|
Emissions Trading
Emissions trading is a market-oriented approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). One prominent example is carbon emission trading for and other greenhouse gases which is a tool for climate change mitigation. Other schemes include sulfur dioxide and other pollutants. In an emissions trading scheme, a central authority or governmental body allocates or sells a limited number (a "cap") of permits that allow a discharge of a specific quantity of a specific pollutant over a set time period. Polluters are required to hold permits in amount equal to their emissions. Polluters that want to increase their emissions must buy permits from others willing to sell them. Emissions trading is a type of flexible environmental regulation that allows organizations and markets to decide how best to meet policy targets. This is in contrast to comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Price
Carbon pricing (or pricing) is a method for governments to mitigate climate change, in which a monetary cost is applied to greenhouse gas emissions. This is done to encourage polluters to reduce fossil fuel combustion, the main driver of climate change. A carbon price usually takes the form of a carbon tax, or an emissions trading scheme (ETS) that requires firms to purchase allowances to emit. The method is widely agreed to be an efficient policy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon pricing seeks to address the economic problem that emissions of and other greenhouse gases are a negative externality – a detrimental product that is not charged for by any market. 21.7% of global GHG emissions are covered by carbon pricing in 2021, a major increase due to the introduction of the Chinese national carbon trading scheme. Regions with carbon pricing include most European countries and Canada. On the other hand, top emitters like India, Russia, the Gulf states and many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants. Although environmental pollution can be caused by natural events, the word pollution generally implies that the contaminants Human impact on the environment, have a human source, such as manufacturing, Extractivism, extractive industries, poor waste management, transportation or Agricultural pollution, agriculture. Pollution is often classed as point source pollution, point source (coming from a highly concentrated specific site, such as a factory, Environmental effects of mining, mine, construction site), or nonpoint source pollution (coming from a widespread distributed sources, such as microplastics or agricultural runoff). Many sources of po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid rain has a pH level lower than this and ranges from 4–5 on average. The more acidic the acid rain is, the lower its pH is. Acid rain can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals, and infrastructure. Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the Properties of water, water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Acid rain has been shown to have adverse impacts on forests, Fresh water, freshwaters, soils, microbes, insects and aquatic life-forms. In ecosystems, persistent acid rain reduces tree bark durability, leaving flora more susceptible to environmental stressors such as drought, heat/cold and pest infestation. Acid rain is also capable of detriment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Rain Program
The Acid Rain Program is a market-based initiative taken by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in an effort to reduce overall atmospheric levels of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which cause acid rain. The program is an implementation of emissions trading that primarily targets coal-burning power plants, allowing them to buy and sell emission permits (called "allowances") according to individual needs and costs. In 2011, the trading program that existed since 1995 was supplemented by four separate trading programs under the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR). On August 21, 2012, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia issued its Opinion and Order in the appeal of the Cross State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) for two independent legal reasons. The stay on CSAPR was lifted in October 2014, allowing implementation of the law and its trading programs to begin. A 2021 study found that the "Acid Rain Program caused lasting improvements in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollutant
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be gases like ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles like soot and dust. It affects both outdoor air and indoor air. Natural sources of air pollution include wildfires, dust storms, and volcanic eruptions. Indoor air pollution is often caused by the use of biomass (e.g. wood) for cooking and heating. Outdoor air pollution comes from some industrial processes, the burning of fossil fuels for electricity and transport, waste management and agriculture. Many of the contributors of local air pollution, especially the burning of fossil fuels, also cause greenhouse gas emissions that cause global warming. Air pollution causes around 7 or 8 million deaths each year. It is a significant risk factor for a number of diseases, including stroke, heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma and lung cancer. Particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Deduction
A tax deduction or benefit is an amount deducted from taxable income, usually based on expenses such as those incurred to produce additional income. Tax deductions are a form of tax incentives, along with exemptions and tax credits. The difference between deductions, exemptions, and credits is that deductions and exemptions both reduce taxable income, while credits reduce tax. Above and below the line Above and below the line refers to items above or below adjusted gross income, which is item 37 on the tax year 2017 1040 tax form. Tax deductions above the line lessen adjusted gross income, while deductions below the line can only lessen taxable income if the aggregate of those deductions exceeds the standard deduction, which in tax year 2018 in the U.S., for example, was $12,000 for a single taxpayer and $24,000 for married couple. Limitations Often, deductions are subject to conditions, such as being allowed only for expenses incurred that produce current benefits. Capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven M
Stephen or Steven is an English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie (given name), Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Template:Stephen-surname, Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan (given name), Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (given name), Stefan (pronounced or in English) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur O'Sullivan (economist)
Arthur O'Sullivan (born 1953) is an American economist, Professor of Economics Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ... at Lewis & Clark College, and author of college textbooks on economics. Works ;Sole author * ''Urban Economics'', Irwin / McGraw-Hill Series in Urban Economics, 1990 (First Edition) – 2008 (Seventh Edition). ;With Steven M. Sheffrin * ''Economics: Principles in Action'', Pearson Prentice Hall, 2003. * ''Microeconomics: Principles and Tools'', Prentice-Hall, 2004. References 21st-century American economists Living people 1953 births Lewis & Clark College faculty {{US-economist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
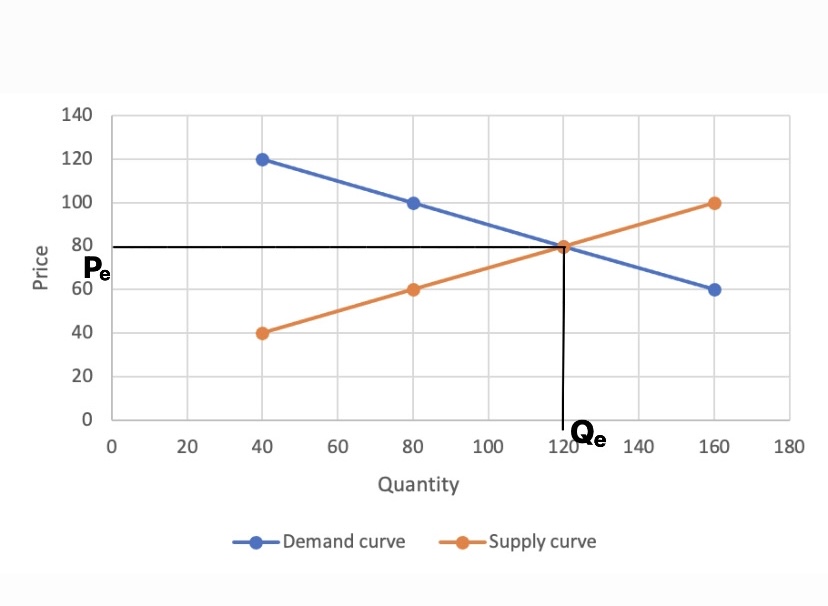
Law Of Demand
In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on ceteris paribus, all else being equal, as the price of a Goods, good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change. The law of demand is represented by a graph called the demand curve, with quantity demanded on the x-axis and price on the y-axis. Demand curves are downward sloping by defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Group
The environmental movement (sometimes referred to as the ecology movement) is a social movement that aims to protect the natural world from harmful environmental practices in order to create sustainable living. In its recognition of humanity as a participant in (not an enemy of) ecosystems, the movement is centered on ecology, health, as well as human rights. The environmental movement is an international movement, represented by a range of environmental organizations, from enterprises to grassroots and varies from country to country. Due to its large membership, varying and strong beliefs, and occasionally speculative nature, the environmental movement is not always united in its goals. At its broadest, the movement includes private citizens, professionals, religious devotees, politicians, scientists, nonprofit organizations, and individual advocates like former Wisconsin Senator Gaylord Nelson and Rachel Carson in the 20th century. Since the 1970s, public awareness, envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Derivative
In finance, a derivative is a contract between a buyer and a seller. The derivative can take various forms, depending on the transaction, but every derivative has the following four elements: # an item (the "underlier") that can or must be bought or sold, # a future act which must occur (such as a sale or purchase of the underlier), # a price at which the future transaction must take place, and # a future date by which the act (such as a purchase or sale) must take place. A derivative's value depends on the performance of the underlier, which can be a commodity (for example, corn or oil), a financial instrument (e.g. a stock or a bond), a price index, a currency, or an interest rate. Derivatives can be used to insure against price movements ( hedging), increase exposure to price movements for speculation, or get access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Most derivatives are price guarantees. But some are based on an event or performance of an act rather than a pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of .Le Treut, H., R. Somerville, U. Cubasch, Y. Ding, C. Mauritzen, A. Mokssit, T. Peterson and M. Prather, 2007:Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change. In:Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. olomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |