|
Duchy Of Luxembourg
The Duchy of Luxembourg (; ; ; ) was a Imperial state, state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, competing against the House of Habsburg for supremacy in Central Europe. They would be the heirs to the Přemyslid dynasty in the Kingdom of Bohemia, succeeding to the Kingdom of Hungary and contributing four Holy Roman Emperors until their own line of male heirs came to an end and the House of Habsburg received the territories that the two Houses had originally agreed upon in the Treaty of Brünn in 1364. In 1443, the duchy passed to Duke Philip the Good of Burgundy of the French House of Valois-Burgundy, House of Valois, and, in 1477, by marriage to Archduke Maximilian I of Austria of the House of Habsburg. The Seventeen Provinces of the former Burgundian Netherlands were formed into an integral union by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenceslaus I, Duke Of Luxembourg
Wenceslaus I (also ''Wenceslas'', ''Venceslas'', ''Wenzel'', or ''Václav'', often called Wenceslaus of Bohemia in chronicles) (25 February 1337 – 7 December 1383) was the first Duke of Luxembourg from 1354. He was the son of John of Bohemia, John the Blind, King of Bohemia, and Beatrice of Bourbon (1320-1383), Beatrice of Bourbon. Life The marriage contract of Wenceslaus' parents stipulated that if a son was born from the marriage, the County of Luxembourg (King John's paternal heritage), as well as lands belonging to it, would go to the child.''Luxemburg in the Middle Ages'', Brill Archive Beatrice of Bourbon, Queen of Bohemia, Beatrice of Bourbon, gave birth to her only child, Duke Wenceslaus I, on 25 February 1337, in Prague. In 1353 Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV King of Bohemia, Count of Luxembourg and elected Holy Roman King, entrusted the county, their father's inheritance, to his half-brother Wenceslaus. In 1352, Wenceslaus married Joanna, Duchess of Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or, in his stead, a viscount (''vicomte'').C. W. Onions (Ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology''. Oxford University Press, 1966. Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including , , , , , , , and Slavic '' zhupa''; terms equivalent to 'commune' or 'community' are now often instead used. When the Normans conquered England, they brought the term with them. Although there were at first no counts, ''vicomtes'' or counties in Anglo-Norman England, the earlier Anglo-Saxons did have earls, sheriffs and shires. The shires were the districts that became the historic counties of England, and given the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the predecessor state of the modern Czech Republic. The Kingdom of Bohemia was an Imperial State in the Holy Roman Empire. The List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia itself, also ruled other Lands of the Bohemian Crown, lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia, Silesia, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony, Brandenburg, and Bavaria. The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty in the 12th century by the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Přemyslid Dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemysl (, , ) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–1306), as well as in parts of Poland (including Silesia), Hungary and Austria. Origin and rise The dynasty's origin dates back to the 9th century, when the Přemyslids ruled a tiny territory around Prague, populated by a tribe of the Western Slavs. Their name comes from the mythical ancestor figure of Přemysl the Ploughman. Gradually they expanded, conquering much of the region of Bohemia, located in the Bohemian basin where it was not threatened by the expansion of the Frankish Empire. The first historically-documented Přemyslid duke was Bořivoj I (867). DNA testing on the remains of his son, Spytihněv I, reveal the family's Y-haplogroup to be R1b, second most common haplogroup in Czech republic. In the following century, the Přemyslids also ruled over Silesia and founded the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in this region also share some historical and cultural similarities. The region is variously defined, but it’s minimum definition could be considered of consisting of Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, the Czech Republic, eastern France, Germany, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland. But also the Baltic States, the Alsace in north-east France, and South Tyrol, northern Belluno , and Friuli-Venezia Giulia in north-east Italy are culturally usually considered to be part of Central Europe. From the early 16th century until the early 18th century, parts of Croatia and Hungary were ruled by the Ottoman Empire. During the 17th century, the empire also occupied southern parts of present-day Slovakia. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial State
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise significant rights and privileges and were "Imperial immediacy, immediate", meaning the only authority above them was that of the Holy Roman Emperor. They were thus able to rule their territories with a considerable degree of autonomy. The system of imperial states replaced the more regular division of Germany into stem duchy, stem duchies in the early medieval period. The old Carolingian Empire, Carolingian stem duchies were retained as the major divisions of Germany under the Salian dynasty, but they became increasingly obsolete during the early high medieval era, period under the Hohenstaufen, and they were finally abolished in 1180 by Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa in favour of more numerous territorial divisions. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourgish Language
Luxembourgish ( ; also ''Luxemburgish'', ''Luxembourgian'', ''Letzebu(e)rgesch''; ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 400,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide. The language is standardized and officially the national language of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. As such, Luxembourgish is different from the German language also used in the Grand Duchy. The German language exists in a national standard variety of Luxembourg, which is slightly different from the standard varieties in Germany, Austria or Switzerland. Another important language of Luxembourg is French, which had a certain influence on both the national language, Luxembourgish, and the Luxembourg national variety of German. Luxembourgish, German and French are the three official languages ''(Amtssprachen)'' of Luxembourg. As a standard form of the Moselle Franconian language, Luxembourgish has similarities with other High German dialects and the wider group of West Germanic lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg (city)
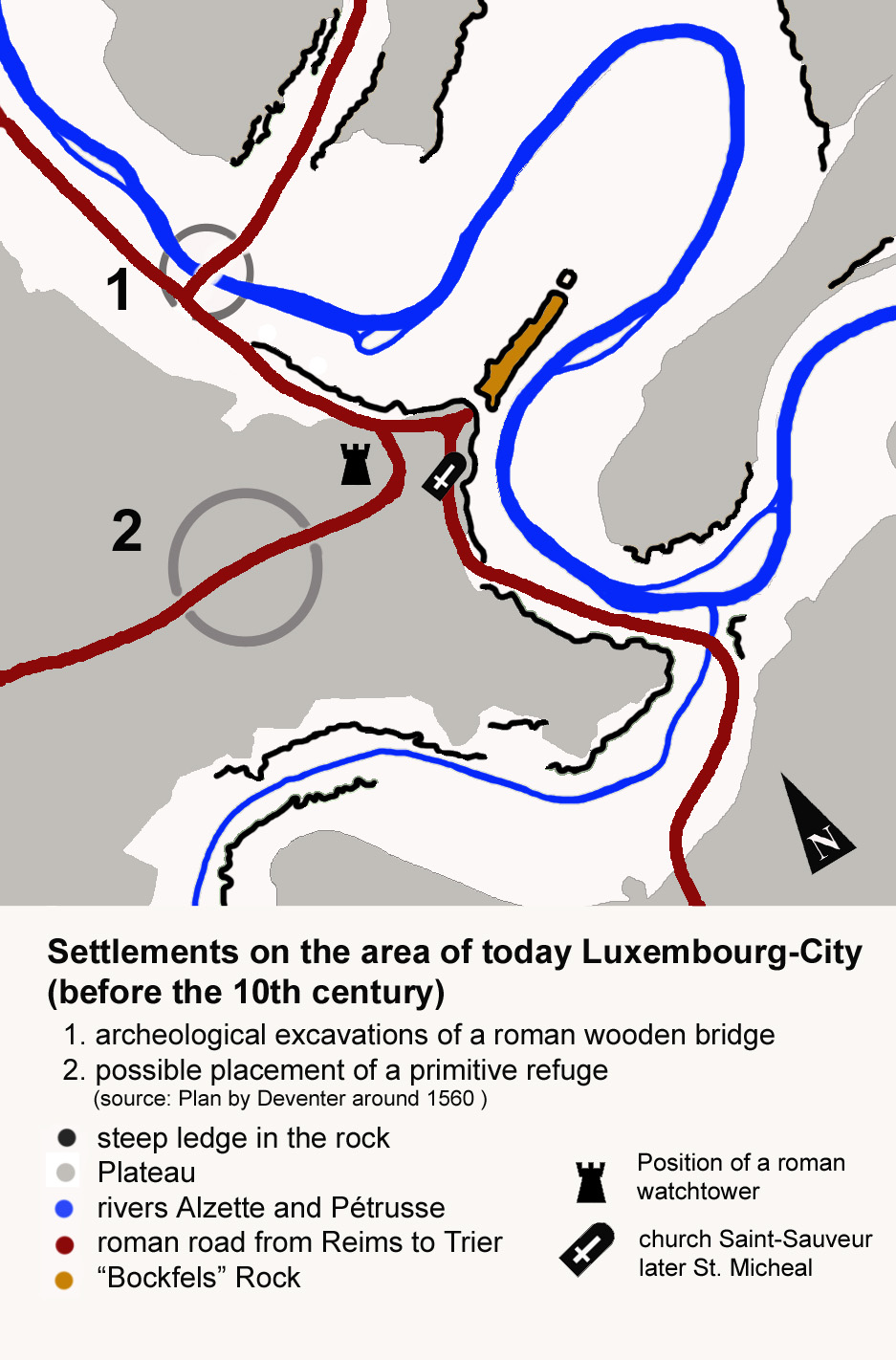
Luxembourg (; ; ), also known as Luxembourg City ( or ; ; or ), is the capital city of Luxembourg and the Communes of Luxembourg, country's most populous commune. Standing at the confluence of the Alzette and Pétrusse rivers in southern Luxembourg, the city lies at the heart of Western Europe, situated by road from Brussels and from Cologne. The city contains Luxembourg Castle, established by the Franks in the Early Middle Ages, around which a settlement developed. , Luxembourg City has a population of 136,208 inhabitants, which is more than three times the population of the country's second most populous commune (Esch-sur-Alzette). The population consists of 160 nationalities. Foreigners represent 70.4% of the city's population, whilst Luxembourgers represent 29.6% of the population; the number of foreign-born residents in the city rises steadily each year. In 2024, Luxembourg was ranked by the International Monetary Fund, IMF as having the highest GDP per capita in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (), was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First French Empire, First Empire on 18 May 1804 under Napoleon, Napoléon Bonaparte, although the form of government changed several times. On 21 September 1792, the deputies of the Convention, gathered for the first time, unanimously decide the Proclamation of the abolition of the monarchy, abolition of the constitutional monarchy in France. Although the Republic was never officially proclaimed on 22 September 1792, the decision was made to date the acts from the year I of the Republic. On 25 September 1792, the Republic was declared "one and indivisible". From 1792 to 1802, France was at war with the rest of Europe. It also experienced internal conflicts, including the War in the Vendée, wars in Vendée. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |