|
Microsauria
Microsauria is an Extinction, extinct, possibly polyphyletic Order (biology), order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the Evolutionary grade, grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria. The microsaurs all had short tails and small legs, but were otherwise quite varied in form. The group included lizard-like animals that were relatively well-adapted to living on dry land, burrowing forms, and others that, like the modern axolotl, retained their gills into adult life, and so presumably never left the water. Their skeleton was heavily ossified, and their development was likely gradual with no metamorphosis. Distribution Microsaur remains have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
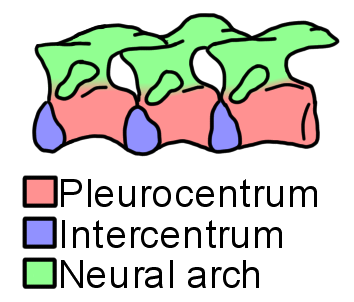 |
Trihecaton
''Trihecaton'' is an extinct genus of microsaur from the Late Pennsylvanian of Colorado. Known from a single species, ''Trihecaton howardinus'', this genus is distinctive compared to other microsaurs due to possessing a number of plesiomorphic ("primitive") features relative to the rest of the group. These include large intercentra (wedge-like components of the vertebrae), folded enamel, and a large coronoid process of the jaw. Its classification is controversial due to combining a long body with strong limbs, features which typically are not present at the same time in other microsaurs. Due to its distinctiveness, ''Trihecaton'' has been given its own monospecific family, Trihecatontidae. Discovery ''Trihecaton'' is known from well-preserved fossils discovered in Fremont County, Colorado by a UCLA field expedition in 1970. These fossils were found at a quarry near the town of Howard. The quarry preserved sediments from the Sangre de Cristo Formation, a geological formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Lepospondyl
Lepospondyli is a diverse clade of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco ('' Diplocaulus minimus''), lepospondyls lived from the Visean stage of the Early Carboniferous to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large (the biggest genus, the diplocaulid '' Diplocaulus'', reached a meter in length, but most were much smaller), and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Hapsidopareiidae
Hapsidopareiidae is an extinct family of microsaurs. Hapsidopareiids are known from the Early Permian of the United States and possibly Germany and the Czech Republic. Hapsidopareiids are characterized by a large temporal embayment near the cheek region in which the quadratojugal is greatly reduced or absent. Members of Ostodolepidae, another microsaur family, also possess temporal embayments, but they not as extensive as those of hapsidopareiids, which extend into the skull roof The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium. In com .... In hapsidopareiids, the embayment may have provided space for an enlarged jaw adductor musculature, although certain characteristics of the skull do not support this idea. '' Hapsidopareion'' and '' Llistrofus'' both possess this embayment, but in '' Sax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Rhynchonkos
''Rhynchonkos'' is an extinct genus of rhynchonkid microsaur. Originally known as ''Goniorhynchus'', it was renamed in 1981 because the name had already been given to another genus; the family, likewise, was originally named Goniorhynchidae but renamed in 1988. The type and only known species is ''R. stovalli'', found from the Early Permian Fairmont Shale in Cleveland County, Oklahoma. ''Rhynchonkos'' shares many similarities with ''Eocaecilia'', an early caecilian from the Early Jurassic of Arizona. Similarities between ''Rhynchonkos'' and ''Eocaecilia'' have been taken as evidence that caecilians are descendants of microsaurs. However, such a relationship is no longer widely accepted. Description ''Rhynchonkos'' has an elongated body with at least 37 presacral vertebrae. Most vertebrae have ribs. Unlike other microsaurs, the atlas of ''Rhynchonkos'' lacks ribs. Both ''Rhynchonkos'' and '' Euryodus'' have atlases that bear a strong resemblance to those of nectrideans. Like ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Recumbirostra
Recumbirostra is a clade of tetrapods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They are thought to have had a fossorial (burrowing) lifestyle and the group includes both short-bodied and long-bodied snake-like forms. At least one species, the long-bodied molgophid '' Nagini mazonense,'' lost its forelimbs entirely. Recumbirostra includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Rhynchonkidae and Brachystelechidae, with additional families such as Microbrachidae and Molgophidae being included by some authors. Brachystelechidae and Molgophidae have also been grouped together in the suggested clade Chthonosauria. Recumbirostra was erected as a clade in 2007 to include many of the taxa traditionally grouped in " Microsauria", which has since been shown to be a paraphyletic or polyphyletic grouping. Like other "microsaurs", the recumbirostrans have traditionally been considered to be members of the subclass Lepospondyli; however, many phylogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Tuditanidae
Tuditanidae is an extinct family (biology), family of microsaurian tetrapods. Fossils have been found from Nova Scotia, Ohio, and the Czech Republic and are Late Carboniferous in age. Tuditanids were medium-sized terrestrial microsaurs that resembled lizards. Postcranial material is best known from the genus ''Tuditanus'', showing that it had size, proportions, and skull configuration that were similar to Captorhinidae, captorhinids. Tuditanids have also developed an Talus bone, astragalus in the ankle (a reptilian feature) from the fusion of several other bones. In comparison to other microsaurs, tuditanids were short-bodied, with fewer than 30 presacral vertebrae. The limbs are large and well developed. Unlike other microsaurs such as Gymnarthridae, gymnarthrids, the jaw articulation is at the posterior margin of the skull. The teeth are blunt and peg-like. Tuditanids are thought to have had a similar lifestyle to reptiles such as captorhinids. They were terrestrial and likel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Utaherpeton
''Utaherpeton'' is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibian from the Carboniferous of Utah. It is one of the oldest and possibly one of the most basal ("primitive") known lepospondyls. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species ''Utaherpeton franklini''. ''Utaherpeton'' was named in 1991 from the Manning Canyon Shale Formation, which dates to the Mississippian- Pennsylvanian boundary. It was originally classified within Microsauria, a group of superficially lizard- and salamander-like lepospondyls that is now no longer considered to be a valid clade or evolutionary grouping, but rather an evolutionary grade consisting of the most basal lepospondyls. ''Utaherpeton'' has been proposed as both the most basal lepospondyl and the oldest "microsaur", although more derived lepospondyls are known from earlier in the Carboniferous. However, its position within Lepospondyli remains uncertain due to the incomplete preservation of the only known specimen. The inclusion of ''U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
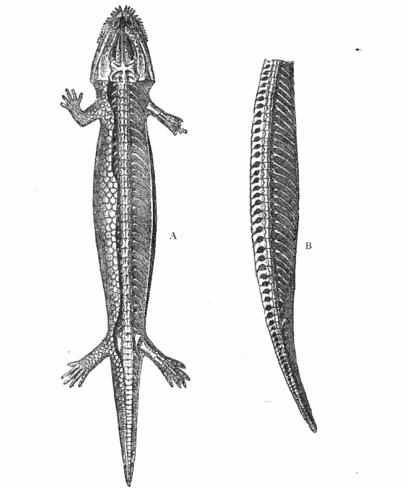 |
Hyloplesion
''Hyloplesion'' is an extinct genus of microbrachomorph microsaur. It is the type and only genus within the family Hyloplesiontidae. Fossils have been found from the Czech Republic near the towns of Plzeň, Nýřany, and Třemošná, and date back to the Middle Pennsylvanian. The type species is ''H. longicostatum'', named in 1883. Two species belonging to different genera, ''Seeleya pusilla'' and ''Orthocosta microscopica'', have been synonymized with ''H. longicostatum'' and are thought to represent very immature individuals. Description ''Hyloplesion'' was about as large as a medium-sized salamander, with the length of known specimens ranging from 17-77mm. The skull is triangular in shape. Unlike many other microsaurs, the palate of ''Hyloplesion'' contains large vacuities, or openings. The fifth maxillary tooth is enlarged and resembles a canine. The skull of ''Hyloplesion'' superficially resembles that of the unrelated romeriid reptile '' Romeria'' in lateral view d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pantylus
''Pantylus'' (from , 'all' and , 'knob') is an extinct microsaurian tetrapod from the Permian period of North America. ''Pantylus'' was probably a largely terrestrial animal, judging from its well-built legs. It was about long, and resembled a lizard with a large skull and short limbs. It had numerous blunt teeth, and probably chased after invertebrate Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ... prey. References External links Skull cast Microsauria Cisuralian tetrapods of North America Taxa named by Edward Drinker Cope Fossil taxa described in 1881 {{Paleo-tetrapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Microbrachis BW
''Microbrachis'' is an extinct genus of microsaurian tetrapod from the Carboniferous Kladno Formation of the Czech Republic. Description ''Microbrachis'' was an elongated, salamander-like creature, about long, with over 40 vertebrae instead of the average 15–26 in its living relatives. It had minute limbs, and probably swam using fish-like lateral body movements. ''Microbrachis'' probably fed on fresh water plankton such as shrimp. ''Microbrachis'' was pedomorphosis, pedomorphic, retaining its larval gills in adulthood. Similar traits are found in the extant axolotl. References Further reading * Andrew R. Milner, "The Tetrapod Assemblage from Nýrany, Czechoslovakia", in Systematics Association Special Volume No.15, "The Terrestrial Environment and the Origin of Land Vertebrates", ed. by A. L. Panchen, 1980, pp. 439–496, Academic Press, London and New York External links Microbrachis, The Type Microsaur (abstract) * Microsauria Pennsylvanian tetrapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |