|
Hydroxy Acids
Hydroxycarboxylic acids are carboxylic acids containing one or more Hydroxy group, hydroxy (Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol) functional groups. They are of particular interest because several are bioactive and some are useful precursors to polyesters. The inventory is large. Important or common examples *Glycolic acid, , the parent hydroxycarboxylic acid, precursor to laquers *Hydroxypropionic acids, e.g., (lactic acid), component of milk. chiral *Hydroxybutyric acids, (beta-Hydroxybutyric acid), carbon-storage compound *Citric acid, , energy-carrying compound and iron-chelator *Salicylic acid, , precursor to aspirin *Ricinoleic acid (12-hydroxy-9-''cis''-octadecenoic acid)), a major component of the seed oil obtained from castor plant *Common amino acids: **Serine (2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid), **Threonine **Tyrosine, {{chem2, 4\sHOC6H4CH2CH(NH2)CO2H *Aldonic acids are Sugar acid, sugar acids with the general chemical formula, HO2C(CHOH)nCH2OH. **Gluconic acid, a particularly c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
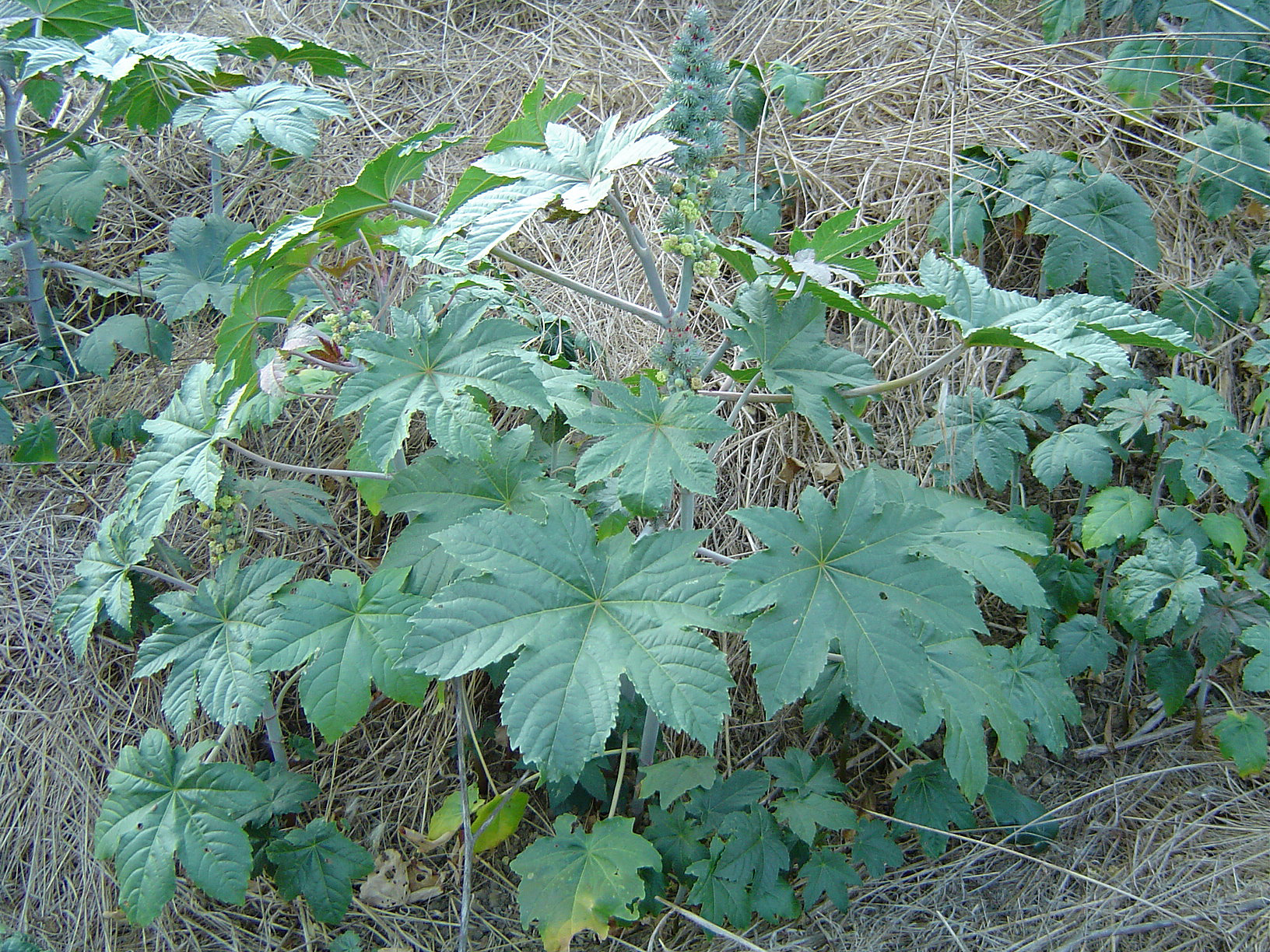
Castor Plant
''Ricinus communis'', the castor bean or castor oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus, ''Ricinus'', and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of castor and its relation to other species are currently being studied using modern genetic tools. It reproduces with a mixed pollination system which favors selfing by geitonogamy but at the same time can be an out-crosser by anemophily (wind pollination) or entomophily (insect pollination). Its seed is the castor bean, which despite the term is not a bean (as it is not the seed of a member of the family Fabaceae). Castor is indigenous to the southeastern Mediterranean Basin, East Africa, and India, but is widespread throughout tropical regions (and widely grown elsewhere as an ornamental plant). Castor seed is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The seeds contain between 40% and 60% oil that is rich in triglycerides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Hydroxy Acid
Omega hydroxy acids (ω-hydroxy acids) are a class of naturally occurring straight-chain aliphatic organic acids ''n'' carbon atoms long with a carboxyl group at position 1 (the starting point for the family of carboxylic acids), and a hydroxyl at terminal position ''n'' where ''n'' > 3. They are a subclass of hydroxycarboxylic acids. The C16 and C18 omega hydroxy acids 16-hydroxy palmitic acid and 18-hydroxy stearic acid are key monomers of cutin in the plant cuticle. The polymer cutin is formed by interesterification of omega hydroxy acids and derivatives of them that are substituted in mid-chain, such as 10,16-dihydroxy palmitic acid.T.J. Walton TJ and P.E. Kolattukudy (1972) Enzymatic conversion of 16-hydroxypalmitic acid into 10,16-dihydroxypalmitic acid in ''Vicia faba'' epidermal extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Communications 46, (1), 16–21P. J. Holloway (1982) The chemical constitution of plant cutins. p45-85 in In "The Plant Cuticle". ed. by DF Cutler, KL Alvin and CE Price. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Hydroxy Acid
A beta hydroxy carboxylic acid or β-hydroxy carboxylic acid (BHA) is a carboxylic acid containing a hydroxy functional group separated by ''two'' carbon atoms. They are related to alpha hydroxy acids, in which the two functional groups are separated by only ''one'' carbon atom. Reactions Upon dehydration, beta-hydroxy acids yield an alpha-beta unsaturated acid. Compared to their non-hydroxylated counterpart, beta hydroxy carboxylic acids are stronger, although weaker than the alpha hydroxy acids. Due to the larger distance, the intramolecular hydrogen bridge is less easily formed compared to the alpha hydroxy acids. The table summarizes some values on the propionic series. {, class="wikitable" ! Name ! p''K''a , - , Propanoic acid , , 4.87Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC press, 58th edition page D150-151 (1977) , - , α-Hydroxypropionic acid , , 3.86Dawson, R. M. C. ''et al''., ''Data for Biochemical Research'', Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959. , - , β-Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Hydroxy Acid
Alpha hydroxy carboxylic acids, or α-hydroxy carboxylic acids (AHAs), are a group of carboxylic acids featuring a hydroxy group located ''one'' carbon atom away from the acid group. This structural aspect distinguishes them from beta hydroxy acids, where the functional groups are separated by ''two'' carbon atoms. Notable AHAs include glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid, and citric acid. α-Hydroxy acids are stronger acids compared to their non-alpha hydroxy counterparts, a property enhanced by internal hydrogen bonding. AHAs serve a dual purpose: industrially, they are utilized as additives in animal feed and as precursors for polymer synthesis. In cosmetics, they are commonly used for their ability to chemically exfoliate the skin. Occurrence Aldonic acids, a type of sugar acid, are a class of naturally occurring hydroxycarboxylic acids. They have the general chemical formula, HO2C(CHOH)''n''CH2OH. Gluconic acid, a particularly common aldonic acid, the oxidized deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
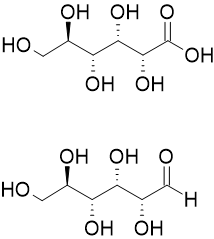
Gluconic Acid
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4CO2H. A white solid, it forms the gluconate anion in neutral aqueous solution. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates. Chemical structure The chemical structure of gluconic acid consists of a six-carbon chain, with five hydroxyl groups positioned in the same way as in the open-chained form of glucose, terminating in a carboxylic acid group. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid. Production Gluconic acid is typically produced by the aerobic oxidation of glucose in the presence of the enzyme glucose oxidase. The conversion produces gluconolactone and hydrogen peroxide. The lactone spontaneously hydrolyzes to gluconic acid in water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Acid
In organic chemistry, a sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its Polymer backbone, chain. Main classes of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group () located at the initial end (Monosaccharide#Linear-chain monosaccharides, position 1) of an aldose is oxidized. * Ulosonic acids, in which the hydroxymethyl group () at the initial end of a 2-ketose is oxidized creating an α-ketoacid. * Uronic acids, in which the group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized. * Aldaric acids, in which both ends ( and ) of an aldose are oxidized. Examples Examples of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids ** Glyceric acid (3C) ** Xylonic acid (5C) ** Gluconic acid (6C) ** Ascorbic acid (6C, unsaturated lactone) * Ulosonic acids ** Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glyceraldehyde, ''glycero''-D-galactose, ''galacto''-non-2-ulosonic acid) ** Ketodeoxyoctulosonic acid (KDO or 3-deoxy-D-mannose, ''mann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldonic Acid
Aldonic acids are sugar acids with the general chemical formula, HO2C(CHOH)nCH2OH. They are obtained by oxidizing the aldehyde (-CHO group) of an aldose to form a carboxylic acid (-COOH group). Aldonic acids are generally found in their ring form. However, these rings do not have a chiral carbon at the terminal end bearing the aldehyde, and they cannot form R−O−R′ linkages between different molecules. The nomenclature of aldonic acids and their lactones is based on replacing the suffix "-ose" with "onic acid" or "onolactone". Hence, D-glucose is oxidized to D-gluconic acid and D- gluconolactone. Inventory Sugar acids are white, water-soluble solids. They tend to dehydrate to the lactone derivative, often before they can be melted. All are chiral and, at least in nature, enantiopure. Synthesis Oxidation by bromine and water Aldonic acids are most commonly prepared by the oxidation of the sugar with bromine and water under neutral pH. Strecker reaction Alternatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form when dissolved in water), and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as ''E. coli''. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC (ACU, ACC, ACA, and ACG). Threonine sidechains are often hydrogen bonded; the most common small motifs formed are based on interactions with serine: ST turns, ST motifs (often at the beginning of alpha helices) and ST staples (usually at the middle of alpha helices). Modifications The threonine residue is susceptible to numerous posttranslational modifications. The hydroxyl side-chain can und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |