|
Islamic Manuscripts
Islamic manuscripts had a variety of functions ranging from Qur'anic recitation to scientific notation. These manuscripts were produced in many different ways depending on their use and period. Parchment (vellum) was a common way to produce manuscripts. Manuscript creators eventually transitioned to using paper in later centuries with the diffusion of paper-making in the Islamic empire. When Muslims encountered paper in Central Asia, its use and production spread to Iran, Iraq, Syria, Egypt, and North Africa during the 8th century. The Al-Furqan Islamic Heritage Foundation has estimated that 3 million Islamic manuscripts have survived. Other academics talk of 7 million surviving manuscripts out of 90 million manuscripts written between the 7th and 14th centuries. The estimates vary due to several challenges, such as limited access to manuscripts located in conflict zones or held in private libraries. Scripts The development of scripts in the Islamic empir, demonstrates the tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qur'anic
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic, Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad through the Angel#Islam, angel Gabriel#Islam, Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Night of Power, Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important Islamic view of miracles, miracle, a proof of his prophet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Quranic Manuscripts
In Muslim tradition the Quran is the final revelation from God, Islam's divine text, believed to be delivered to the Islamic prophet Muhammad through the angel Gabriel#Islam, Jibril (Gabriel). Muhammad's revelations were said to have been recorded orally and in writing, through Muhammad and his followers up until his death in 632 CE. These revelations were then compiled by first caliph Abu Bakr and codified during the reign of the third caliph Uthman ( CE) so that the standard codex edition of the Quran or was completed around 650 CE, according to Muslim scholars.#MCKaVSI2000, Cook (2000): p. 6 This has been critiqued by some western scholarship, suggesting the Quran was Canonization of Islamic scripture, canonized at a later date, based on the dating of classical Islamic narratives, i.e. hadiths, which were written 150–200 years after the death of Muhammad,#HBMaToJW2000, Berg (2000): p. 495 and partly because of the textual variations present in the Sana'a manuscript. Muslim sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalili Collection Islamic Art Qur 0323 Fol 3b-4a
Khalili () is a common Arabic-based surname, meaning "originating from Al-Khalil also known as Hebron". It is composed of root word Khalil (meaning "companion" or "friend") plus the Arabic suffix "i" meaning "from" or "of". Khalili is also commonly used in Persian, Afghani and other Muslim surnames. Khalili may refer to: Persons Khalili * Abbas Khalili, also known as Abbas al-Khalili (1896–1972), Iraqi-born Iranian diplomat, newspaper publisher * Abdul Khalili (born 1992), full name Abdul Rahman Khalili, Swedish football player of Palestinian origin *Anousheh Khalili (born 1983), Iranian-American singer-songwriter * Aram Khalili (born 1989), Norwegian football player of Iranian Kurdish origin *Sir David Khalili: see Nasser Khalili * Fowzieh Khalili (born 1958), Indian female cricketer * Imad Khalili (born 1987), Swedish football player of Palestinian origin * Karim Khalili, Afghani politician, Vice President of Afghanistan *Khalilullah Khalili (1907–1987), alternative spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surah
A ''surah'' (; ; ) is an Arabic word meaning 'chapter' in the Quran. There are 114 ''suwar'' in the Quran, each divided into ayah, verses (). The ''suwar'' are of unequal length; the shortest ''surah'' (al-Kawthar) has only three verses, while the longest (al-Baqara, al-Baqarah) contains 286 verses.Muhammad Mustafa Al-A'zami (2003), ''The History of The Qur'anic Text: From Revelation to Compilation: A Comparative Study with the Old and New Testaments'', p.70. UK Islamic Academy. . The Qur'an consists of one short introductory chapter (Q1), eight very long chapters, making up one-third of the Qur'an (Al-Baqara, Q2‒At-Tawbah, 9); 19 mid-length chapters, making up another one-third (Q10‒28); and 86 short and very short ones of the last one-third (Q29‒114). Of the 114 ''suwar'' in the Quran, 86 are classified as Meccan surah, Meccan (), as according to Islamic tradition they were revealed before Muhammad's migration to Medina (''hijrah''), while 28 are Medinan surah, Medinan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naskh (script)
Naskh is a small, round script of Islamic calligraphy. Naskh is one of the first scripts of Islamic calligraphy to develop, commonly used in writing administrative documents and for transcribing books, including the Qur’an, because of its easy legibility. Origin The Naskh style of writing can be found as early as within the first century of the Islamic calendar. The Naskh script was established in the first century of the Hijri calendar by order of Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan due to the presence of defects in the Kufic script. Two centuries before it was recorded by Ibn Muqla Like Al-Muwatta written by Malik ibn Anas in a soft, rounded script Ibn Muqla is credited with standardizing the "Six Pens" of Islamic calligraphy, also including , , , , and . These are known as "the proportioned scripts" () or "the six scripts" (). Kufic is commonly believed to predate naskh, but historians have traced the two scripts as coexisting long before their codification by Ibn Muqla, as the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
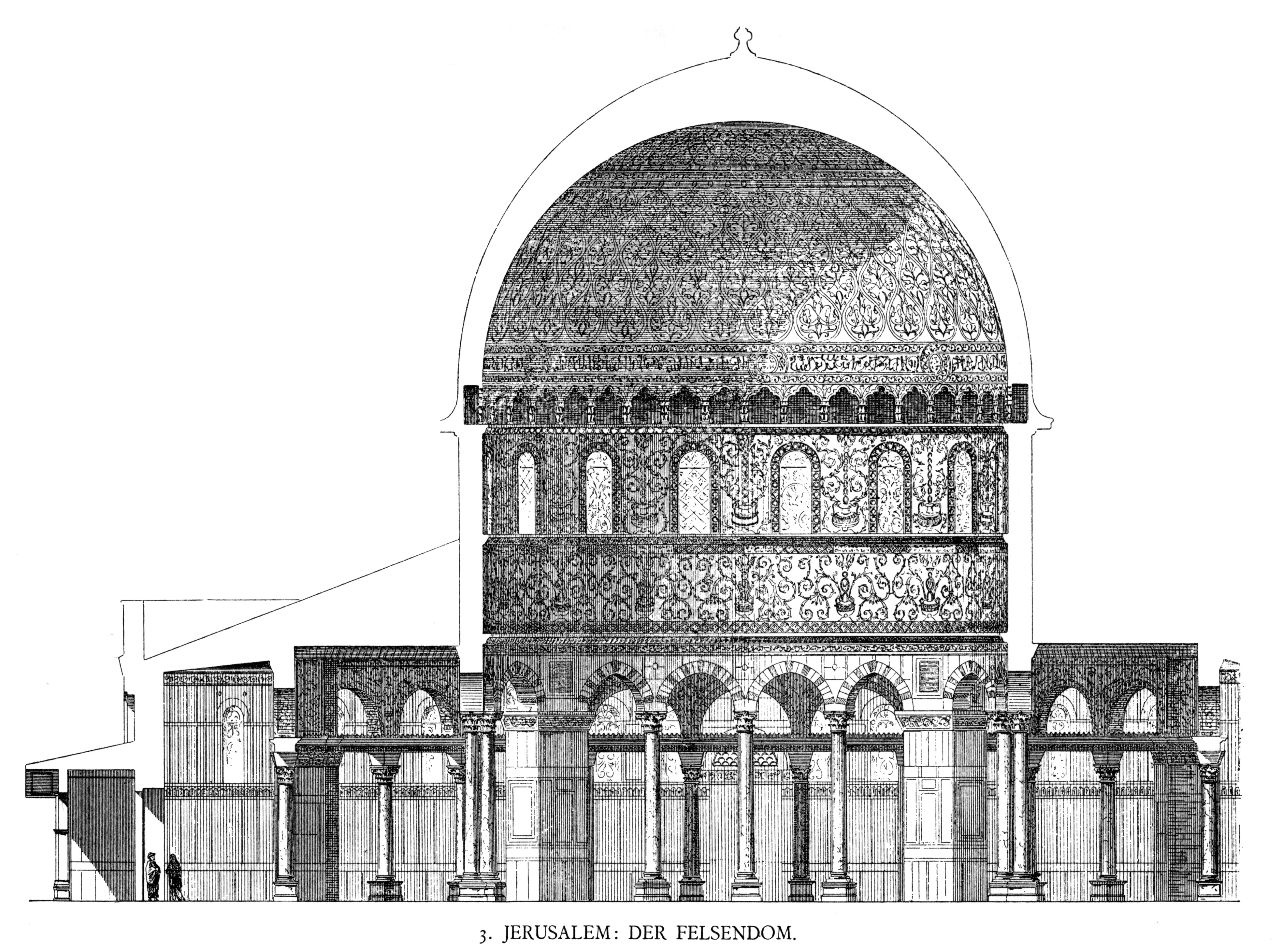
Dome Of The Rock
The Dome of the Rock () is an Islamic shrine at the center of the Al-Aqsa mosque compound on the Temple Mount in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem. It is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture, the List_of_the_oldest_mosques, earliest archaeologically attested religious structure to be built by a Muslim ruler and its inscriptions contain the earliest Epigraphy, epigraphic proclamations of Islam and of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Temple, Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple and rebuilt by Herod the Great), which was Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. Its architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Malik Ibn Marwan
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam (; July/August 644 or June/July 647 – 9 October 705) was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 until his death in October 705. A member of the first generation of born Muslims, his early life in Medina was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under Caliph Mu'awiya I (), founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, and his own father, Caliph Marwan I (). By the time of Abd al-Malik's accession, Umayyad authority had collapsed across the Caliphate as a result of the Second Fitna and had been reconstituted in Bilad al-Sham, Syria and Egypt in the Middle Ages, Egypt during his father's reign. Following a Battle of Khazir, failed invasion of Iraq in 686, Abd al-Malik focused on securing Syria before making further attempts to conquer the greater part of the Caliphate from his principal rival, the Mecca-based caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. To that end, he concluded an unfavorable truce with the reinvigorated Byz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scriptio Continua
(Latin for 'continuous script'), also known as or , is a style of writing without spaces or other marks between the words or sentences. The form also lacks punctuation, diacritics, or distinguished letter case. In the West, the oldest Greek and Latin inscriptions used word dividers to separate words in sentences; however, Classical Greek and late Classical Latin both employed as the norm. The ''scriptio continua'' is also known as Latin skeleton script. History Although is evidenced in most Classic Greek and Classic Latin manuscripts, different writing styles are depicted in documents that date back even further. Classical Latin often used the interpunct, especially in monuments and inscriptions. The earliest texts in Classical Greek that used the Greek alphabet, as opposed to Linear B, were formatted in a constant string of capital letters from right to left. Later, that evolved to boustrophedon, which included lines written in alternating directions. The Latin languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijazi Script
Hijazi script () is the collective name for several early Arabic scripts that developed in the Hejaz (the northwest of the Arabian Peninsula), a region that includes the cities of Mecca and Medina. This type of script was already in use at the time of the emergence of Islam. A calligraphic Hijazi script is called a Ma'il script (); these are found in a number of the earliest Qur'anic manuscripts. The two terms are often used interchangeably. Hijazi was one of the earliest scripts, along with Mashq and Kufic. Earlier scripts included Ancient North Arabian and the South Arabian script. The script is notably angular in comparison with other Arabic scripts and tends to slope to the right. The script does not yet contain any dots or diacritical marks to indicate vowel sounds: but does differentiate consonants by the intermittent use of dashes above the graphic letter forms. Historicity Ancient manuscripts are divided into two major types, Hijazi and Kufic. Kufic style also has its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Known colloquially in Syria as () and dubbed, poetically, the "City of Jasmine" ( ), Damascus is a major cultural center of the Levant and the Arab world. Situated in southwestern Syria, Damascus is the center of a large metropolitan area. Nestled among the eastern foothills of the Anti-Lebanon mountain range inland from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean on a plateau above sea level, Damascus experiences an arid climate because of the rain shadow effect. The Barada, Barada River flows through Damascus. Damascus is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. First settled in the 3rd millennium BC, it was chosen as the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate from 661 to 750. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijazi Script - Qur'anic Verses
Hijazi, Hijazy, Hejazi or Hegazy () is an Arabic surname originally designating a person (or their ancestor) from the Hejaz region in Saudi Arabia. People Hijazi * Abdallah Hijazi, Lebanese basketball player * Ahmed Hijazi (poet), Egyptian contemporary poet * Ali Hijazi, Sierra Leonean basketball player * Amal Hijazi, Lebanese singer * Farouk Hijazi, Iraqi diplomat * Fouad Hijazi, Lebanese footballer * Naseem Hijazi, Urdu novelist * Nawal Hijazi, Lebanese voice actress * Zane Hijazi, American Vine creator and YouTuber, member of David Dobrik's Vlog Squad *Daniel Hijazi,Lebanese person Hejazi * Abdol Hossein Hejazi (1904–1969), Iranian military officer * Attila Hejazi, Iranian football player and coach * Mohammad Hejazi, Iranian military commander * Nasser Hejazi, Iranian football goalkeeper See also * Hejazi Arabic * Hejazi turban Hijazi, Hijazy, Hejazi or Hegazy () is an Arabic surname originally designating a person (or their ancestor) from the Hejaz region in Saudi Arabia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginans
Ginans (, ; derived from ''jñana,'' meaning "knowledge") are devotional hymns or poems recited by Shia Ismaili Muslims. Literally meaning gnosis, ginans are the devotional literature of the Nizari Ismailis of South Asia, spanning topics of divine love, cosmology, rituals, eschatology, ethical behavior and meditation. Ranging from three verses to hundreds of pages, ginans are attributed to the Pirs, who were second only to the Imams in the Ismaili hierarchy.Virani, Shafique N. “Symphony of Gnosis: A Self-Definition of the Ismaili Ginān Literature.” Chap. 55. ''Reason and Inspiration in Islam: Theology, Philosophy and Mysticism in Muslim Thought.'' Edited by Todd Lawson, 503-521. London: I.B. Tauris in association with Institute of Ismaili Studies, 2005. www.academia.edu/36984287/Symphony_of_Gnosis_A_SelfDefinition_of_the_Ismaili_Ginan_Literature. It was originally an oral rendition mostly by Pirs, first among whom to come to South Asia was Pir Satgurnur in the 12th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |