|
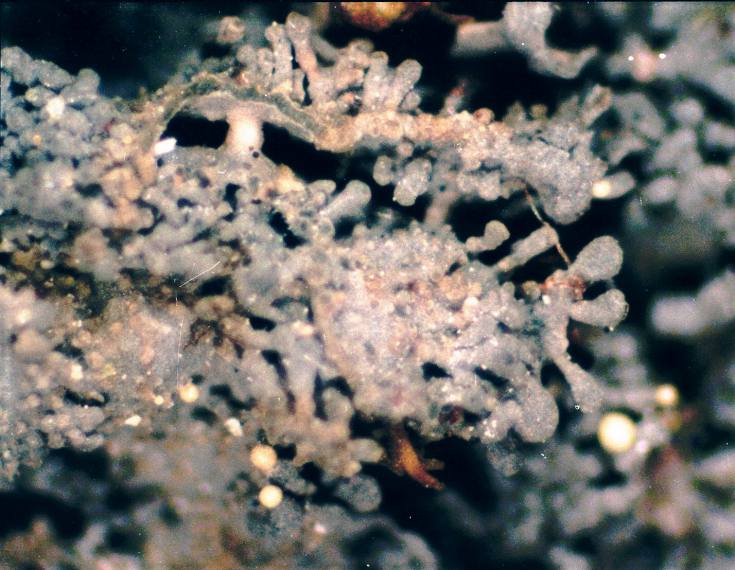
Leptogium
''Leptogium'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Collemataceae. It has about 110 species. Species formerly classified under ''Leptogium'' have since been divided among the genera ''Leptogium'', '' Pseudoleptogium'', and '' Scytinium''. ''Leptogium'' lichens are predominantly found on tree bark or soil, often among mosses, and sometimes on rocks in moist environments. Taxonomy In 2013, a proposal supported by molecular phylogenetics data was made to conserve the genus ''Leptogium'' with a conserved type, aiming to maintain the current broader classification including both small- and larger foliose species within ''Leptogium'', while segregating the smaller squamulose species into '' Scytinium''. This conservation was recommended by a vote of 14-0-1 to prevent the necessity of reclassifying about 100 species into new genera such as '' Malotium''. The proposal was widely supported by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi as it simplifies the taxonomy and maintains hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptogium Phyllocarpum
''Leptogium'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Collemataceae. It has about 110 species. Species formerly classified under ''Leptogium'' have since been divided among the genera ''Leptogium'', '' Pseudoleptogium'', and '' Scytinium''. ''Leptogium'' lichens are predominantly found on tree bark or soil, often among mosses, and sometimes on rocks in moist environments. Taxonomy In 2013, a proposal supported by molecular phylogenetics data was made to conserve the genus ''Leptogium'' with a conserved type, aiming to maintain the current broader classification including both small- and larger foliose species within ''Leptogium'', while segregating the smaller squamulose species into '' Scytinium''. This conservation was recommended by a vote of 14-0-1 to prevent the necessity of reclassifying about 100 species into new genera such as '' Malotium''. The proposal was widely supported by the Nomenclature Committee for Fungi as it simplifies the taxonomy and maintains histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidia
An isidium (plural: isidia) is a tiny, wart- or finger-like outgrowth on the thallus surface of certain lichen species. It is one of two principal types of vegetative reproduction, vegetative reproductive structures in lichens, the other being soredium, soredia. Each isidium contains both fungus, fungal and algae, algal partners and is wrapped in a thin protective layer (the ), distinguishing it from soredia, which lack this covering. While both function in vegetative reproduction, the heavier, corticate structure of isidia means they tend to establish in microhabitats close to the parent thallus, often favouring stable, humid niches where mechanical protection improves survival. Unlike spores, which are microscopic and easily carried over long distances by wind, isidia are larger, multicellular fragments that rely on external forces such as wind, rain, or animal contact, but typically disperse over much shorter ranges. Isidia are morphology (biology), morphologically diverse, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoleptogium
''Pseudoleptogium'' is a fungal genus in the family Collemataceae. It comprises the single species ''Pseudoleptogium diffractum'', a saxicolous (rock-dwelling) crustose lichen that grows on calcareous rocks. Taxonomy The genus was originally proposed by the Swiss lichenologist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1885 as a section of the genus ''Collema''. The genus was resurrected and redescribed in 2014 as part of a molecular phylogenetics-informed reorganisation of the family Collemataceae, the jelly lichens. Description The thallus of ''Pseudoleptogium'' is made up of tiny to small (scale-like structures) that range from 0.5 to 1.0 cm in diameter. These squamules create a patchy appearance, with two different types present. Along the edges, the squamules are tightly pressed to the surface, elongated like fingers, and range from 0.4 to 1.0 mm in length and 0.2 to 0.5 mm in width. In the centre of the thallus, the squamules are much smaller, resembling tiny, conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collemataceae
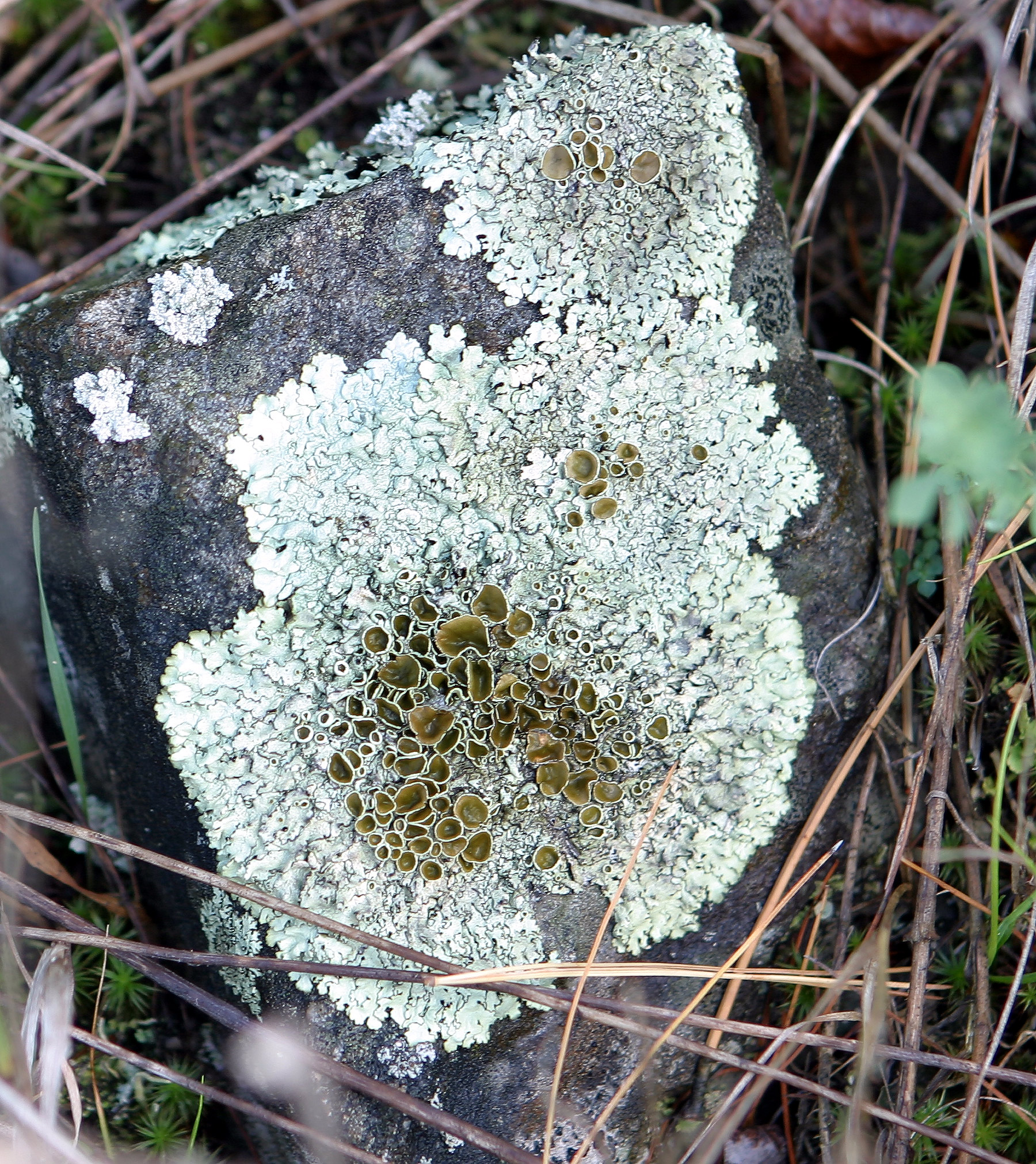
The Collemataceae are a family of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the order Peltigerales. The family contains twelve genera and about 325 species. The family has a widespread distribution. Taxonomy The family was circumscribed by Jonathan Carl Zenker in 1827; ''Collema'' is the type genus. Description Collemataceae members have a thallus that is either foliose, crustose, squamulose or minutely shrubby. The thallus is gelatinous, sometimes swelling when wet, with a colour ranging from dark olive-green to brown-black, reddish brown or rarely grey-blue. The upper and lower cortex is either absent or composed of angular brick-like cells, more rarely of flattened compressed cells. The medulla contains loosely interwoven narrow hyphae or is compact with broad-short-celled hyphae; these hyphae are intermixed with the photobiont. The texture of the upper cortex surface ranges from smooth to wrinkled or ridged, and is often glossy, but rarely arachnoid. The underside of the cortex is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scytinium
''Scytinium'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Collemataceae. It has 49 species. These lichens are typically found on basic rocks, soil, and trees, occasionally in association with mosses. Despite the morphological and ecological diversity within ''Scytinium'', its species share similar ascospore features, such as shape and septation, as well as a small to medium-sized thallus with at least a partial . Description ''Scytinium'' encompasses lichen species that exhibit a variety of thallus forms, such as crustose, squamulose, , or . These lichens have a gelatinous texture, and their colour ranges from dark brown and bluish-grey to olive-green. The of ''Scytinium'' can be spreading, elongate, or somewhat cylindrical in shape. The upper and lower , when present, is composed of either cuboid cells or flattened, degraded tissue. The medulla contains loosely interwoven or compact hyphae, along with the photobiont ''Nostoc''–a common genus of cyanobacteria. Both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia ( basidiomycetes) or paraphyses ( ascomycetes). Cystidia are often important for microscopic identification. The subhymenium consists of the supportive hyphae from which the cells of the hymenium grow, beneath which is the hymenophoral trama, the hyphae that make up the mass of the hymenophore. The position of the hymenium is traditionally the first characteristic used in the classification and identification of mushrooms. Below are some examples of the diverse types which exist among the macroscopic Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. * In agarics, the hymenium is on the vertical faces of the gills. * In boletes and polypores, it is in a spongy mass of downward-pointing tubes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomata
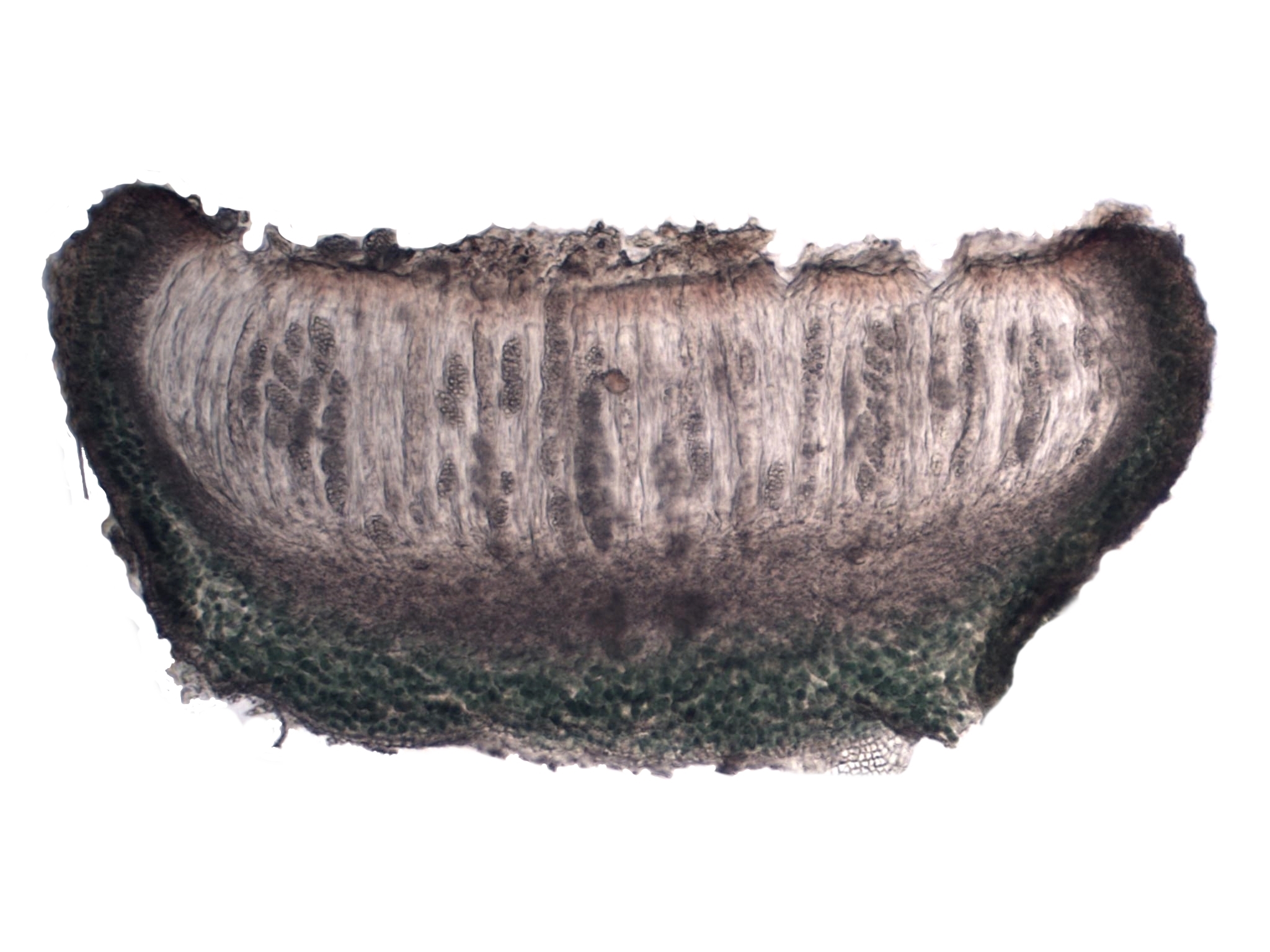
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body (sporocarp (fungi), sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded ascus, asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utilize its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform
Fusiform (from Latin ''fusus'' ‘spindle’) means having a spindle (textiles), spindle-like shape that is wide in the middle and tapers at both ends. It is similar to the lemon (geometry), lemon-shape, but often implies a focal broadening of a structure that continues from one or both ends, such as an aneurysm on a blood vessel. Examples * Fusiform, a body shape common to many aquatic animals, characterized by being tapered at both the head and the tail * Fusiform, a classification of aneurysm * Fusiform bacteria (spindled rods, that is, fusiform bacilli), such as the Fusobacteriota * Fusiform cell (biology) * Fusiform face area, a part of the human visual system which seems to specialize in facial recognition * Fusiform gyrus, part of the temporal lobe of the brain * Fusiform muscle, where the fibres run parallel along the length of the muscle * Fusiform neuron, a spindle-shaped neuron References {{Reflist Geometric shapes See also * Streamliner, a fusiform hydro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |