-detection fixtures or land-based spotters. A patrol consists of a ship, submarine, aircraft or satellite examining the patrolled area and seeking out activities to be identified and reported. Maritime patrol is critical in wartime situations for navies to locate enemy forces to engage or defend against. Peacetime patrols are important for interdiction of criminal activities and for ensuring legal use of waters. Maritime patrols can be conducted by surface ships and submarines, by aircraft (e.g. MPA) and other aerial vehicles, and even by satellites. Human spotting remains an important part of detecting activity, but increasingly electronic systems are used. Typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambezi River
The Zambezi (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of the Nile's. The river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi's most noted feature is Victoria Falls. Its other falls include the Chavuma Falls at the border between Zambia and Angola and Ngonye Falls near Sioma in western Zambia. The two main sources of hydroelectric power on the river are the Kariba Dam, which provides power to Zambia and Zimbabwe, and the Cahora Bassa Dam in Mozambique, which provides power to Mozambique and South Africa. Additionally, two smaller power stations are along the Zambezi River i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
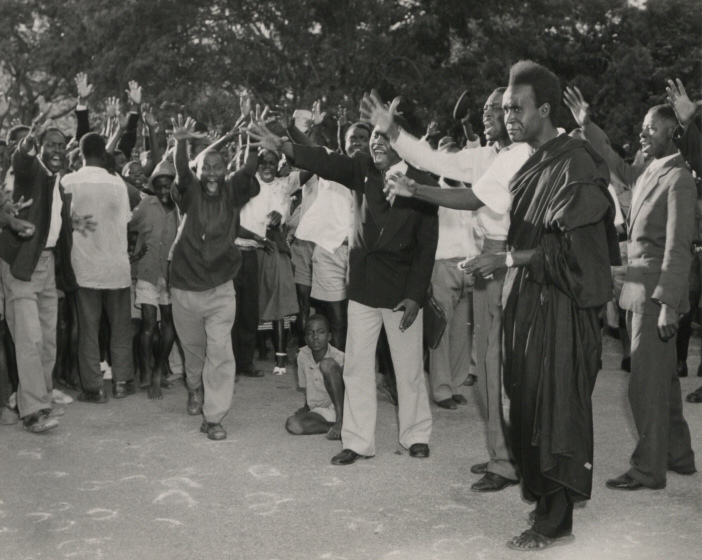
Kenneth Kaunda
Kenneth Kaunda (28 April 1924 – 17 June 2021), also known as KK, was a Zambian politician who served as the first president of Zambia from 1964 to 1991. He was at the forefront of the struggle for independence from Northern Rhodesia, British rule. Dissatisfied with Harry Nkumbula's leadership of the Zambian African National Congress, Northern Rhodesian African National Congress, he broke away and founded the Zambian African National Congress (1958–1959), Zambian African National Congress, later becoming the head of the socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP). Kaunda was the first president of independent Zambia. In 1973, following tribal and inter-party violence, all political parties except UNIP were banned through an amendment of the constitution after the signing of the Choma Declaration. At the same time, Kaunda oversaw the acquisition of majority stakes in key foreign-owned companies. The 1973 oil crisis and a slump in export revenues put Zambia in a state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration Of Independence
Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) was a statement adopted by the Cabinet of Rhodesia on 11 November 1965, announcing that Rhodesia (previously Southern Rhodesia), a British crown colony in southern Africa that had responsible government, governed itself since 1923, now regarded itself as an independent sovereign state. The culmination of a protracted dispute between the British and Rhodesian governments regarding the terms under which the latter could become fully independent, it was the first Unilateral declaration of independence, unilateral break from the United Kingdom by one of its colonies since the United States Declaration of Independence in 1776. The UK, the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth, and the United Nations all deemed Rhodesia's UDI illegal, and economic sanctions, the first in the UN's history, were imposed on the breakaway colony. With the help of the Commonwealth Secretariat, members of the Commonwealth were able to cooperate and ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armored Car (military)
A military armored (Commonwealth English, also spelled armoured) car is a wheeled armoured fighting vehicle, historically employed for reconnaissance, internal security, armed escort, and other subordinate battlefield tasks. With the gradual decline of mounted cavalry, armored cars were developed for carrying out duties formerly assigned to light cavalry. Following the invention of the tank, the armoured car remained popular due to its faster speed, comparatively simple maintenance and low production cost. It also found favor with several Colonial troops, colonial armies as a cheaper weapon for use in underdeveloped regions. During World War II, most armoured cars were engineered for reconnaissance and passive observation, while others were devoted to communications tasks. Some equipped with heavier armament could even substitute for tracked combat vehicles in favorable conditions—such as pursuit or flanking maneuvers during the North African campaign. Since World War II t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Command And General Staff College
The United States Army Command and General Staff College (CGSC or, obsolete, USACGSC) at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, is a graduate school for United States Army and sister service officers, interagency representatives, and international military officers. The college was established in 1881 by William Tecumseh Sherman as the School of Application for Infantry and Cavalry (later simply the Infantry and Cavalry School), a training school for infantry and cavalry officers. In 1907 it changed its title to the School of the Line. The curriculum expanded throughout World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War and continues to adapt to include lessons learned from current conflicts. In addition to the main campus at Fort Leavenworth, the college has satellite campuses at Fort Belvoir, Virginia; Fort Gregg-Adams (Virginia), Fort Gregg-Adams, Virginia; Fort Eisenhower, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia; and Redstone Arsenal, Alabama. The college also maintains a distance-lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyasaland
Nyasaland () was a British protectorate in Africa that was established in 1907 when the former British Central Africa Protectorate changed its name. Between 1953 and 1963, Nyasaland was part of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. After the Federation was dissolved, Nyasaland became independent from Britain on 6 July 1964 and was renamed Malawi. Nyasaland's history was marked by the massive loss of African communal lands in the early colonial period. In January 1915, the Reverend John Chilembwe staged Chilembwe uprising, an attempted rebellion to protest against colonial forced labour and discrimination against Africans, among other grievances. Although the rebellion was unsuccessful, colonial authorities responded by reassessing some of their policies. Throughout the 1930s, a growing class of educated African elite, many educated in the United Kingdom, became increasingly politically active and vocal about gaining independence. They established associations and, after 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in Southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally known as South Zambesia until annexation by Britain, at the behest of Cecil Rhodes's British South Africa Company (for whom the colony was named). The bounding territories were Bechuanaland (Botswana), Northern Rhodesia (Zambia), Portuguese Mozambique (Mozambique) and the Transvaal Republic (for two brief periods known as the British Transvaal Colony; from 1910, the Union of South Africa and, from 1961, the Republic of South Africa). Since 1980, the colony's territory is the independent nation of Zimbabwe. This southern region, known for its extensive gold reserves, was first purchased by the BSAC's Pioneer Column on the strength of a mineral concession extracted from its Matabele king, Lobengula, and various majority Mashona vassal chiefs in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Rhodesia
Northern Rhodesia was a British protectorate in Southern Africa, now the independent country of Zambia. It was formed in 1911 by Amalgamation (politics), amalgamating the two earlier protectorates of Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia and North-Eastern Rhodesia.''Commonwealth and Colonial Law'' by Kenneth Roberts-Wray, London, Stevens, 1966. p. 753 It was initially administered, as were the two earlier protectorates, by the British South Africa Company (BSAC), a chartered company, on behalf of the British Government. From 1924, it was administered by the British Government as a protectorate, under similar conditions to other British-administered protectorates, and the special provisions required when it was administered by BSAC were terminated.Northern Rhodesia Order in Council 1924 (SR&O 1924/324), S.R.O. & S.I. Rev VIII, 154 Although under the BSAC charter it had features of a charter colony, the BSAC's treaties with local rulers, and British legislation, gave it the status of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |