|
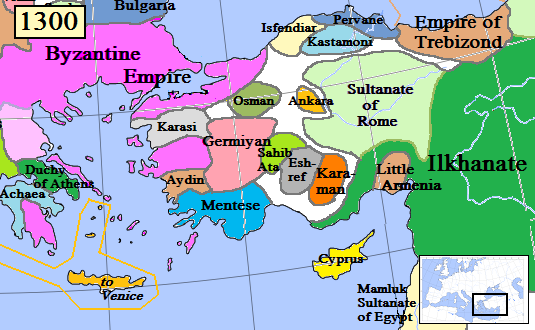
Karamanids
The Karamanids ( or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman (), was a Turkish people, Turkish Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian beylik (principality) of Salur tribe origin, descended from Oghuz Turks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the mid 14th century until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. states and territories disestablished in the 1480s History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sofi, Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (Caucasus), Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of The Mongol Invasions, the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolian Beyliks
Anatolian beyliks (, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik''; ) were Turkish principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by ''beys'', the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A second and more extensive period of establishment took place as a result of the decline of the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm in the latter half of the 13th century. One of the ''beyliks'', that of the ''Osmanoğlu'' of the Kayı branch of Oghuz Turks, from its capital in Bursa completed its incorporation of the other ''beyliks'' to form the Ottoman Empire by the late 15th century. The word ''beylik'' denotes a territory under the jurisdiction of a ''bey'', equivalent to a duchy or principality in other parts of Europe. History Following the 1071 Seljuk victory over the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert and the subsequent conquest of Anatolia, Oghuz Turkic clans began settling in present-day Turkey. The Seljuk Sultanate of Rum's central powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karaman Bey
Karim al-Dīn Ḳarāmān Beg was a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman chieftain who ruled the Karamanids in the 13th century. Ḳarāmān Beg's emergence coincides with the defeat of the Sultanate of Rum by the Mongol Empire in 1256 and the tension between Kaykaus I and his rival brother Kilij Arslan IV, which allowed local lords living along the boundaries of the state to exercise some autonomy. Early life He was the son of Nure Sofi, Nûre Sûfî Bey, a Turkish people, Turkish leader from Caucasian Albania, Arran, who established himself in the Taurus Mountains near Karaman, Larandia and who became a Seljuks, Seljuk vassal. Some time before 1256, Karaman Bey officially succeeded his father (who had already left him the effective power several years prior in order to pursue a life in seclusion). In about 1260 Karaman makes his first appearance in the Cilicia, Isaurian-Cilician Taurus regions. Although the points of detail can probably never be determined, it can be accepted that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerîmeddin Karaman Bey
Karim al-Dīn Ḳarāmān Beg was a Turkoman chieftain who ruled the Karamanids in the 13th century. Ḳarāmān Beg's emergence coincides with the defeat of the Sultanate of Rum by the Mongol Empire in 1256 and the tension between Kaykaus I and his rival brother Kilij Arslan IV, which allowed local lords living along the boundaries of the state to exercise some autonomy. Early life He was the son of Nûre Sûfî Bey, a Turkish leader from Arran, who established himself in the Taurus Mountains near Larandia and who became a Seljuk vassal. Some time before 1256, Karaman Bey officially succeeded his father (who had already left him the effective power several years prior in order to pursue a life in seclusion). In about 1260 Karaman makes his first appearance in the Isaurian-Cilician Taurus regions. Although the points of detail can probably never be determined, it can be accepted that Karaman started life as a woodcutter and timber merchant who brought supplies from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nure Sofi
Nûre Sûfi Bey () was the founder of Karamanid dynasty, a Turkic dynasty which ruled part of Anatolia in the 14th and 15th centuries as a rival of the Ottoman Empire. He was the son of Hodja Sad al-Din () who had come from Arran, staying for some years near Sivas. This, when generalized, is a reference to the actual migrations brought about by Khwārizmian and Mongol pressure, and moreover it suggests some perceptible connection, if not precisely with Baba Ishak, at least with circles influenced by religious influence of that kind - there is a reference to a Khorasanian Șūfī, Baba Ilyās, with whom both Nûre Sûfi and Baba Ishāq are said to have been in touch - and also to the fact that the first chiefs who brought in these Turkmens were equally leaders in the field of religion. Nure Sofi was a member of Afşar tribe of Turkmens. Originally living in West Turkmenistan the tribe moved west to Anatolia in 1228 probably to escape from the invading Mongols. They were wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afshar Tribe
Afshar ( ; , ; ; ) is a tribe of Oghuz Turkic origin that split into several groups in Iran, Turkey and Afghanistan. Afshar means "obedient". According to Rashid-al-Din Hamadani, Afshar, the eponymous founder of the tribe, was a son of Yildiz Khan, the third son of Oghuz Khan. During the Seljuk conquests of the 11th century, they moved from Central Asia into the Middle East. They are noted in history for being one of the Qizilbash tribes that helped establish the Safavid dynasty, and for being the source of descent of Afsharid dynasty. Nader Shah, who became the monarch of Iran in 1736, was from the Qereklu clan () of Afshars. The founders of the Germiyanids, and the Khalkhal Khanate were also of Afshar descent. The founder of the Karamanids may have also been of Afshar descent. Today, Afshars mainly inhabit Iran, where they remain a largely nomadic group. They are variously grouped as a branch of the Azerbaijanis or Turkomans (a common general term used for people of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konya
Konya is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium. In 19th-century accounts of the city in English its name is usually spelt Konia or Koniah. In the late medieval period, Konya was the capital of the Seljuk Turks' Sultanate of Rum, from where the sultans ruled over Anatolia. As of 2024, the population of the Metropolitan Province was 2 330 024 of whom 1 433 861 live in the three urban districts (Karatay, Selcuklu, Meram), making it the sixth most populous city in Turkey, and second most populous of the Central Anatolia Region, after Ankara. City has Konya is served by TCDD high-speed train ( YHT) services from Istanbul, Ankara and Karaman. The local airport ( Konya Havalimanı, KYA) is served by frequent flights from Istanbul whereas flights to and from İzmir are offered few times a week. Name Konya is believed to corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larende
Karaman is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the seat of Karaman Province and Karaman District.İl Belediyesi , Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 175,390 (2022). The town lies at an average elevation of . The Karaman Museum is one of the major sights. 
Etymology The town owes its name to |
Mut (District), Mersin
Mut is a municipality and district of Mersin Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,718 km2, and its population is 62,874 (2022). Mut is a rural district at the foot of the Sertavul Pass on the road over the Taurus Mountains from Ankara and Konya to the Mediterranean coast at Anamur or Silifke. Mut is known for its special apricot variety, ''Mut şekerparesi'', and a statue of a girl carrying a basket of them stands at the entrance to the town. The summer is hot and the people of Mut retreat to high meadows (so called yayla) even further up the mountainside. The forests up here are home to wild boar, and the Gezende reservoir on the Ermenek River is a welcome patch of blue in this dry district. The dam has a hydro-electric power station built in Romania. History The area has probably been inhabited since the time of the Hittites (2000 BC), and was later part of ancient Cilicia. Roman period Under the Roman Empire, the town was called Claudiopolis.''Alahan Monastery: A Masterpiec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman ( or ''Türkmân'') by the 13th century.Lewis, G. ''The Book of Dede Korkut''. Penguin Books, 1974, p. 10. The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Karluk allies of the Uyghurs. In the 9th century, the Oghuz from the Aral steppes drove Pechenegs westward from the Emba and Ural River region. In the 10th century, the Oghuz inhabited the steppe of the rivers Sari-su, Turgai and Emba north of Lake Balkhash in modern-day Kazakhstan. They embraced Islam and adapted their traditions and institutions to the Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salur Tribe
Salur, Salyr or Salgur (, , ) was an ancient Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic peoples, Turkic (or Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman) tribe and a sub-branch of the ''Üçok'' tribal federation. The Middle Ages, medieval Karamanids, Karamanid principality in Anatolia belonged to the Karaman branch of the Salur. The Salghurids of Fars (Atabegs of Fars), were also a dynasty of Salur origin. The patriarchs of the modern Turkmens, Turkmen tribe of the Salyr in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Iraq, and Iran, as well as the Salar people, Salars of China, claim descent from the original Oghuz Salur. Etymology Historian and statesman of the Ilkhanate, Rashid al-Din Hamadani, in his literary work ''Oghuzname'', which is part of his extensive history book Jami' al-tawarikh (Compendium of Chronicles), writes that the name ''Salyr'' means “''wherever you go, you fight with a sword and a club''”. The khan of the Khanate of Khiva and simultaneously a historian, Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur, in his ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish People
Turks (), or Turkish people, are the largest Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group, comprising the majority of the population of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. They generally speak the various Turkish dialects. In addition, centuries-old Turkish communities in the former Ottoman Empire, ethnic Turkish communities still exist across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. Article 66 of the Constitution of Turkey defines a ''Turk'' as anyone who is a citizen of the Turkish state. While the legal use of the term ''Turkish'' as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition, the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70 to 75 percent) are of Turkish ethnicity. The vast majority of Turks are Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, with a notable minority practicing Alevism. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye and Hatay. Name The name of Cilicia () was derived from (), which was the name used by the Neo-Assyrian Empire to designate the western part of what would become Cilicia. The English spelling is the same as the Latin, as it was transliterated directly from the Greek form Κιλικία. The palatalization of c occurring in Western Europe in later Vulgar Latin () accounts for its modern pronunciation in English. Geography Cilicia extends along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separate it from Syria. North and east of Cilicia stand the rugged Taurus Mountains, which separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, and which are pierced by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |