|
Lattice Shell Structures
Lattice may refer to: Arts and design * Latticework, an ornamental criss-crossed framework, an arrangement of crossing laths or other thin strips of material * Lattice (music), an organized grid model of pitch ratios * Lattice (pastry), an ornamental pattern of crossing strips of pastry Companies * Lattice Engines, a technology company specializing in business applications for marketing and sales * Lattice Group, a former British gas transmission business * Lattice Semiconductor, a US-based integrated circuit manufacturer Science, technology, and mathematics Mathematics * Lattice (group), a repeating arrangement of points ** Lattice (discrete subgroup), a discrete subgroup of a topological group whose quotient carries an invariant finite Borel measure ** Lattice (module), a module over a ring that is embedded in a vector space over a field ** Lattice graph, a graph that can be drawn within a repeating arrangement of points ** Lattice-based cryptography, encryption sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latticework
__NOTOC__ Latticework is an openwork framework consisting of a criss-crossed pattern of strips of building material, typically wood or metal. The design is created by crossing the strips to form a grid or weave. Latticework may be functional – for example, to allow airflow to or through an area; structural, as a truss in a lattice girder; used to add privacy, as through a lattice screen; purely ornament (art), decorative; or some combination of these. Latticework in stone or wood from the Classical antiquity, classical period is also called Roman lattice or ''transenna'' (plural ''transenne''). In India, the house of a rich or noble person may be built with a ''baramdah'' or verandah surrounding every level leading to the living area. The upper floors often have balconies overlooking the street that are shielded by latticed screens carved in stone called jalis which keep the area cool and give privacy. Examples File:Amber Fort Screen (6652771501).jpg, Lattice screen at A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
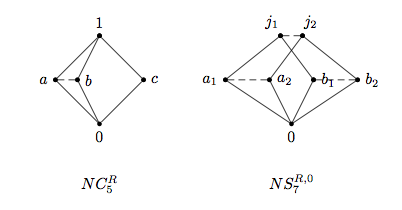
Skew Lattice
In abstract algebra, a skew lattice is an algebraic structure that is a non-commutative generalization of a lattice (order), lattice. While the term ''skew lattice'' can be used to refer to any non-commutative generalization of a lattice, since 1989 it has been used primarily as follows. Definition A skew lattice is a Set (mathematics), set ''S'' equipped with two associative, idempotent binary operations \wedge and \vee, called ''meet'' and ''join'', that validate the following dual pair of absorption laws x\wedge (x\vee y) = x = (y\vee x)\wedge x , x\vee (x\wedge y) = x = (y\wedge x)\vee x . Given that \vee and \wedge are associative and idempotent, these identities are equivalent to validating the following dual pair of statements: x\vee y= x if and only if x\wedge y=y, x\wedge y=x if and only if x\vee y=y. Historical background For over 60 years, noncommutative variations of lattices have been studied with differing motivations. For some the motivation has been an int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grid (other)
Grid, The Grid, or GRID may refer to: Space partitioning * Regular grid, a tessellation of space with translational symmetry, typically formed from parallelograms or higher-dimensional analogs ** Grid graph, a graph structure with nodes connected in a regular grid ** Square grid, a grid of squares ** Triangular grid, a grid of triangles ** Hexagonal grid, a grid of hexagons ** Unstructured grid, a tessellation of a space by simple shapes such as triangles or tetrahedra in an irregular pattern * Grid reference system, a coordinate system relative to a particular map projection * Grid (spatial index), a discretization of a geometric domain into a set of contiguous cells, used to organize information ** Discrete global grid (DGG), a grid that covers the entire Earth's surface * Grid (graphic design) (or typographic grid), organized lines for guiding graphic design * Grid plan, a city design with streets running at right angles * Grid paper, paper with a regular grid printe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Model (finance)
In quantitative finance, a lattice model is a numerical approach to the valuation of derivatives in situations requiring a discrete time model. For dividend paying equity options, a typical application would correspond to the pricing of an American-style option, where a decision to exercise is allowed at the closing of any calendar day up to the maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as the standard Black–Scholes one, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is limited to the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, because of path dependence in the payoff. Traditional Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, but some methods now exist for so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Truss Bridge
A lattice truss bridge is a form of truss bridge that uses many small, closely spaced diagonal elements forming a latticework, lattice. The design was patented in 1820 by architect Ithiel Town. Originally a means of erecting a substantial bridge from mere planks employing lower–skilled labor, rather than heavy timbers and more expensive carpenters and equipment, the lattice truss has also been constructed using many relatively light iron or steel members. The individual elements are more easily handled by the construction workers, but the bridge also requires substantial support during construction. A simple lattice truss will transform the applied loads into a thrust, as the bridge will tend to change length under load. This is resisted by pinning the lattice members to the top and bottom chords, which are more substantial than the lattice members, but which may also be fabricated from relatively small elements rather than large beams. Belfast truss The ''Belfast truss'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Tower
A lattice tower or truss tower is a freestanding vertical latticework, framework tower. This construction is widely used in transmission towers carrying high-voltage electric power lines, in radio masts and towers (a self-radiating tower or as a support for Antenna (radio), aerials) and in observation towers. Its advantage is good shear strength at a much lower weight than a tower of solid construction would have as well as lower wind resistance. In structural engineering, the term ''lattice tower'' is used for a freestanding structure, while a ''lattice mast'' is a guyed mast supported by guy lines. Lattices of triangular (three-sided) cross-section are most common, particularly in North America. Square (four-sided) lattices are also widely used and are most common in Eurasia. A lattice towers is often designed as either a space frame or a hyperboloid structure. Before 1940, they were used as radio transmission towers especially for short and medium wave. Occasionally lattice to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Model (physics)
In mathematical physics, a lattice model is a mathematical model of a physical system that is defined on a lattice, as opposed to a continuum, such as the continuum of space or spacetime. Lattice models originally occurred in the context of condensed matter physics, where the atoms of a crystal automatically form a lattice. Currently, lattice models are quite popular in theoretical physics, for many reasons. Some models are exactly solvable, and thus offer insight into physics beyond what can be learned from perturbation theory. Lattice models are also ideal for study by the methods of computational physics, as the discretization of any continuum model automatically turns it into a lattice model. The exact solution to many of these models (when they are solvable) includes the presence of solitons. Techniques for solving these include the inverse scattering transform and the method of Lax pairs, the Yang–Baxter equation and quantum groups. The solution of these models has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Mast
Lattice masts, or cage masts, or basket masts, are a type of observation mast common on United States Navy major warships in the early 20th century. They are a type of hyperboloid structure, whose weight-saving design was invented by the Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov. They were used most prominently on American dreadnought battleships and armored cruisers of the World War I era. In the age of sail, masts were required to support the sails, and lookouts were posted on them; with the advent of engine-powered warships, masts were retained and used for observation and to spot fall of shot. The purpose of the lattice structure was to make the posts less vulnerable to shells from enemy ships, and to better absorb the shock caused by firing heavy guns, isolating the delicate fire control equipment (rangefinders, etc.) mounted on the mast tops. However, the masts were found to be easily damaged by the inclement weather experienced at sea by naval ships during typhoons and hurrican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice C
The Lattice C Compiler was released in June 1982 by Lifeboat Associates and was the first C compiler for the IBM Personal Computer. The compiler sold for $500 and would run on PC DOS or MS-DOS (which at the time were the same product with different brandings). The first hardware requirements were given as 96KB of RAM and one (later two) floppy drives. It was ported to many other platforms, such as mainframes ( MVS), minicomputers ( VMS), workstations (UNIX), OS/2, Amiga, Atari ST, and Sinclair QL. The compiler was subsequently repackaged by Microsoft under a distribution agreement as Microsoft C version 2.0. Microsoft developed their own C compiler that was released in April 1985 as Microsoft C Compiler 3.0. Lattice was purchased by SAS Institute in 1987 and rebranded as SAS/C. After this, support for other platforms dwindled until compiler development ceased for all platforms except IBM mainframes. The product is still available in versions that run on other platforms, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bravais Lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by : \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n_3 \mathbf_3, where the ''ni'' are any integers, and a''i'' are ''primitive translation vectors'', or ''primitive vectors'', which lie in different directions (not necessarily mutually perpendicular) and span the lattice. The choice of primitive vectors for a given Bravais lattice is not unique. A fundamental aspect of any Bravais lattice is that, for any choice of direction, the lattice appears exactly the same from each of the discrete lattice points when looking in that chosen direction. The Bravais lattice concept is used to formally define a ''crystalline arrangement'' and its (finite) frontiers. A crystal is made up of one or more atoms, called the ''basis'' or ''motif'', at each lattice point. The ''basis'' may consist of atoms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethe Lattice
In statistical mechanics and mathematics, the Bethe lattice (also called a regular tree) is an infinite symmetric regular tree where all vertices have the same number of neighbors. The Bethe lattice was introduced into the physics literature by Hans Bethe in 1935. In such a graph, each node is connected to ''z'' neighbors; the number ''z'' is called either the coordination number or the degree, depending on the field. Due to its distinctive topological structure, the statistical mechanics of lattice models on this graph are often easier to solve than on other lattices. The solutions are related to the often used Bethe ansatz for these systems. Basic properties When working with the Bethe lattice, it is often convenient to mark a given vertex as the root, to be used as a reference point when considering local properties of the graph. Sizes of layers Once a vertex is marked as the root, we can group the other vertices into layers based on their distance from the root. The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Multiplication
Lattice multiplication, also known as the Italian method, Chinese method, Chinese lattice, gelosia multiplication, sieve multiplication, shabakh, diagonally or Venetian squares, is a method of multiplication that uses a Lattice (group), lattice to multiply two multi-digit numbers. It is mathematically identical to the more commonly used long multiplication algorithm, but it breaks the process into smaller steps, which some practitioners find easier to use. The method had already arisen by medieval times, and has been used for centuries in many different cultures. It is still being taught in certain curricula today. Method A grid is drawn up, and each cell is split diagonally. The two multiplicands of the product to be calculated are written along the top and right side of the lattice, respectively, with one digit per column across the top for the first multiplicand (the number written left to right), and one digit per row down the right side for the second multiplicand (the numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |