|
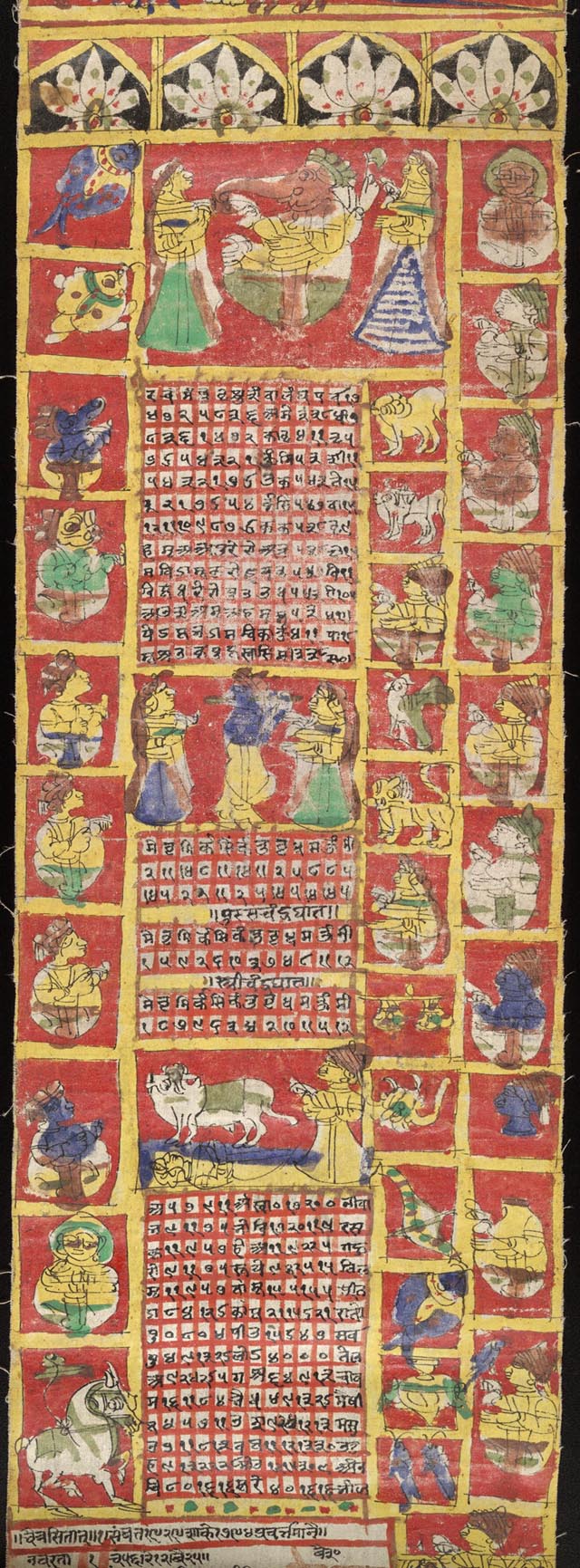
Hindu Astronomy
Astronomy has a long history in the Indian subcontinent, stretching from pre-historic to modern times. Some of the earliest roots of Indian astronomy can be dated to the period of Indus Valley civilisation or earlier. Astronomy later developed as a discipline of Vedanga, or one of the "auxiliary disciplines" associated with the study of the Vedas dating 1500 BCE or older. The oldest known text is the ''Vedanga Jyotisha'', dated to 1400–1200 BCE (with the extant form possibly from 700 to 600 BCE). Indian astronomy was influenced by Greek astronomy beginning in the 4th century BCEHighlights of Astronomy, Volume 11B: As presented at the XXIIIrd General Assembly of the IAU, 1997. Johannes Andersen Springer, 31 January 1999 – Science – 616 pages. p. 72/ref>Babylon to Voyager and Beyond: A History of Planetary Astronomy. David Leverington. Cambridge University Press, 29 May 2010 – Science – 568 pages. p. 4/ref>The History and Practice of Ancient Astronomy. James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lalla
Lalla ( 720–790 CE) was an Indian Indian mathematics, mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer who belonged to a family of astronomers. Lalla was the son of Trivikrama Bhatta and the grandson of Śâmba."Lalla." Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography. He lived in central India, possibly in the Lāṭa region in modern south Gujarat. Lalla was known as being one of the leading Indian astronomers of the eighth century. Only two of his works are currently thought to be extant.Bracher, Katherine His best-known work is the ''Śiṣyadhīvṛddhidatantra'' ("Treatise which expands the intellect of students"). This text is one of the first major Sanskrit astronomical texts known from the period following the 7th-century works of Brahmagupta and Bhāskara I. It generally treats the same astronomical subject matter and demonstrates the same computational techniques as earlier authors, although there are some significant innovations, such that Lalla’s treatise offers a compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Campaign Of Alexander The Great
The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327BC and lasted until 325BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the Indus Valley of Northwestern Indian subcontinent. Within two years, Alexander expanded the Macedonian Empire, a kingdom closely linked to the broader Greek world, to include Gandhara and the Indus Valley of Punjab and Sindh (now in India and Pakistan), surpassing the earlier frontiers established by the Persian Achaemenid conquest. Following Macedon's absorption of Gandhara (a former Persian satrapy), including the city of Taxila, Alexander and his troops advanced into Punjab, where they were confronted by Porus, the regional Indian king. In 326 BC, Alexander defeated Porus and the Pauravas during the Battle of the Hydaspes,Fuller, p. 198 but that engagement was possibly the Macedonians' most costly battle. Alexander's continued eastward march was leading his army into a confrontation wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synodic Month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive Syzygy (astronomy), syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Variations In Shona people, Shona, Middle Eastern, and European traditions, the month starts when the new moon, young crescent moon first becomes visible, at evening, after Astronomical conjunction, conjunction with the Sun one or two days before that evening (e.g., in the Islamic calendar). In Egyptian calendar, ancient Egypt, the lunar month began on the day when the waning moon could no longer be seen just before sunrise. Others run from full moon to full moon. Yet others use calculation, of varying degrees of sophistication, for example, the Hebrew calendar, the Chinese calendar, or the Computus, ecclesiastical lunar calendar. Calendars count integer days, so months may be 29 or 30 days in length, in some regular or irregular sequence. Lunar Cycles, Lunar cycles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Day
Sidereal time ("sidereal" pronounced ) is a system of timekeeping used especially by astronomers. Using sidereal time and the celestial coordinate system, it is easy to locate the positions of celestial objects in the night sky. Sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars". A sidereal day (also known as the sidereal rotation period) represents the time for one rotation about the planet axis relative to the stars. Viewed from the same location, a star seen at one position in the sky will be seen at the same position on another night at the same time of day (or night), if the day is defined as a sidereal day. This is similar to how the time kept by a sundial (Solar time) can be used to find the location of the Sun. Just as the Sun and Moon appear to rise in the east and set in the west due to the rotation of Earth, so do the stars. Both solar time and sidereal time make use of the regularity of Earth's rot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunisolar Calendar
A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, that combines monthly lunar cycles with the solar year. As with all calendars which divide the year into months, there is an additional requirement that the year have a whole number of months (Moon cycles). The majority of years have twelve months but every second or third year is an embolismic year, which adds a thirteenth intercalary, embolismic, or leap month. Lunisolar calendars are lunar calendars but, in contrast to purely lunar calendars such as the Islamic calendar, have additional intercalation rules that reset them periodically into a rough agreement with the solar year and thus with the seasons. Examples The Chinese, Buddhist, Burmese, Assyrian, Hebrew, Jain, traditional Nepali, Hindu, Japanese, Korean, Mongolian, Tibetan, and Vietnamese calendars (in the East Asian Chinese cultural sphere), plus the ancient Hellenic, Coligny, and Babylonian calendars are all lunisolar. Also, some of the ancient pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
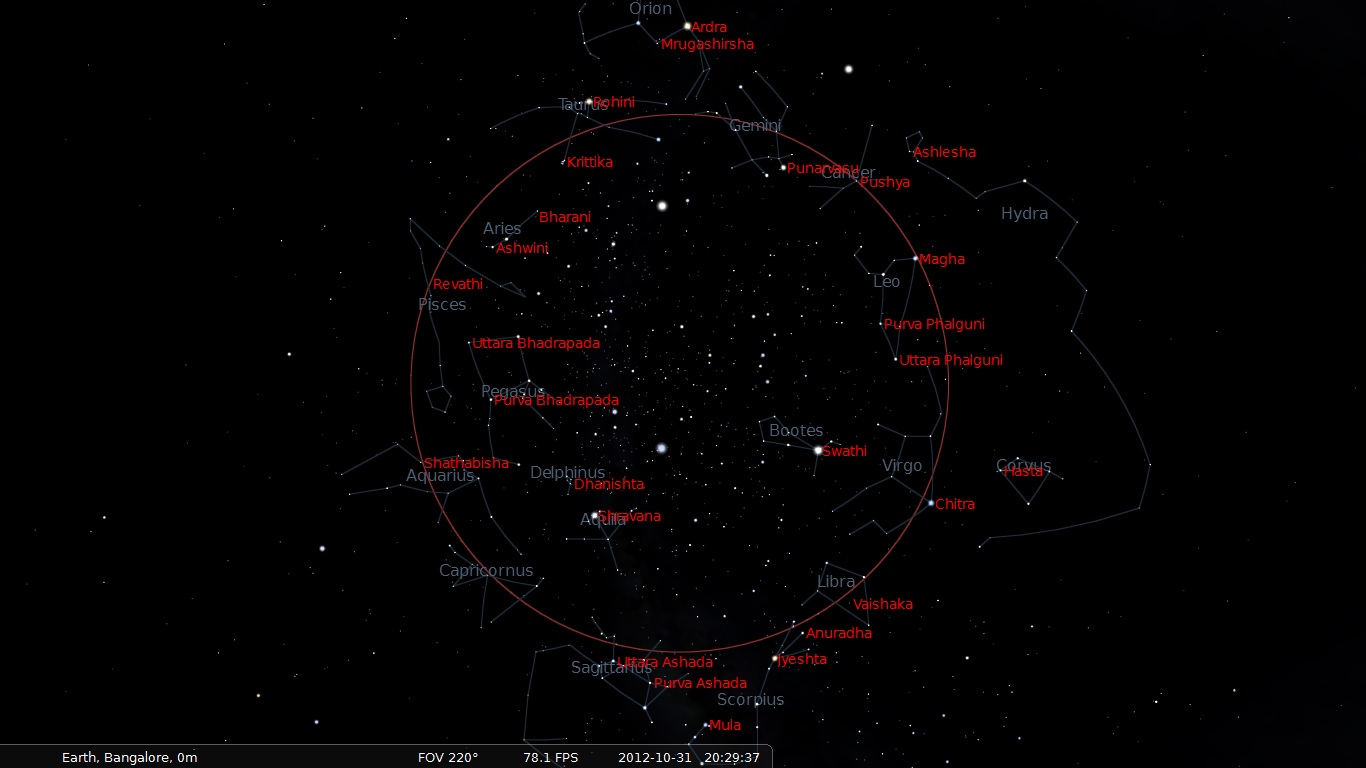
Nakshatra
Nakshatra () is the term for Lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Buddhist astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a constellation. Every nakshatra is divided into four ''padas'' ( "steps"). The starting point for the nakshatras according to the ''Vedas'' is "Krittika" (it has been argued, because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the ''Vedas'' were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite the star Spica, called ''Chitrā'' in Sanskrit. This translates to Ashwinī, a part of the modern constellation of Aries. These compilations, therefore, may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through Aries at the time of the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shulba Sutras
The ''Shulva Sutras'' or ''Śulbasūtras'' (Sanskrit: शुल्बसूत्र; ': "string, cord, rope") are sutra texts belonging to the Śrauta ritual and containing geometry related to vedi (altar), fire-altar construction. Purpose and origins The Shulba Sutras are part of the larger corpus of texts called the Kalpa (Vedanga), Shrauta Sutras, considered to be appendices to the Vedas. They are the only sources of knowledge of Indian mathematics from the Vedic period. Unique Vedi (altar), Vedi (fire-altar) shapes were associated with unique gifts from the Gods. For instance, "he who desires heaven is to construct a fire-altar in the form of a falcon"; "a fire-altar in the form of a tortoise is to be constructed by one desiring to win the world of Brahman" and "those who wish to destroy existing and future enemies should construct a fire-altar in the form of a rhombus"., p. 387, "Certain shapes and sizes of fire-altars were associated with particular gifts that the sacrif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopraxy
In the study of religion, orthopraxy is correct conduct, both ethical and liturgical, as opposed to faith or grace. Orthopraxy is in contrast with orthodoxy, which emphasizes correct belief. The word is a neoclassical compound— () meaning 'right practice'. While orthodoxies make use of codified beliefs in the form of creeds and ritualism more narrowly centers on the strict adherence to prescribed rites or rituals, orthopraxy is focused on issues of family, cultural integrity, the transmission of tradition, sacrificial offerings, concerns of purity, ethical system, and the enforcement thereof. In Hinduism, orthopraxy and ritualism are often interconnected. Judaism and Christianity are also considered both religions and orthopraxies, as they guide adherents in both practice and belief. Biale, David, ''Not in the Heavens: The Tradition of Jewish Secular Thought'', Princeton University Press, 2011, p.15 Etymology The term ''orthopraxy'' comes from the Greek , meaning "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy And Religion
Astronomy has been a favorite and significant component of mythology and religion throughout history. Astronomy and cosmology are parts of the myths of many cultures and religion around the world. Astronomy and religion have long been closely intertwined, particularly during the early history of astronomy. Archaeological evidence of many ancient cultures demonstrates that celestial bodies were the subject of worship during the Stone and Bronze Ages. Amulets and stone walls in northern Europe depict arrangements of stars in constellations that match their historical positions, particularly circumpolar constellations. These date back as much as 30,000–40,000 years. In many ancient religions, the northern circumpolar stars were associated with darkness, death and the underworld of the dead. For the Aztecs, the northern stars were associated with Tezcatlipoca. In Peking, China, was a shrine devoted to the North Star deity. Such worship of the northern stars may have been as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedas
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest Hindu texts, scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas (mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread, its sites spanning an area including much of Pakistan, Northwest India, northwestern India and northeast Afghanistan. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra River, Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan. The term ''Harappan'' is sometimes applied to the Indus Civilisation after its type site Harappa, the first to be exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |