|
Konkani
__NOTOC__ Konkani may refer to: Language * Konkani language is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Konkan region of India. * Konkani alphabets, different scripts used to write the language **Konkani in the Roman script, one of the scripts used to write the language * Konkani phonology * Konkani language agitation, historic agitations in support of the language in Goa, India * Maharashtrian Konkani, a dialect of the Konkani language spoken in Maharashtra, India * Marathi-Konkani languages, Indic languages of Maharashtra and Konkan, including Marathi and Konkani Ethnic groups * Konkani people, south-western India ** Konkani Muslims * People of the Konkan Division, in Konkan Division, Maharashtra, India See also * Konkan (other) * Kokna language (other) * Konkani literature * Konkani liturgical music * Konkani Wikipedia, Konkani-language edition of Wikipedia {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Language
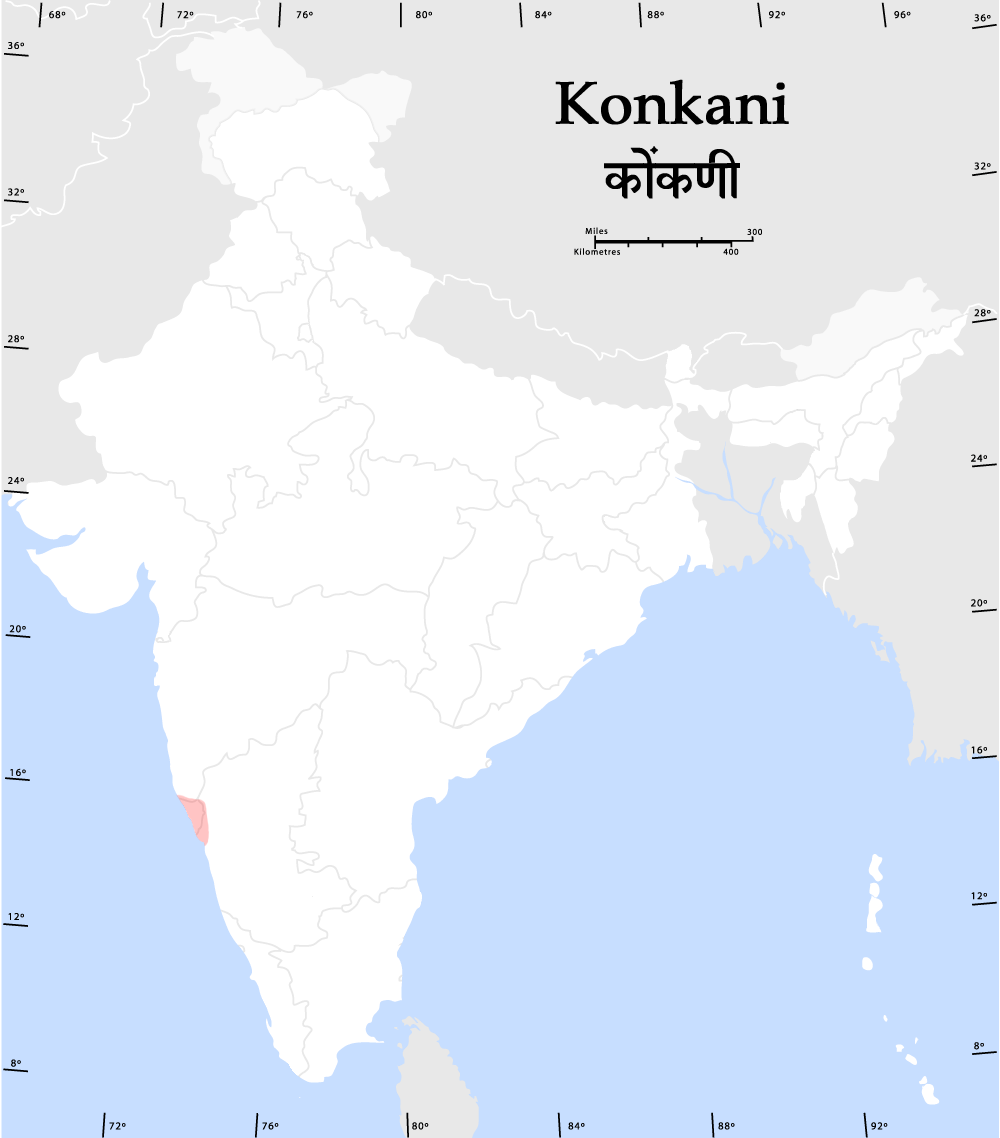
Konkani, (Devanagari: , Konkani in the Roman script, Romi: , Kannada script, Kannada: , Koleluttu: , Nastaliq: ; IAST: , ) formerly Concani or Concanese, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 Scheduled languages of India, scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution, and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is also spoken in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat as well as Damaon, Diu & Silvassa. Konkani is a member of the Indo-Aryan languages#Southern Zone, Southern Indo-Aryan language group. It retains elements of Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic structures and shows similarities with both Indo-Aryan languages#Western Zone, Western and Indo-Aryan languages#Eastern Zone, Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 AD. There are many Konkani dialects spoken along and beyond the Konkan region, from Damaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani In The Roman Script
Konkani in the Roman script, commonly known as Roman Konkani or ''Romi Konknni'' () refers to the writing of the Konkani language in the Roman script. While Konkani is written in five different scripts altogether, Roman Konkani is widely used. Roman Konkani is known to be the oldest preserved and protected literary tradition beginning from the 16th century AD. An estimated 500,000 people use Roman Konkani. The use of Devanagari script for Konkani, which is now its official script, first occurred in AD 1187.Mother Tongue blues nbsp;— Madhavi Sardesai Roman Konkani was not mandated as official script by law, for decades even after the Konkani language agitation of the 1960s. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Language Agitation
The Konkani language agitations were a series of protests in India, concerning the uncertain future of the Konkani language. They were held by Goans in the former territory of Goa, Daman and Diu; then under the administration of the Maharashtrawadi Gomantak Party (MGP). The protests involved citizen journalism, student activism & political demonstrations. The civil unrest ceased when premier official status for Konkani in the Devnagari script was granted. Marathi was declared an associate official language of Goa. History Pre-Portuguese Goa Historically, Konkani was neither the official nor the administrative language of the pre-Portuguese rulers. Under the Kadambas (c. 960 – 1310), the court language was Kannada. When under Muslim rule (1312 - 1370 and 1469 - 1510), the official and cultural language was Persian. Various stones in the Archaeological Museum and Portrait Gallery from the period are inscribed in Kannada and Persian. During the period in between the two p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani People
The Konkani people are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the Konkan region of the Indian subcontinent. They speak various dialects of the Konkani language. Following the Konkani language agitation, Konkani became the premier official language of Goa state, while Mahratti, Marathi remains as the associate official language of Goa. Konkani is also spoken by populations in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Damaon, Kerala, & Gujarat. A large percentage of Konkani people are bilingual. Etymology The word ''Konkan, Koṅkaṇa'' (कोंकण) and, in turn ''Koṅkaṇi'', is derived from ' (कुङ्कण) or (कुङ्कणु). Different authorities elaborate etymology of this word differently. They include: *''Koṇa'' (कोण) meaning top of the mountain. *The name of aboriginal mother goddess, which is sometimes Sanskritisation, Sanskritised to mean goddess Renuka. *Some scholars believe that (कोङ्कण) comes from (कोण) "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Alphabets
Konkani alphabets refers to the five different scripts (Devanagari, Roman, Kannada, Malayalam and Perso-Arabic scripts) currently used to write the Konkani language. As of 1987, the "Goan Antruz dialect" in the Devanagari script has been declared Standard Konkani and promulgated as an official language in the Indian state of Goa.On 20 August 1992 the Parliament of India, by effecting the 78th amendment to the Constitution of India, included Konkani in Devanagari script in the VIIIth Schedule of the Constitution of India. Konkani in the Roman script is not mandated as an official script by law. However, an ordinance passed by the government of Goa allows the use of Roman script for official communication. This ordinance has been put into effect by various ministries in varying degrees. For example, the 1996 Goa Panchayat Rules stipulate that the various forms used in the election process must be in both the Roman and Devanagari script. Ancient The earliest inscription in Konkani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Wikipedia
Konkani Wikipedia is the Konkani language edition of Wikipedia, run by the Wikimedia Foundation. It was started in July 2015. Prior to this, it had been in incubation since 2006. Currently, there are content articles in the project. The total number of edits on this Wikipedia is . History Konkani Wikipedia went live in July 2015, after being in incubation since 2006. Earlier in September 2013, 4 volumes of ''Konkani vishwakosh'' (encyclopedia) were relicensed under Creative Commons Licenses. Information from these volumes of encyclopedias were used to write articles on Konkani Wikipedia. In the same year, a Wikipedia-related workshop was organized at Goa University. In April 2014, two introductory sessions on editing Wikipedia were conducted at Roshni Nilaya School of Social Work in Goa. In July 2015, the Wikipedia went live after incubation for 9 years. At the time of the official inauguration, the Wikipedia contained 2500 articles. The project was supported by Goa Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathi-Konkani Languages
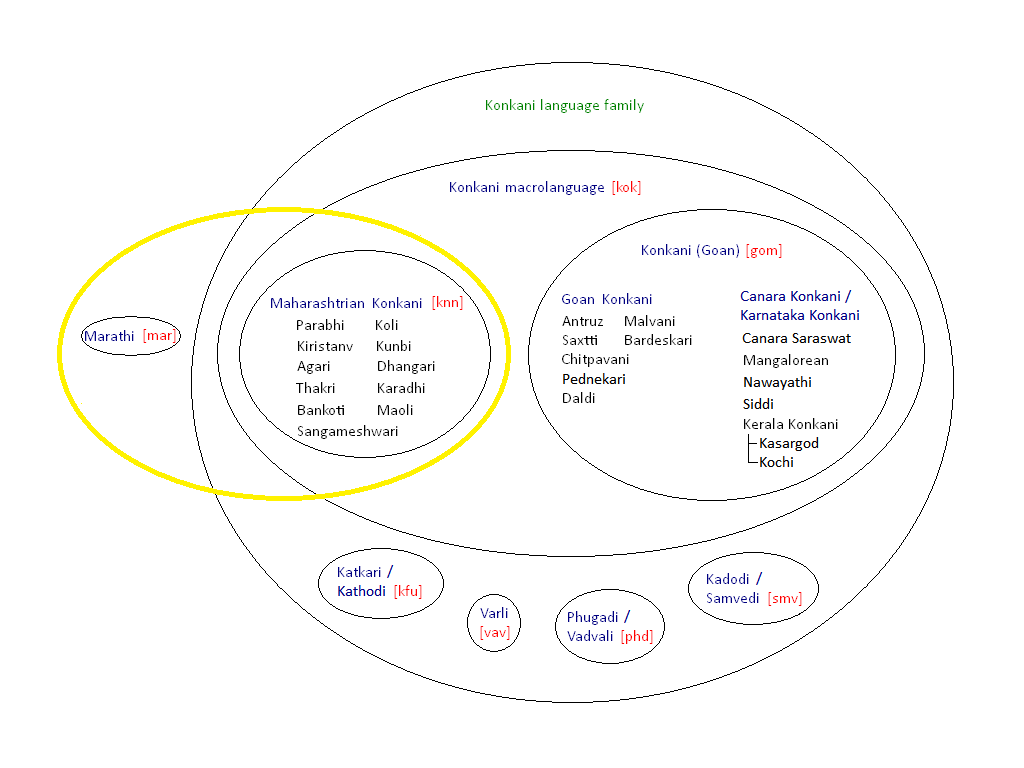
The Marathi—Konkani languages are the mainland Southern Indo-Aryan languages, spoken in Maharashtra and the Konkan region of India. The other branch of Southern Indo-Aryan languages is called Insular Indic languages, which are spoken in Insular South Asia (predominantly the island countries, Sri Lanka and Maldives). Languages The languages are: Marathi, Konkani, Phudagi, Kadodi (Samavedi), Katkari, Varli and Andh. Several of the Marathi-Konkani languages have been variously claimed to be dialects of both Marathi and Konkani. Maharashtrian Konkani A collection of dialects of Marathi-Konkani languages spoken in the Konkan region is referred to as Maharashtrian Konkani. It is often mistakenly extended to cover Goan Konkani which is an independent language. George Abraham Grierson has referred to this dialect as the ''Konkan Standard of Marathi'' in order to differentiate it from Konkani language. The sub dialects of Konkani gradually merge from standard Marathi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Muslims
Konkani Muslims (or ''Kokani'' Muslims) are an ethnoreligious subgroup of the Konkani people of the Konkani region along the west coast of India, who practice Islam. '' Nawayath'' and " Nakhuda" Muslims from the North Canara district of Karnataka have similar origin as Konkani Muslims, but show a distinct ethnolinguistic identity due to geographical isolation of the Canara coast from the Konkan coast. Geography The Konkani Muslim community forms a part of the larger Konkani-speaking demographic and are predominantly located in the Konkan division of the Indian state of Maharashtra. This includes the administrative districts of Mumbai, Mumbai Suburban, Palghar, Thane, Raigad, Ratnagiri, and Sindhudurg. There is a diaspora Konkani Muslim community based in Persian Gulf states, the United Kingdom, and South Africa. Some Konkani Muslims migrated to Pakistan during the Partition of India in 1947, and are presently settled in Karachi, as part of the larger Muhajir commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Literature
Konkani literature is literature in the Konkani language, mostly produced in three scripts: Roman, Devanagari and Kannada. Konkani literature is eligible for the Sahitya Akademi Award. History While the earliest inscriptions in Konkani date from around the end of the first millennium, the first writer in the history of Konkani language known to us today is Shamaraja; who was also known as Krishnadas Shama as he was an ardent devotee of Lord Krishna. He was born in the 15th century AD in the village of Quelossim in Goa. As per the date mentioned in his ''Shrikrishnacharitrakatha'', he began writing his book on 13th of the Vaishakha month of the Hindu lunar calendar, which is 25 April 1526, according to the Gregorian calendar. He authored ''Ramayana'', ''Mahabharata'', and ''Krishnacharitrakatha'' in prose style. The manuscripts have not been found, although transliterations in Roman script are found in Braga in Portugal. The script used by him for his work still remains a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Phonology
KonkaniDisambiguation: Konkani is a name given to a group of several cognate dialects spoken along the narrow strip of land called Konkan, on the west coast of India. This is, however, somewhat an over-generalisation. Geographically, Konkan is defined roughly as the area between the river Damanganga to the north and river Kali to the south, the north–south length being approx. and east–west breadth about , going to around in some places. A major part of Konkan is in Maharashtra and most people in the area speak some dialects of Marathi. But the language spoken in Goa and further south in coastal Karnataka and in some parts of northern Kerala has its distinct features, and is rightly identified as a separate language called Konkani and whose phonology is within the purview of this article. is a southern Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-European family of languages spoken in the Konkan coastal region of India. It has approximately 3.6 million speakers. Konkani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Liturgical Music
Konkani liturgical music refers to the sacred music used in the liturgy in the Konkani language. Konkani is used in liturgy in the Archdiocese of Goa and Daman, and the dioceses of Diocese of Mangalore, Mangalore, Roman Catholic Diocese of Karwar, Karwar, Roman Catholic Diocese of Udupi, Udupi and Diocese of Sindhudurg, Sindhudurg. History Prior to Vatican II, most of the liturgy was in Latin. When liturgy in vernacular languages was introduced in Vatican II, Fr. Vasco do Rego SJ led the effort to compose the needed Konkani liturgical music. Goan composers developed a rich and unique form of motets for the Lent, Lenten season, which were accompanied by violins, clarinets and double bass. Goan church authorities had obtained special permission from the Holy See to use these instruments during the Holy Week services. Unfortunately, most of these Konkani motets were not preserved and have been lost. There were similar efforts made independently in Mangalore in the field of Konkani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |