|
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (; ; 31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894; "von" since 1883) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, was named in his honour. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, colour vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy and on the electrical double layer, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. Although credit is shared with Julius von Mayer, James Joule, and Daniel Bernoulli—among others—for the energy conservation principles that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic languages, Slavic origin. Potsdam was a residence of the Prussian kings and the German Emperor until 1918. Its planning embodied ideas of the Age of Enlightenment: through a careful balance of architecture and landscape, Potsdam was intended as "a picturesque, pastoral dream" which would remind its residents of their relationship with nature and reason. The city, which is over 1,000 years old, is widely known for its palaces, its lakes, and its overall historical and cultural significance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violin Acoustics
Violin acoustics is an area of study within musical acoustics concerned with how the sound of a violin is created as the result of interactions between its many parts. These acoustic qualities are similar to those of other members of the violin family, such as the viola. The energy of a vibrating string is transmitted through the bridge to the body of the violin, which allows the sound to radiate into the surrounding air. Both ends of a violin string are effectively stationary, allowing for the creation of standing waves. A range of simultaneously produced harmonics each affect the timbre, but only the fundamental frequency is heard. The frequency of a note can be raised by the increasing the string's tension, or decreasing its length or mass. The number of harmonics present in the tone can be reduced, for instance by the using the left hand to shorten the string length. The loudness and timbre of each of the strings is not the same, and the material used affects sound qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin–Helmholtz Mechanism
The Kelvin–Helmholtz mechanism is an astronomical process that occurs when the surface of a star or a planet cools. The cooling causes the internal pressure to drop, and the star or planet shrinks as a result. This compression, in turn, heats the core of the star/planet. This mechanism is evident on Jupiter and Saturn and on brown dwarfs whose central temperatures are not high enough to undergo hydrogen fusion. It is estimated that Jupiter radiates more energy through this mechanism than it receives from the Sun, but Saturn might not. Jupiter has been estimated to shrink at a rate of approximately 1 mm/year by this process, corresponding to an internal flux of 7.485 W/m2. The mechanism was originally proposed by Kelvin and Helmholtz in the late nineteenth century to explain the source of energy of the Sun. By the mid-nineteenth century, conservation of energy had been accepted, and one consequence of this law of physics is that the Sun must have some energy source to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith–Helmholtz Invariant
In optics the Smith–Helmholtz invariant is an invariant quantity for paraxial beams propagating through an optical system. Given an object at height \bar and an axial ray passing through the same axial position as the object with angle u, the invariant is defined by :H = n\baru, where n is the refractive index. For a given optical system and specific choice of object height and axial ray, this quantity is invariant under refraction In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo .... Therefore, at the ith conjugate image point with height \bar_i and refracted axial ray with angle u_i in medium with index of refraction n_i we have H = n_i \bar_i u_i. Typically the two points of most interest are the object point and the final image point. The Smith–Helmholtz invariant has a close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability
The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (after Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz) is a fluid instability that occurs when there is shear velocity, velocity shear in a single continuum mechanics, continuous fluid or a velocity difference across the interface between two fluids. Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are visible in the atmospheres of planets and moons, such as in List of cloud types, cloud formations on Earth or the Great Red Spot#Great Red Spot, Red Spot on Jupiter, and the Stellar atmosphere, atmospheres of the Sun and other stars. Theory overview and mathematical concepts Fluid dynamics predicts the onset of instability and transition to turbulent flow within fluids of different density, densities moving at different speeds. If surface tension is ignored, two fluids in parallel motion with different velocities and densities yield an interface that is unstable to short-wavelength perturbations for all speeds. However, surface tension is able to stabilize the short w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs–Helmholtz Equation
The Gibbs–Helmholtz equation is a thermodynamic equation used to calculate changes in the Gibbs free energy of a system as a function of temperature. It was originally presented in an 1882 paper entitled " Die Thermodynamik chemischer Vorgänge" by Hermann von Helmholtz. It describes how the Gibbs free energy, which was presented originally by Josiah Willard Gibbs, varies with temperature. It was derived by Helmholtz first, and Gibbs derived it only 6 years later. The attribution to Gibbs goes back to Wilhelm Ostwald, who first translated Gibbs' monograph into German and promoted it in Europe. The equation is:Physical chemistry, P. W. Atkins, Oxford University Press, 1978, where ''H'' is the enthalpy, ''T'' the absolute temperature and ''G'' the Gibbs free energy of the system, all at constant pressure ''p''. The equation states that the change in the ''G/T'' ratio at constant pressure as a result of an infinitesimally small change in temperature is a factor ''H/T''2. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
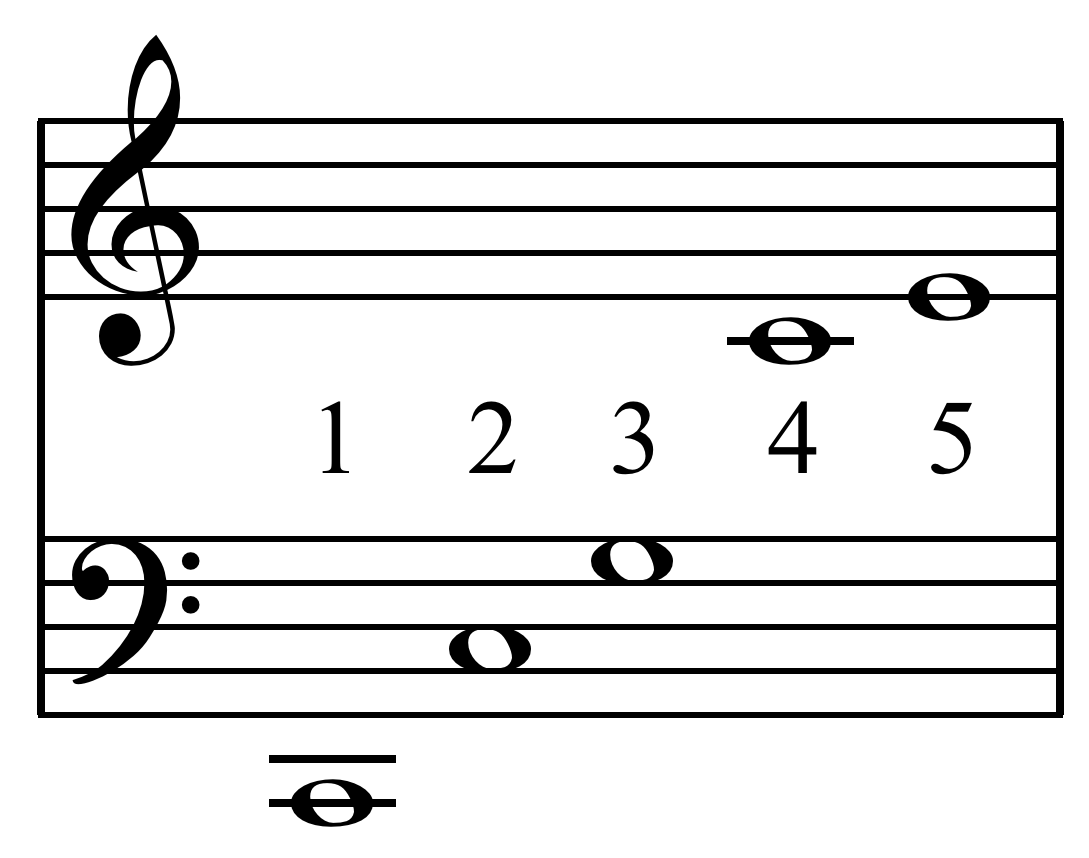
Helmholtz-Ellis Notation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a tuning system in which the space between notes' frequencies (called intervals) is a whole number ratio. Intervals spaced in this way are said to be pure, and are called just intervals. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth. In Western musical practice, bowed instruments such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses are tuned using pure fifths or fourths. In contrast, keyboard instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire for different keys to have identical intervals in Western music makes this impractical. Some instruments of fixed pitch, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz-Smoluchowski Equation
A streaming current and streaming potential are two interrelated electrokinetic phenomena studied in the areas of surface chemistry and electrochemistry. They are an electric current or potential which originates when an electrolyte is driven by a pressure gradient through a channel or porous plug with charged walls. The first observation of the streaming potential is generally attributed to the German physicist Georg Hermann Quincke in 1859. Applications Streaming currents in well-defined geometries are a sensitive method to characterize the zeta potential of surfaces, which is important in the fields of colloid and interface science. In geology, measurements of related spontaneous potential are used for evaluations of formations. Streaming potential has to be considered in design for flow of poorly conductive fluids (e.g., gasoline lines) because of the danger of buildup of high voltages. The streaming current monitor (SCM) is a fundamental tool for monitoring coagulation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz–Kohlrausch Effect
The Helmholtz–Kohlrausch effect (named after Hermann von Helmholtz and V. A. Kohlrausch) is a perceptual phenomenon wherein the intense saturation of spectral hue is perceived as part of the color's luminance. This brightness increase by saturation, which grows stronger as saturation increases, might better be called chromatic luminance, since "white" or achromatic luminance is the standard of comparison. It appears in both self-luminous and surface colors, although it is most pronounced in spectral (monochromatic) colors. Lightness Even when they have the same luminance, colored lights seem brighter to human observers than white light does. The way humans perceive the brightness of the lights is different for everyone. When the colors are more saturated, our eyes interpret it as the color's luminance and chroma. This makes us believe that the colors are actually brighter. An exception to this is when the human observer is red-green colorblind, they cannot distinguish the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz's Theorems
In fluid mechanics, Helmholtz's theorems, named after Hermann von Helmholtz, describe the three-dimensional motion of fluid in the vicinity of vortex lines. These theorems apply to inviscid flows and flows where the influence of viscous forces are small and can be ignored. Helmholtz's three theorems are as follows: ;Helmholtz's first theorem: :The strength of a vortex line is constant along its length. ;Helmholtz's second theorem: :A vortex line cannot end in a fluid; it must extend to the boundaries of the fluid or form a closed path. ;Helmholtz's third theorem: :A fluid element that is initially irrotational remains irrotational. Helmholtz's theorems apply to inviscid flows. In observations of vortices in real fluids the strength of the vortices always decays gradually due to the dissipative effect of viscous forces. Alternative expressions of the three theorems are as follows: # The strength of a vortex tube does not vary with time. # Fluid elements lying on a vortex line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Temperament
A schismatic temperament is a musical tuning system that results from tempering the schisma of 32805:32768 (1.9537 cents) to a unison. It is also called the schismic temperament, Helmholtz temperament, or quasi-Pythagorean temperament. Construction In Pythagorean tuning all notes are tuned as a number of perfect fifths (701.96 cents ). The major third above C, E, is considered four fifths above C. This causes the Pythagorean major third, E (407.82 cents ), to differ from the just major third, E (386.31 cents ): the Pythagorean third is sharper than the just third by 21.51 cents (a syntonic comma ). :C — G — D — A — E Ellis's "skhismic temperament". instead uses the note eight fifths ''below'' C, F (384.36 cents ), the Pythagorean diminished fourth or schismatic major third. Though spelled "incorrectly" for a major third, this note is only 1.95 cents (a schisma) flat of E, and thus more in tune than the Pythagorean major third. As Ellis puts it, "the Fifths should b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |