|
History Of Neuroscience
From the ancient Egyptian mummifications to 18th-century scientific research on "globules" and neurons, there is evidence of neuroscience practice throughout the early periods of history. The early civilizations lacked adequate means to obtain knowledge about the human brain. Their assumptions about the inner workings of the mind, therefore, were not accurate. Early views on the function of the brain regarded it to be a form of "cranial stuffing" of sorts. In ancient Egypt, from the late Middle Kingdom onwards, in preparation for mummification, the brain was regularly removed, for it was the heart that was assumed to be the seat of intelligence. According to Herodotus, during the first step of mummification: "The most perfect practice is to extract as much of the brain as possible with an iron hook, and what the hook cannot reach is mixed with drugs." Over the next five thousand years, this view came to be reversed; the brain is now known to be the seat of intelligence, although co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herophilos
Herophilos (; ; 335–280 BC), sometimes Latinised Herophilus, was a Greek physician regarded as one of the earliest anatomists. Born in Chalcedon, he spent the majority of his life in Alexandria. He was the first scientist to systematically perform scientific dissections of human cadavers. He recorded his findings in over nine works, which are now all lost. The early Christian author Tertullian states that Herophilos vivisected at least 600 live prisoners; however, this account has been disputed by many historians.Scarboroug"Celsus on Human Vivisection at Ptolemaic Alexandria" ''Clio Medica. Acta Academiae Internationalis Historiae Medicinae. Vol. 11'', 1976 He is often seen as the father of anatomy. Biography Herophilos was born in Chalcedon in Asia Minor (now Kadıköy, Turkey), c. 335 BC. Not much is known about his early life other than he moved to Alexandria at a fairly young age to begin his schooling. As an adult Herophilos was a teacher, and an author of at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
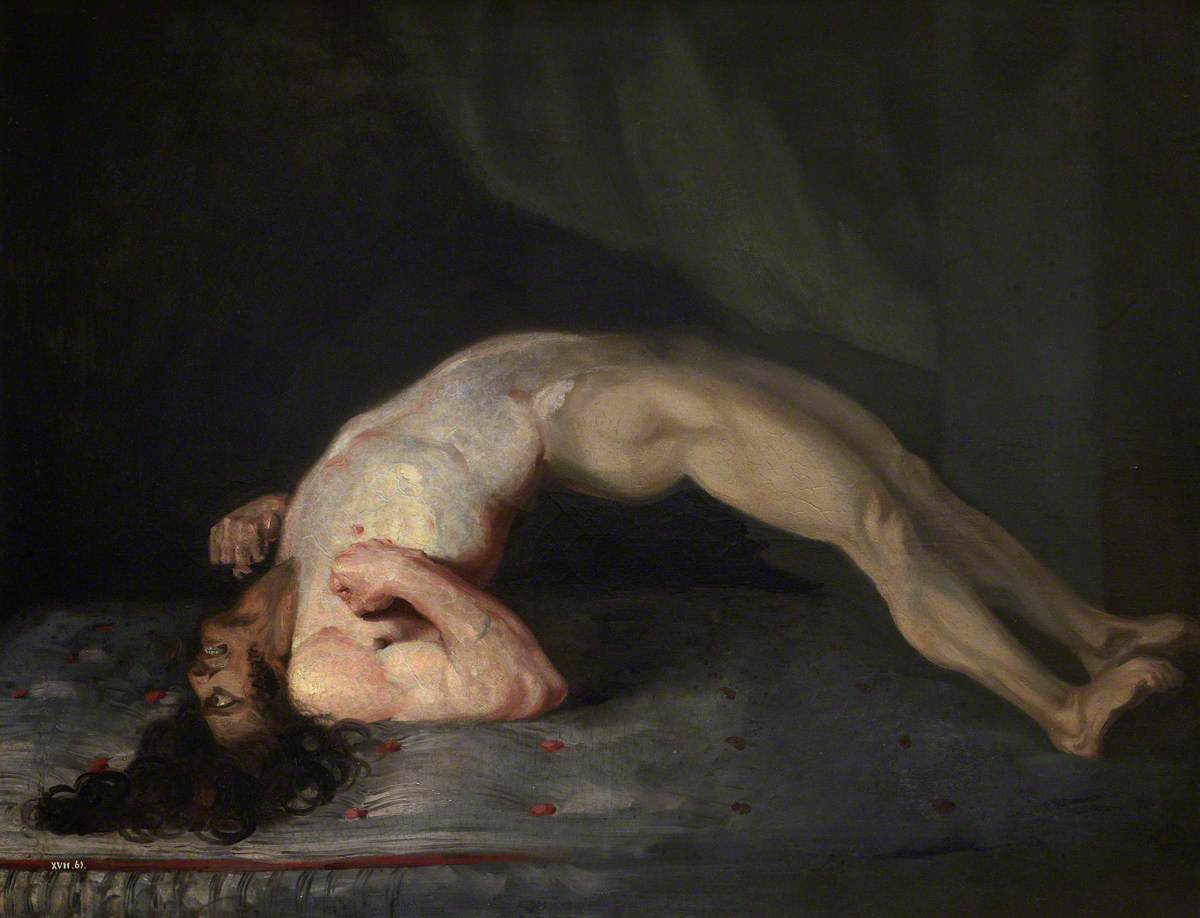
Charles Bell
Sir Charles Bell (12 November 177428 April 1842) was a Scottish surgeon, anatomist, physiologist, neurologist, artist, and philosophical theologian. He is noted for discovering the difference between sensory nerves and motor nerves in the spinal cord. He is also noted for describing Bell's palsy. His three older brothers included Robert Bell (1757–1816) a Writer to the Signet, John Bell (1763–1820), also a noted surgeon and writer; and the advocate George Joseph Bell (1770–1843) who became a professor of law at the University of Edinburgh and a principal clerk at the Court of Session. Early life and education Charles Bell was born in Edinburgh on 12 November 1774, as the fourth son of the Reverend William Bell, a clergyman of the Episcopal Church of Scotland. Charles's father died in 1779 when he was five years old, and so his mother had a unique influence on his early life, teaching him how to read and write. In addition to this, his mother also helped Charles' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Magendie
__NOTOC__ François Magendie (6 October 1783 – 7 October 1855) was a French physiologist, considered a pioneer of experimental physiology. He is known for describing the foramen of Magendie. There is also a ''Magendie sign'', a downward and inward rotation of the eye due to a lesion in the cerebellum. Magendie was a faculty at the College of France, holding the Chair of Medicine from 1830 to 1855 (he was succeeded by Claude Bernard, who worked previously as his assistant). In 1816 he published ''Précis élementaire de Physiologie'' which described an experiment first illustrating the concept of empty calories: :I took a dog of three years old, fat, and in good health, and put it to feed upon sugar alone...It expired the 32nd day of the experiment. His most important contribution to science was also his most disputed. Contemporaneous to Sir Charles Bell, Magendie conducted a number of experiments on the nervous system, in particular verifying the differentiation b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbary Macaque
The Barbary macaque (''Macaca sylvanus''), also known as Barbary ape, is a macaque species native to the Atlas Mountains of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco, along with a small introduced population in Gibraltar. It is the type species of the genus ''Macaca''. The species is of particular interest because males play an atypical role in rearing young. Because of uncertain paternity, males are integral to raising all infants. Generally, Barbary macaques of both sexes and all ages contribute in alloparental care of young. The diet of the Barbary macaque consists primarily of plants and insects and they are found in a variety of habitats. Males live to around 25 years old while females may live up to 30 years. Besides humans, they are the only free-living primates in Europe. Although the species is commonly referred to as the "Barbary ape", the Barbary macaque is a true monkey. Its name refers to the Barbary Coast of Northwest Africa. The population of the Barbary macaques in Gibraltar i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
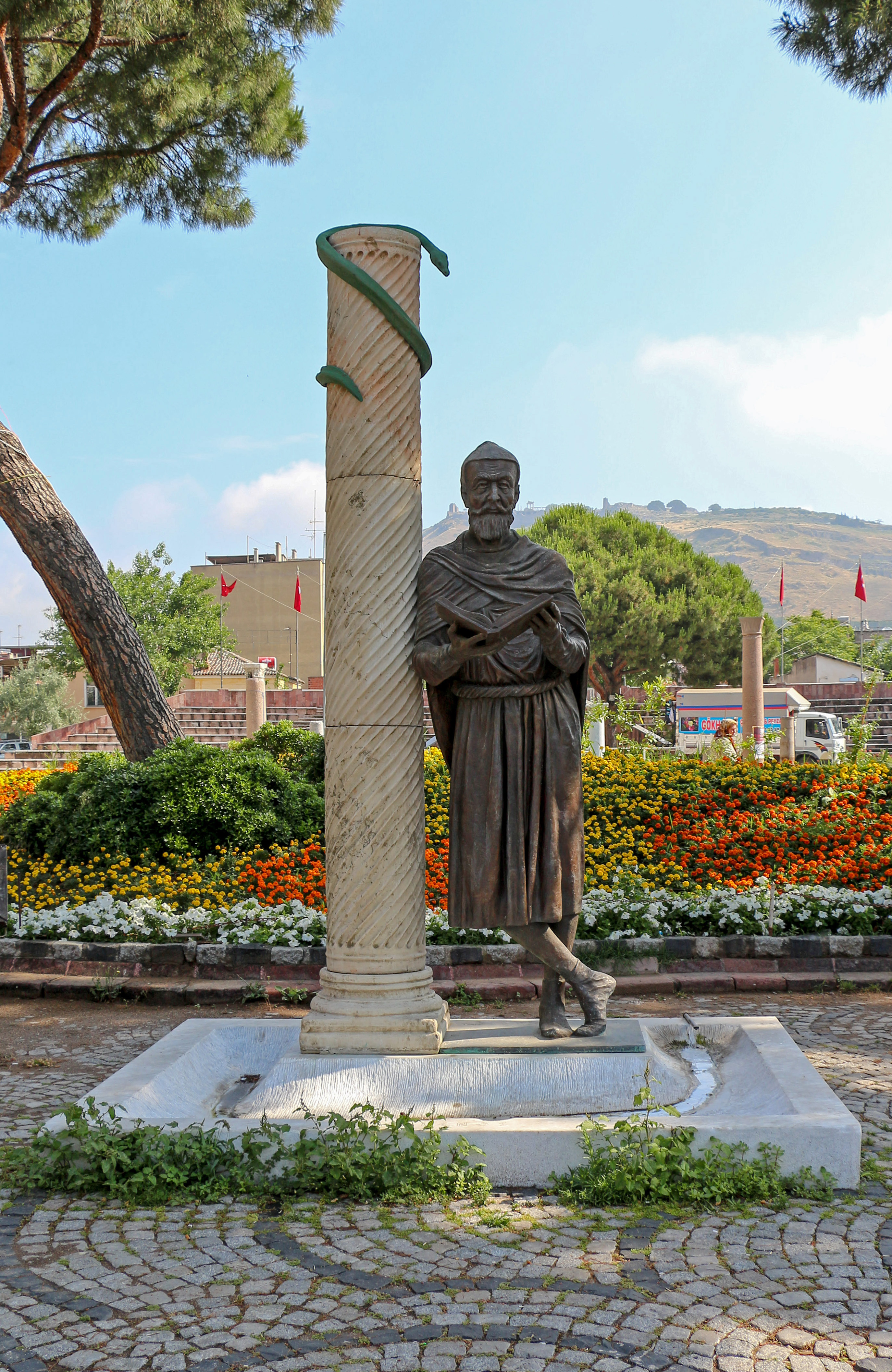
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of Ancient history, antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Ancient Rome, Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |