|
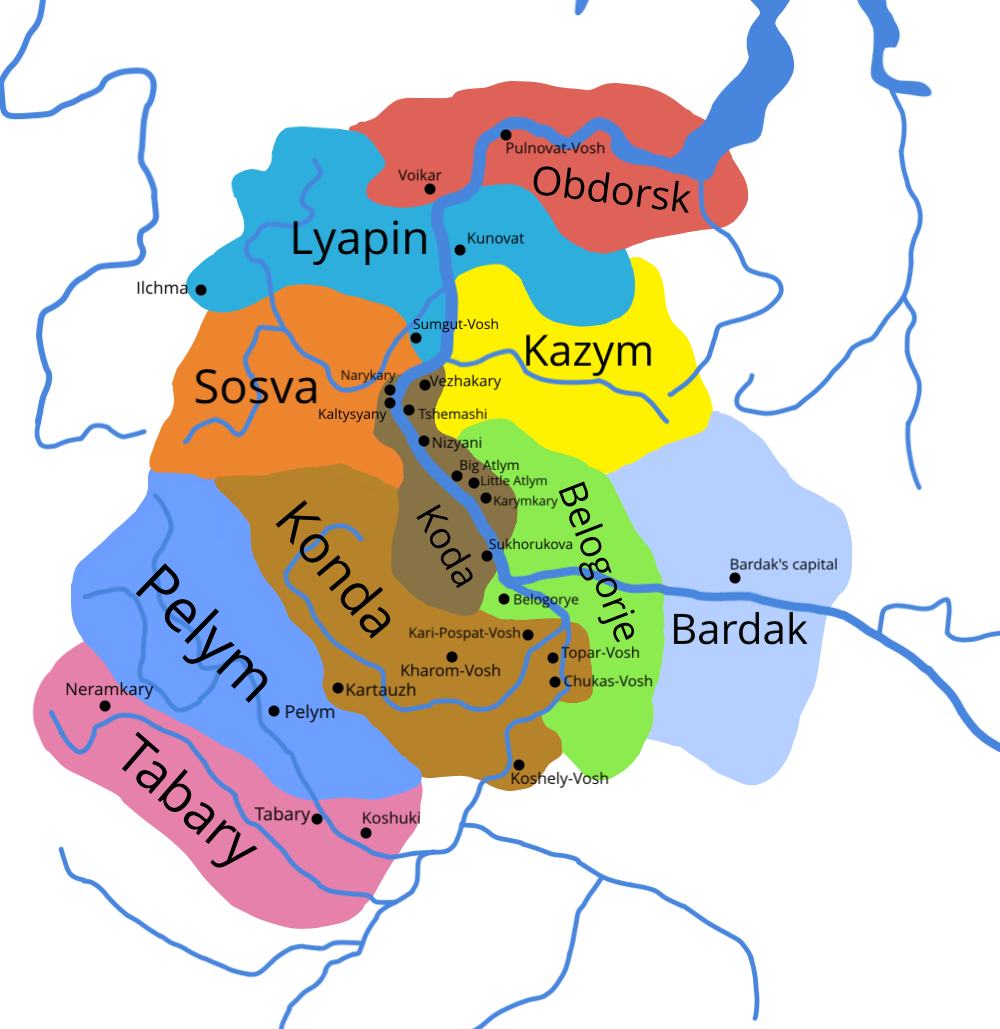
Khanty
The Khanty (), also known in older literature as Ostyaks (), are a Ugric Indigenous people, living in Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, a region historically known as " Yugra" in Russia, together with the Mansi. In the autonomous okrug, the Khanty and Mansi languages are given co-official status with Russian. In the 2021 Census, 31,467 persons identified themselves as Khanty. Of those, 30,242 were resident in Tyumen Oblast, of whom 19,568 were living in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and 9,985—in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. 495 were residents of neighbouring Tomsk Oblast, and 109 lived in Sverdlovsk Oblast. Ethnonym Since the Khanty language has about 10 dialects which can be united in 3 main branches, there are several slightly different words used by these people to describe themselves: *''Khanti, Khante'' (in Northern Khanty language, North) *''Khande'' (in South) *''Kantek, Kantakh'' (in East) All these words mean 'human'. They also call themselves ''As Kho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty Language
Khanty (also spelled Khanti or Hanti), previously known as Ostyak (), is a branch of the Ugric languages composed of multiple dialect continuum, dialect continua. It is varyingly considered a language or a collection of distinct languages spoken in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Khanty-Mansi and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrugs in Siberia. It belongs to the wider Uralic languages, Uralic language family. There were thought to be around 7,500 speakers of Northern Khanty language, Northern Khanty and 2,000 speakers of Eastern Khanty language, Eastern Khanty in 2010, with Southern Khanty language, Southern Khanty being extinct since the early 20th century. The number of speakers reported in the 2020 census was 13,900. The Khanty language has many dialects. The western group includes the Salekhard, Obdorian, Ob (river), Ob, and Irtysh dialects. The eastern group includes the Surgut and Vakh-Vasyugan dialects, which in turn are subdivided into 13 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug
Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra, also known as Khanty-Mansia (Khantia-Mansia), is a federal subject of Russia (an autonomous okrug of Tyumen Oblast). It has a population of 1,532,243 as of the 2010 Census. Its administrative center is located at Khanty-Mansiysk. The peoples native to the region are the Khanty and the Mansi, known collectively as Ob-Ugric peoples, but today the two groups only constitute 2.5% of the region's population. The local languages, Khanty and Mansi, are part of the Ugric branch of the Finno-Ugric language family, and enjoy a special status in the autonomous okrug. Russian remains the only official language. In 2012, the majority (51%) of the oil produced in Russia came from Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, giving the region great economic importance in Russia and the world. It borders Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug to the north, Komi Republic to the northwest, Sverdlovsk Oblast to the west, Tyumen Oblast to the south, Tomsk Oblast to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Khanty Language
Northern Khanty is a Uralic language, frequently considered a dialect of a unified Khanty language, spoken by about 9,000 people. It is the most widely spoken out of all the Khanty languages, the majority composed of 5,000 speakers in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, in Russia. The reason for this discrepancy is that dialects of Northern Khanty have been better preserved in its northern reaches, and the Middle Ob and Kazym dialects are losing favor to Russian. All four dialects have been literary, beginning with the Middle Ob dialects, but shifting to Kazym, and back to Middle Ob, now the most used dialect in writing. The Shuryshkar dialects are also written, primarily due to an administrative division between the two, as the latter is spoken in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Dialects Dialects of Northern Khanty: * Obdorsk ( Priuralsky District) * Berjozov (Synja, Muzhi, Shuryshkar), Kazym, Sherkal Transitional * Atlym, Nizyam Phonology Kazym Consonants Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Khanty Language
Eastern Khanty is a Uralic languages, Uralic language, frequently considered a dialect of a Khanty languages, Khanty language, spoken by about 1,000 people. The majority of these speakers speak the Surgut dialect, as the Vakh-Vasyugan and Salym varieties have been rapidly declining in favor of Russian. The former two have been used as literary languages since the late 20th century, with Surgut being more widely used due to its less isolated location and higher number of speakers. Classification Dialects Classification of Eastern Khanty dialects: * Far Eastern (Vakh, Vasyugan, Vasjugan, Verkhne-Kalimsk, Vartovskoe) * Surgutsky District, Surgut (Jugan, Malij Jugan, Pim (river), Pim, Likrisovskoe, Tromyogan, Tremjugan-Tromagan) The Vakh, Vasyugan, Alexandrovo and Yugan (Jugan) dialects have less than 300 speakers in total. Transitional The Bolshoy Salym, Salym dialect can be classified as transitional between Eastern and Southern (Honti 1998 suggests closer affinity with Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Khanty Language
Southern Khanty is a Uralic language, frequently considered a dialect of a unified Khanty language, spoken by 56 people in 2010. It is considered to be extinct, its speakers having shifted starting in the 18th century to Russian or Siberian Tatar Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states sin ..., but some speakers of the Kyshikov or Ust-Nazym dialect were found in its former territory. Speakers of Surgut Khanty have moved into the former territory of the Demyanka dialect. It was transitional between the Northern Khanty and Eastern Khanty dialect groups, but it is now a distinct language. Classification Southern and Northern Khanty share various innovations and can be grouped together as Western Khanty. These include loss of full front rounded vowels: *üü, *öö, *ɔ̈ɔ̈ > * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansi People
The Mansi (Mansi language, Mansi: Мāньси / Мāньси мāхум, ''Māńsi / Māńsi māhum'', ) are an Ob-Ugrians, Ob-Ugric Indigenous people living in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, Khanty–Mansia, an Autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrug within Tyumen Oblast in Russia. In Khanty–Mansia, the Khanty language, Khanty and Mansi language, Mansi languages have co-official status with Russian. The Mansi language is one of the postulated Ugric languages of the Uralic languages, Uralic family. The Mansi people were formerly known as the Voguls. Together with the Khanty, Khanty people, the Mansi are politically represented by the Association to Save Yugra, an organisation founded during Perestroika in the late 1980s. This organisation was among the first regional indigenous associations in Russia. Demographics According to the 2021 census, there were 12,228 Mansi in Russia. History The ancestors of the Mansi people populated the areas west of the Urals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugra
Yugra or Yugor Land (; also spelled ''Iuhra'' in contemporary sources) was a collective name for lands and peoples in the region east of the northern Ural Mountains in modern Russia given by Russian chroniclers in the 12th to 17th centuries. During this period, the region was inhabited by the Khanty (Ostyaks) and Mansi (Voguls) peoples. In a modern context, the term ''Yugra'' generally refers to a political constituent of the Russian Federation formally known as Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug–Yugra, located in the lands historically known as Ioughoria. In modern Russian, this word is rendered "Югория" (''Yugoria''), and is used as a poetic synonym of the region. At the beginning of the 16th century, the similarity between ''Yugria'' (the latinized form of the name) and ''ugry'', an old Russian ethnonym for the Hungarians, was noted by scholars such as Maciej Miechowita. The modern name of the Ugric language family, which includes Khanty and Mansi together with H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ob-Ugric Languages
The Ob-Ugric languages are a commonly proposed branch of the Uralic languages, grouping together the Khanty (Ostyak) and Mansi (Vogul) languages. Both languages are split into numerous and highly divergent dialects, more accurately referred to as languages. The Ob-Ugric languages and Hungarian comprise the proposed Ugric branch of the Uralic language family. The languages are spoken in the region between the Urals and the Ob River and the Irtysh in central Russia. The forests and forest steppes of the southern Urals are thought to be the original homeland of the Ugric branch. Beginning some 500 years ago the arrival of the Russians pushed the speakers eastward to the Ob and Irtysh. Some Mansi speakers remained west of the Urals until as late as the early 20th century. Hungarian split off during the 11th century BC. The Ob-Ugric languages have also been strongly influenced by nearby Turkic languages, especially Tatar. Mansi has about 1,000 speakers while Khanty has about 10, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Okrug
Autonomous okrugs, () which are also referred to as "autonomous districts" or "autonomous areas" are a type of federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russia, Russian Federation and simultaneously an administrative division type of some federal subjects. As of 2024, Russia has four autonomous okrugs of its 83 federal subjects. The Chukotka Autonomous Okrug is the only okrug which is not subordinate to an Oblasts of Russia, oblast. The Nenets Autonomous Okrug is a part of Arkhangelsk Oblast, the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug are parts of Tyumen Oblast. According to the Constitution of the Soviet Union, in case of a union republic voting on leaving the Soviet Union, Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics, autonomous republics, autonomous oblasts of the Soviet Union, autonomous oblasts, and autonomous okrugs had the right, by means of a referendum, to independently resolve whether they will stay in the USSR or leave with the republi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansi Language
The Mansi languages are spoken by the Mansi people in Siberia, Russia along the Ob River and its tributaries, in the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, and Sverdlovsk Oblast. Traditionally considered a single language, they constitute a branch of the Ugric languages, within the broader Uralic language family. They are often considered most closely related to neighbouring Khanty and then to Hungarian. The base dialect of the Mansi literary language is the Sosva dialect, a representative of the northern language. Fixed word order is typical in Mansi. Adverbials and participles play an important role in sentence construction. In the 2020–2021 census, 2229 people claimed to speak Mansi natively. All current speakers use Northern Mansi, as the other variants have become extinct. Dialects Mansi is subdivided into four main dialect groups which are to a large degree mutually unintelligible, and therefore best considered four languages. A primary split can be set up b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostyak
Ostyak () is a name formerly used to refer to several Indigenous peoples and languages in Siberia, Russia. Both the Khanty people and the Ket people were formerly called Ostyaks, whereas the Selkup people were referred to as Ostyak-Samoyed. Khanty The Khanty people, who also call themselves ''Khanti'', ''Khande'', or ''Kantek'' were known to the Russians as ''Yugra'' in the eleventh century, with the name ''Ostyak'' first appearing in the sixteenth century. The Soviet Union began using the endonym ''Khant'' or ''Khanty'' during the 1930s. some 28,000 people identify as Khanty, primarily in Tyumen Oblast, which includes the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug. The Khanty languages, also known as Hanty, Khant, Xanty, or Ostyak, are a Uralic language group with about 9,500 native speakers. Ket The Kets historically lived near the Yenisei River in the Krasnoyarsk Krai district of Russia. The Imperial Russians originally called them ''Ostyak'', and later ''Yenisei Ostyak''. Fewer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |