|
Information Sensitivity
Information sensitivity is the control of access to information or knowledge that might result in loss of an advantage or level of security if disclosed to others. Loss, misuse, modification, or Access control, unauthorized access to sensitive information can adversely affect the privacy or welfare of an individual, trade secrets of a business or even the national security, security and international relations of a nation depending on the level of sensitivity and nature of the information. Non-sensitive information Public information This refers to information that is already a matter of public record or knowledge. With regard to government and private organizations, access to or release of such information may be requested by any member of the public, and there are often formal processes laid out for how to do so. The accessibility of government-held public records is an important part of government transparency, accountability to its citizens, and the values of democracy. Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
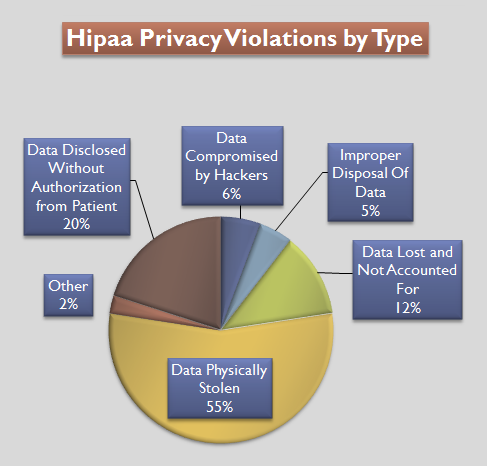
Health Insurance Portability And Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Ted Kennedy, Kennedy–Nancy Kassebaum, Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It aimed to alter the transfer of healthcare information, stipulated the guidelines by which personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on Health insurance in the United States, healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits Health professional, healthcare providers and businesses called covered entities from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. The bill does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves (with limited exceptions). Furthermore, it does not proh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Protection Directive
The Data Protection Directive, officially Directive 95/46/EC, enacted in October 1995, was a European Union directive which regulated the processing of personal data within the European Union (EU) and the free movement of such data. The Data Protection Directive was an important component of EU privacy and human rights law. The principles set out in the Data Protection Directive were aimed at the protection of fundamental rights and freedoms in the processing of personal data. The General Data Protection Regulation, adopted in April 2016, superseded the Data Protection Directive and became enforceable on 25 May 2018. Context The right to privacy is a highly developed area of law in Europe. All the member states of the Council of Europe (CoE) are also signatories of the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). Article 8 of the ECHR provides a right to respect for one's "private and family life, his home and his correspondence", subject to certain restrictions. The European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Data Protection Regulation
The General Data Protection Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2016/679), abbreviated GDPR, is a European Union regulation on information privacy in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA). The GDPR is an important component of EU privacy law and human rights law, in particular Article 8(1) of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. It also governs the transfer of personal data outside the EU and EEA. The GDPR's goals are to enhance individuals' control and rights over their personal information and to simplify the regulations for international business. It supersedes the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC and, among other things, simplifies the terminology. The European Parliament and Council of the European Union adopted the GDPR on 14 April 2016, to become effective on 25 May 2018. As an EU regulation (instead of a directive), the GDPR has direct legal effect and does not require transposition into national law. However, it also provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Privacy Law
Information privacy, data privacy or data protection laws provide a legal framework on how to obtain, use and store data of natural persons. The various laws around the world describe the rights of natural persons to control who is using their data. This includes usually the right to get details on which data is stored, for what purpose and to request the deletion in case the purpose is not given anymore. Over 80 countries and independent territories, including nearly every country in Europe and many in Latin America and the Caribbean, Asia, and Africa, have now adopted comprehensive data protection laws. The European Union has the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), in force since May 25, 2018. The United States is notable for not having adopted a comprehensive information privacy law, but rather having adopted limited sectoral laws in some areas like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). By Jurisdiction The German state of Hessia enacted the world's first data pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Privacy
The secret ballot, also known as the Australian ballot, is a voting method in which a voter's identity in an election or a referendum is anonymous. This forestalls attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote buying. This system is one means of achieving the goal of political privacy. Secret ballots are used in conjunction with various voting systems. The most basic form of a secret ballot uses paper ballots upon which each voter marks their choices. Without revealing the votes, the voter folds the ballot paper in half and places it in a sealed box. This box is later emptied for counting. An aspect of secret voting is the provision of a voting booth to enable the voter to write on the ballot paper without others being able to see what is being written. Today, printed ballot papers are usually provided, with the names of the candidates or questions and respective check boxes. Provisions are made at the polling place for the voters to recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Privacy
Banking secrecy, alternatively known as financial privacy, banking discretion, or bank safety,Guex (2000), p. 240 is a conditional agreement between a bank and its clients that all foregoing activities remain secure, confidential, and private. Most often associated with banking in Switzerland, banking secrecy is prevalent in Luxembourg, Monaco, Hong Kong, Singapore, Ireland, and Lebanon, among other off-shore banking institutions. Otherwise known as bank–client confidentiality or banker–client privilege, the practice was started by Italian merchants during the 1600s near Northern Italy (a region that would become the Italian-speaking region of Switzerland). Geneva bankers established secrecy socially and through civil law in the French-speaking region during the 1700s. Swiss banking secrecy was first codified with the Banking Act of 1934, thus making it a crime to disclose client information to third parties without a client's consent. The law, coupled with a stable Sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Privacy
Medical privacy, or health privacy, is the practice of maintaining the security and confidentiality of patient records. It involves both the conversational discretion of health care providers and the security of medical records. The terms can also refer to the physical privacy of patients from other patients and providers while in a medical facility, and to modesty in medical settings. Modern concerns include the degree of disclosure to insurance companies, employers, and other third parties. The advent of electronic medical records (EMR) and patient care management systems (PCMS) have raised new concerns about privacy, balanced with efforts to reduce duplication of services and medical errors. Most developed countries including Australia, Canada, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States, New Zealand, and the Netherlands have enacted laws protecting people's medical health privacy. However, many of these health-securing privacy laws have proven less effective in practice th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Privacy
Internet privacy involves the right or mandate of personal privacy concerning the storage, re-purposing, provision to third parties, and display of information pertaining to oneself via the Internet. Internet privacy is a subset of data privacy. Privacy concerns have been articulated from the beginnings of large-scale computer sharing and especially relate to mass surveillance. Privacy can entail either personally identifiable information (PII) or non-PII information such as a site visitor's behavior on a website. PII refers to any information that can be used to identify an individual. For example, age and physical address alone could identify who an individual is without explicitly disclosing their name, as these two parameters are unique enough to identify a specific person typically. Other forms of PII may include GPS tracking data used by apps, as the daily commute and routine information can be enough to identify an individual. It has been suggested that the "appeal of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Clearance
A security clearance is a status granted to individuals allowing them access to classified information (state or organizational secrets) or to restricted areas, after completion of a thorough background check. The term "security clearance" is also sometimes used in private organizations that have a formal process to vet employees for access to sensitive information. A clearance by itself is normally not sufficient to gain access; the organization must also determine that the cleared individual needs to know specific information. No individual is supposed to be granted automatic access to classified information solely because of rank, position, or a security clearance.(Abiodun, 2006) Canada United Kingdom National Security Clearance types National Security Clearances are a hierarchy of levels, depending on the classification of materials that can be accessed—Baseline Personnel Security Standard (BPSS), Counter-Terrorist Check (CTC), Enhanced Baseline Standard (EBS), Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Need To Know
The term "need to know" (alternatively spelled need-to-know), when used by governments and other organizations (particularly those related to military or intelligence), describes the restriction of data which is considered very confidential and sensitive. Under need-to-know restrictions, even if one has all the necessary official approvals (such as a security clearance) to access certain information, one would not be given access to such information, or read into a clandestine operation, unless one has a specific ''need to know''; that is, access to the information must be necessary for one to conduct one's official duties. This term also includes anyone that the people with the knowledge deemed necessary to share it with. As with most security mechanisms, the aim is to make it difficult for unauthorized access to occur, without inconveniencing legitimate access. Need-to-know also aims to discourage "browsing" of sensitive material by limiting access to the smallest possible n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classified Information
Classified information is confidential material that a government deems to be sensitive information which must be protected from unauthorized disclosure that requires special handling and dissemination controls. Access is restricted by law or regulation to particular groups of individuals with the necessary security clearance with a need to know. A formal security clearance is required to view or handle classified material. The clearance process requires a satisfactory background investigation. Documents and other information must be properly marked "by the author" with one of several (hierarchical) levels of sensitivity—e.g. Confidential (C), Secret (S), and Top Secret (S). All classified documents require designation markings on the technical file which is usually located either on the cover sheet, header and footer of page. The choice of level is based on an impact assessment; governments have their own criteria, including how to determine the classification of an inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |