|
Islam And Children
The topic of Islam and children includes Islamic principles of child development, the rights of children in Islam, the duties of children towards their parents, and the rights of parents over their children, both biological and foster children. Islam identifies three distinct stages of child development, each lasting 7 years, from age 0-21. Each comes with specific prescriptions for what a child is to learn and what their relationship with their parents should be. Muslims have the right to a marriage arranged by their parents when they are old enough, though the Quran does not specify what age that is. Different traditions and countries have different views on readiness for marriage. Fostering is strongly encouraged, but it is frowned upon to adopt a child and treat them as your own. Instead, they should maintain their own "natal identity." Muhammad's interactions with children Muhammad had seven children, three boys and four girls. All of his sons, including Ibrahim ibn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage In Islam
In Islamic law, marriage is accomplished through the marriage contract, known as a () or more specifically, the bride's acceptance of the groom's dowry ('' mahr'') and the witnessing of her acceptance. The contract has rights and obligations for the man and woman, with rules on consent, financial obligations, and the treatment of partners, developed (according to Islamic sources) from the Quran, (the holy book of Islam) and hadith (the passed down saying and doings of the Islamic prophet Muhammad). In addition to the requirement that a formal, binding contract of rights and responsibilities – either verbal or on paper – be drawn up, there are a number of other rules for marriage in Islam: among them that there be witnesses to the marriage, a gift from the groom to the bride known as a mahr, that both the groom and the bride freely consent to the marriage; that the groom be married to no more than four women (a practice known as polygyny), that the women be married to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Esposito
John Louis Esposito (born May 19, 1940) is an American academic, professor of Middle Eastern studies, Middle Eastern and religious studies, and scholar of Islamic studies, who serves as Professor of Religion, International Affairs, and Islamic Studies at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C. He is also the founding director of the Prince Alwaleed Center for Muslim–Christian Understanding at Georgetown. Biography For nearly twenty years after completing his Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D., Esposito had taught Religious studies, religious studies (including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Islam) at the College of the Holy Cross, a Jesuit college in Massachusetts. At the College of the Holy Cross, Esposito held the Loyola Professor of Middle East Studies position, was the chair of the Department of Religious Studies, and director of the College of the Holy Cross' Center for International Studies.. Center for the Study of Islam & Democracy. . Accessed February 23, 2007 At Georgetown Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intangible divine law; contrary to ''fiqh'', which refers to its interpretations by Ulama, Islamic scholars. Sharia, or fiqh as traditionally known, has always been used alongside urf, customary law from the very beginning in Islamic history; has been elaborated and developed over the centuries by fatwa, legal opinions issued by mufti, qualified jurists – reflecting the tendencies of Schools of Fiqh, different schools – and integrated and with various economic, penal and administrative laws issued by Muslims, Muslim rulers; and implemented for centuries by Qadi, judges in the courts until recent times, when secularism was widely adopted in Islamic societies. Traditional Principles of Islamic jurisprudence, theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
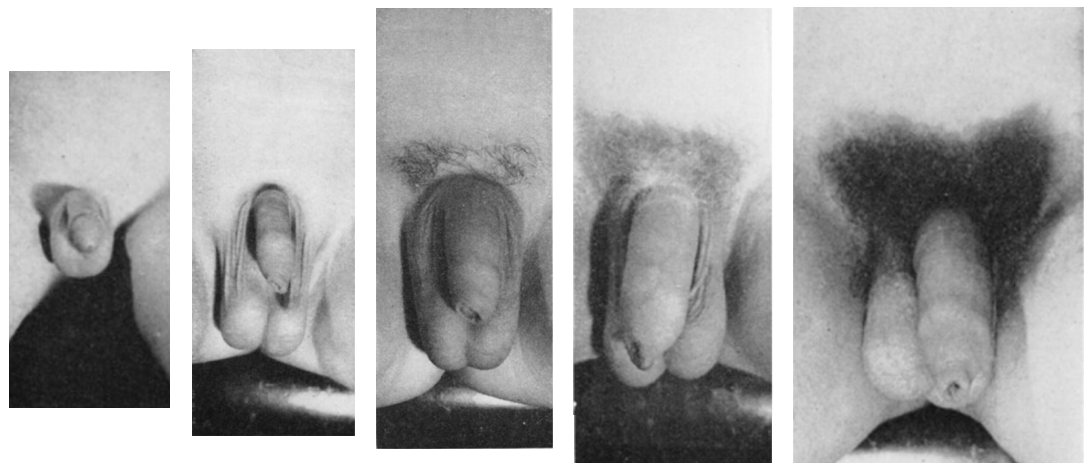
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baligh
In Islamic legal terminology, bāligh (, adult) or mukallāf (, responsible) or muhallāq (, tendril, mentally matured) or murāhiq (, adolescent) or muhtalim (, pubescent) refers to someone who has reached maturity or puberty, and has full responsibility under Islamic law. Quran The Qur'an refers to puberty in 6:152; 12:22; 17:34; 18:82: 22:5; 28:14; 40:67: 46:15 and 3 times in chapter 24 An-Nur (31, 58, 59), where reference is made to a prepubescent child's unawareness of sexual matters, which allows him or her to be with an adult whose state of dress would preclude more mature individuals from being present. One includes children who have not reached puberty in a list of those before whom woman may adopt a more relaxed standard of dress than what is normally stipulated in the verse 31 of An-Nur (24:31). The other makes a distinction between children who have reached puberty and those who have not, with the latter having access to parents who might be in a state of undress. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadi
A qadi (; ) is the magistrate or judge of a Sharia court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works. History The term '' was in use from the time of Muhammad during the early history of Islam, and remained the term used for judges throughout Islamic history and the period of the caliphates. While the and played the role in elucidation of the principles of Islamic jurisprudence () and the Islamic law (), the qadi remained the key person ensuring the establishment of justice on the basis of these very laws and rules. Thus, the qadi was chosen from amongst those who had mastered the sciences of jurisprudence and law. The office of qadi continued to be a very important one in every principality of the caliphates and sultanates of the various Muslim empires over the centuries. The rulers appointed a qadi in every region, town, and village for judicial and administrative cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wali
The term ''wali'' is most commonly used by Muslims to refer to a saint, or literally a "friend of God".John Renard, ''Friends of God: Islamic Images of Piety, Commitment, and Servanthood'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2008); John Renard, ''Tales of God Friends: Islamic Hagiography in Translation'' (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2009), passim. In the traditional Islamic understanding, a saint is portrayed as someone "marked by pecialdivine favor ... ndholiness", and who is specifically "chosen by God and endowed with exceptional gifts, such as the ability to work miracles".Radtke, B., "Saint", in: ''Encyclopaedia of the Qurʾān'', General Editor: Jane Dammen McAuliffe, Georgetown University, Washington, D.C. The doctrine of saints was articulated by Muslim scholars very early on in Islamic history, and particular verses of the Quran and certain hadith were interpreted by early Muslim thinkers as "documentary evidence" of the existence of saints. Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the sharia; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the Quran and the sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions). Fiqh expands and develops Shariah through interpretation (''ijtihad'') of the Quran and ''Sunnah'' by Islamic jurists (''ulama'') and is implemented by the rulings (''fatwa'') of jurists on questions presented to them. Thus, whereas ''sharia'' is considered immutable and infallible by Muslims, ''fiqh'' is considered fallible and changeable. ''Fiqh'' deals with the observance of rituals, morals and social legislation in Islam as well as econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanafi
The Hanafi school or Hanafism is the oldest and largest Madhhab, school of Islamic jurisprudence out of the four schools within Sunni Islam. It developed from the teachings of the Faqīh, jurist and theologian Abu Hanifa (), who systemised the use of reasoning (). Hanafi legal theory primarily derives law from the Quran, the sayings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah''), scholarly consensus () and analogical reasoning (), but also considers juristic discretion () and local customs (). It is distinctive in its greater usage of ''qiyas'' than other schools. The school spread throughout the Muslim world under the patronage of various Islamic empires, including the Abbasids and Seljuk Empire, Seljuks. The Central Asian region of Transoxiana emerged as a centre of classical Hanafi scholarship between the 10th and 12th centuries, which gave rise to the Maturidi school of theology. The Ottoman Empire adopted Hanafism as its official school of law and influenced the legal thought of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuben Levy
Reuben Levy (28 April 1891 – 6 September 1966) was Professor of Persian at the University of Cambridge. He wrote on Persian literature and Islamic history. Life Levy was educated at the Friars School, Bangor, the University College of North Wales, Bangor and Jesus College, Oxford, studying Persian, Turkish and the Semitic languages. His First Persian teacher was Isa Sedigh. During the First World War, he was a captain in General Staff Intelligence in Mesopotamia (1916 to 1918), and worked in the Iraq Political Service (1918 to 1920). He lectured in Persian at Oxford from 1920 to 1923 before living in the United States from 1923 to 1926. He moved to the University of Cambridge in 1926 as Lecturer in Persian, and became Professor of Persian in 1950, the chair being created for him. He was also a Fellow of Christ's College, Cambridge. During the Second World War, he was a Squadron Leader Squadron leader (Sqn Ldr or S/L) is a senior officer rank used by some air forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik Ibn Anas
Malik ibn Anas (; –795) also known as Imam Malik was an Arab Islamic scholar and traditionalist who is the eponym of the Maliki school, one of the four schools of Islamic jurisprudence in Sunni Islam.Schacht, J., "Mālik b. Anas", in: ''Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition'', Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W.P. Heinrichs. Brill Online. Born in Medina into the clan of Humayr which belonged to the Banu Taym of Quraysh, Malik studied under Hisham ibn Urwa, Ibn Shihab al-Zuhri, Ja'far al-Sadiq, Nafi ibn Sarjis and others. He rose to become the premier scholar of hadith in his day, Referred to as the Imam of Medina by his contemporaries, his views in matters of jurisprudence became highly cherished both in his own life and afterward, becoming the eponym of the Maliki school, one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence. His school became the normative rite for Sunni practice in much of North Africa, al-Andalus (until the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |