Central Europe is a geographical region of
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
between
Eastern,
Southern,
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and
Northern Europe.
Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in this region also share some historical and cultural similarities.
The region is variously defined, but it’s minimum definition could be considered of consisting of
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
,
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
,
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
, eastern
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
,
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
,
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
,
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
,
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
and
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
.
But also the
Baltic States
The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern co ...
, the
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
in north-east France, and
South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
, northern
Belluno , and
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
in north-east Italy are culturally usually considered to be part of Central Europe.
From the early 16th century until the early 18th century, parts of Croatia and Hungary were ruled by the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. During the 17th century, the empire also occupied southern parts of present-day Slovakia. During the Early Modern period, the territories of Poland and Lithuania were part of the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
. Meanwhile, the
Archduchy of Austria
The Archduchy of Austria (; ) was a major Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periph ...
, the
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
(Czech Republic), the
Duchy of Carniola
The Duchy of Carniola (, , ) was an imperial estate of the Holy Roman Empire, established under House of Habsburg, Habsburg rule on the territory of the former East Frankish March of Carniola in 1364. A hereditary land of the Habsburg monarc ...
(part of present-day Slovenia), the various
German Principalities and the
Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy, also known as Switzerland or the Swiss Confederacy, was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ), initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerlan ...
were within the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. By the end of the 18th century, the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
, a prominent power within the Holy Roman Empire, came to reign over the territories of Austria,
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia and Slovenia, alongside parts of
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Germany,
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Poland and Switzerland. Between the early 18th and the early 20th centuries, Central Europe had a substantial
Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
population.
Since the
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, the countries that make up Central Europe have historically been and in some cases continue to be divided into either Eastern or Western Europe.
After World War II, Europe was divided by the
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. On the east side of the Iron Curtain were countries connected to the So ...
into two parts, the
capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
Western Bloc
The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, the Freedom Bloc, the Free Bloc, and the American Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of countries that were officially allied with the United States during the Cold War (1947–1991). While ...
and the
socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
, although Austria, Switzerland and
Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
(encompassing the territories of present-day Croatia, Slovenia and various other
Balkan
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
nations) declared neutrality. The
Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (, ) was a guarded concrete Separation barrier, barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the East Germany, German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany). Construction of the B ...
was one of the most visible symbols of this division. Respectively, countries in Central Europe have historical, cultural and
geopolitical
Geopolitics () is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. Geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of states: ''de facto'' independen ...
ties with these wider regions of Europe.
Central Europe began a "strategic awakening" in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, with initiatives such as the
Central European Defence Cooperation
The Central European Defence Cooperation (CEDC) is a military collaboration consisting of the Central European states of Austria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia and Slovenia. Poland has an observer status in this cooperative frame ...
, the
Central European Initiative,
Centrope, and the
Visegrád Four Group. That awakening was accelerated by writers and other intellectuals, who recognized the societal paralysis of decaying dictatorships and felt compelled to speak up against
Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
oppression.
Historical perspective
Middle Ages and early modern period
In the early Middle Ages, Central Europe had a diverse landscape, with various ethnic groups inhabiting the region.
Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
, among them the
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
,
Alemans and
Bavarians
Bavarians are a Germans, German ethnographic group native to Bavaria, a state in Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as Bavarian language, Bavarian, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavaria"), roughly the territory of the historic Electo ...
, were predominantly situated in the west, and
Slavic tribes were predominantly in the east. However, the region encompassed a wide spectrum of additional tribes and communities.
From the late 6th century to the early 9th century, the area roughly corresponding to the
Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
was part of the Avar Khaganate, the realm of the
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
. While the Avars dominated the east of what is now Austria, its north and south were under Germanic and Slavic influence, respectively. Meanwhile, the territories now comprising Germany and Switzerland were under the influence of the
Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
, and later the
Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Franks, Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Pippinids, Arnulfi ...
. Various Slavic tribes that inhabited eastern Central Europe established settlements during this period, primarily in present-day Croatia, Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia.
The territory of Lithuania was inhabited by
Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
tribes. Amongst them were the
Samogitians,
Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
and
Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.''
The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. ...
.
The
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
was founded at the turn of the 9th century, following the coronation of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
by
Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (; died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death on 12 June 816. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlem ...
. At its inception, it incorporated present-day Germany and nearby regions, including parts of what is now Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovenia and Switzerland. Three decades later,
Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
, centred on present-day Czech Republic and Slovakia, became one of the first West Slavic states to be founded in Central Europe. In the late 9th Century, the
Hungarian tribes, originating on the
Asian Steppe, settled in the Carpathian Basin and established the
Principality of Hungary
The Grand Principality of Hungary or Duchy of Hungary (: "Hungarian Grand Principality", ) was the earliest documented Hungarian state in the Carpathian Basin, established in 895 or 896, following the 9th century Magyar invasion of the Carpath ...
.
The earliest recorded concept of Europe as a cultural sphere, instead of simply a geographic term, was formed by
Alcuin of York in the late 8th century during the
Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. Charlemagne's reign led to an intellectual revival beginning in the 8th century and continuing throughout the 9th ...
and was limited to the territories that practised
Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two subdivisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Protestantism, Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the O ...
at the time. "European" as a cultural term did not include much of the territories in which the Orthodox Church represented the dominant religion until the 19th century.
Following the Christianization of various Central European countries, elements of cultural unity emerged within the region, specifically
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. Eastern Europe remained
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, and was dominated by
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
cultural influence. After the
East–West Schism
The East–West Schism, also known as the Great Schism or the Schism of 1054, is the break of communion (Christian), communion between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. A series of Eastern Orthodox – Roman Catholic eccle ...
in 1054, significant parts of Eastern Europe developed cultural unity and resistance to Catholic Western and Central Europe within the framework of the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
,
Church Slavonic
Church Slavonic is the conservative Slavic liturgical language used by the Eastern Orthodox Church in Belarus, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Poland, Russia, Ukraine, Serbia, the Czech Republic and Slovakia, Slovenia and Croatia. The ...
and the
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Easte ...
.
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
and its tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
in 814
East Francia 843.svg, East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
in 843
Great moravia svatopluk.png, Possible furthest extent of Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
under Svatopluk I (870–894)
Duchy of Poland 1000.svg, Duchy of Poland
Civitas Schinesghe (; ), also known as the Duchy of Poland or the Principality of Poland, is the historiographical name given to a polity in Central Europe, which existed during the medieval period and was the predecessor state of the Kingdom of ...
under the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
in 1000
Duchy of Bohemia 1000.svg, Duchy of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia, also later referred to in English as the Czech Duchy, (Old Czech: ) was a monarchy and a Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, principality of the Holy Roman Empire in Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages, Early and High M ...
(Czech Duchy) in 1000
Kingdom of Germany 1004.svg, Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
in 1004
Kingdom of Hungary 1190.svg, Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
in 1190
Croatia 1260.png, Kingdom of Croatia in 1260
Holy Roman Empire (c. 1600).svg, Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
in 1600
Map of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1619–1621).png, Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and its fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
s in 1619
According to the historian
Jenő Szűcs, Central Europe at the end of the 1st millennium became influenced by Western European developments. Szűcs argued that between the 11th and 15th centuries, Christianization influenced the cultures within Central Europe, and well-defined social features were also implemented in the region based on Western characteristics. The keyword of Western social development after the turn of the millennium was the spread of
Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages gr ...
in some cities and towns of Western Europe. They began to spread in the mid-13th century in Central European countries and brought about self-governments of towns and counties.
In 1335, the
Kings of Poland,
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
and
Hungary and Croatia met in the castle of
Visegrád and agreed to cooperate closely in the field of politics and commerce. That has inspired the post-
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
.
In 1386,
Jogaila, the
Grand Duke of Lithuania
This is a list of Lithuanian monarchs who ruled Lithuania from its inception until the fall of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1795. The Lithuanian monarch bore the title of Grand duke, Grand Duke, with the exception of Mindaugas, who was crown ...
, converted to Christianity (specifically Catholicism) and subsequently became King of Poland through marriage to
Queen Jadwiga of Poland. That initiated the
Christianization of Lithuania
The Christianization of Lithuania () occurred in 1387, initiated by the Lithuanian royals Jogaila, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his cousin Vytautas the Great. It signified the official adoption of Catholic Christianity by Li ...
and resulted in the
Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; ; ) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made at Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in regard to his prospectiv ...
, signifying a personal union between the
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ...
and the Kingdom of Poland. The union commenced an enduring political alliance between the two entities and laid the foundations for the later establishment of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569.
Between the 15th and the early 16th centuries, the Kingdom of Croatia, which was then in
personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with the Kingdom of Hungary, served as a significant maritime gateway of Central Europe, with its ports facilitating key trade routes between Central Europe and the Mediterranean.
The
Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
emerged as a prominent hub for cultural exchange during this time.
Following the Ottoman and Habsburg wars of the 16th and 17th centuries, the Kingdom of Croatia,
under Habsburg rule, began to regain its position as a significant trade route, restoring ports and revitalising commercial activity.
Before World War I

Before 1870, the industrialization that had started to develop in Northwestern and Central Europe and the United States did not extend in any significant way to the rest of the world. Even in
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, industrialization lagged far behind.
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, for example, remained largely rural and agricultural, and its autocratic rulers kept the peasants in serfdom.
The concept of Central Europe was already known at the beginning of the 19th century,
but it developed further and became an object of intensive interest towards the 20th century. However, the first concept mixed science, politics, and economy and was strictly connected with the aspirations of German states to dominate a part of European continent called ''Mitteleuropa''. At the
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt National Assembly () was the first freely elected parliament for all German Confederation, German states, including the German-populated areas of the Austrian Empire, elected on 1 May 1848 (see German federal election, 1848).
The ...
, which was established in the wake of the
March Revolution of 1848, there were multiple competing ideas for the integration of German-speaking areas, including the ''mitteleuropäische Lösung'' (Central European Solution) propagated by Austria, which sought to merge the smaller German-speaking states with the multi-ethnic Habsburg monarchy, but was opposed by Prussia and others. An imperialistic idea of ''Mitteleuropa'' also became popular in the
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, which was established in 1871 and experienced intensive economic growth. The term was used when the
Union of German Railway Administrations established the ''Mitteleuropäische Eisenbahn-Zeit'' (Central European Railway Time)
time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
, which was applied by the railways from 1 June 1891 and was later widely adopted in civilian life; the time zone's name has been shortened to the present-day
Central European Time
Central European Time (CET) is a standard time of Central, and parts of Western Europe, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
The UTC offset, time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00.
It is used in most parts of Eur ...
.
The German term denoting Central Europe was so fashionable that other languages started referring to it when indicating territories from
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
to
Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
or even the
Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
and from the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
to the
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
. An example of this vision of Central Europe may be seen in
Joseph Partsch's book of 1903.
On 21 January 1904, ''Mitteleuropäischer Wirtschaftsverein'' (Central European Economic Association) was established in
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
with economic integration of Germany and Austria (with eventual extension to Switzerland,
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
) as its main aim. Another time, the term Central Europe became connected to the German plans of political, economic, and cultural domination. The "bible" of the concept was
Friedrich Naumann
Friedrich Naumann (25 March 1860 – 24 August 1919) was a German Liberalism in Germany, liberal politician and Protestant parish pastor. In 1896, he founded the National-Social Association that sought to combine liberalism, nationalism and ...
's book ''Mitteleuropa'' in which he called for an economic federation to be established after World War I. Naumann's proposed a federation with Germany and the Habsburg monarchy as its centre that would eventually unite all external European nations through economic prosperity. The concept failed after the German defeat in
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The revival of the idea may be observed during the
Hitler era.
Interwar period
The
interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
(1918–1938) brought a new geopolitical system, as well as economic and political problems, and the concept of Central Europe took on a different character. The centre of interest was moved to its eastern part, particularly to the countries that had rappeared or reappared on the map of Europe. Central Europe ceased to be the area of German aspiration to lead or dominate and became a territory of various integration movements aiming at resolving political, economic, and national problems of "new" states, being a way to face German and Soviet pressures. However, the conflict of interests was too major, and neither the
Little Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia from 1929 on) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revisionism and the prospect of ...
nor
Intermarium (''Międzymorze'') ideas succeeded. The Hungarian historian
Magda Ádám wrote in her study ''Versailles System and Central Europe'' (2006): "Today we know that the bane of Central Europe was the
Little Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (Yugoslavia from 1929 on) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revisionism and the prospect of ...
, military alliance of
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
, Romania and
Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" () has been its colloq ...
(later Yugoslavia), created in 1921 not for Central Europe's cooperation nor to fight German expansion, but in a wrong perceived notion that a completely powerless Hungary must be kept down". The
events preceding World War II in Europe, including the so-called
Western betrayal such as the
Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement was reached in Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, the United Kingdom, the French Third Republic, French Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy. The agreement provided for the Occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–194 ...
, were very much enabled by the rising nationalism and ethnocentrism that typified that period.
The interwar period brought new elements to the concept of Central Europe. Before World War I, it embraced mainly German-speaking states, and non-German speaking territories were an area of intended German penetration and domination, with German leadership being the 'natural' result of economic dominance.
Post-war, the Eastern part of Central Europe was placed at the centre of the concept. At the time, the scientists took an interest in the idea: the International Historical Congress in
Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
in 1923 was committed to Central Europe, and the 1933, Congress continued the discussions.
According to
Emmanuel de Martonne, in 1927, Central Europe encompassed Austria, Czechoslovakia, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Switzerland, northern Italy and northern Yugoslavia. The author uses both Human and Physical Geographical features to define Central Europe but failed to take into account the legal development or the social, cultural, economic, and infrastructural developments in those countries.
The avant-garde movements of Central Europe contributed to the evolution of modernism and reached their its peak throughout the continent during the 1920s. The ''Sourcebook of Central European avantgards'' (
Los Angeles County Museum of Art
The Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) is an art museum located on Wilshire Boulevard in the Miracle Mile vicinity of Los Angeles. LACMA is on Museum Row, adjacent to the La Brea Tar Pits (George C. Page Museum).
LACMA was founded in 1961 ...
) contains primary documents of the avant-gardes in the territories of Austria, Germany, Poland (including western parts of present-day
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, and southern parts of Lithuania), Czechoslovakia (including the Czech Republic and Slovakia), Hungary, Romania and Yugoslavia (including present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia,
Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg
, coa_size = 80
, national_motto =
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map = Europe-Mont ...
,
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
and Slovenia) from 1910 to 1930.
Mitteleuropa
With the
dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
The dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire occurred on 6 August 1806, when the last Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, abdicated his title and released all Imperial estate, Imperial s ...
around 1800, there was a consolidation of power among the
Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
and the
Hohenzollerns as the two major states in the area. They had much in common and occasionally cooperated in various channels, but more often competed. One approach in the various attempts at cooperation, was the conception of a set of supposed common features and interests, and this idea led to the first discussions of a ''Mitteleuropa'' in the mid-nineteenth century, as espoused by
Friedrich List
Daniel Friedrich List (6 August 1789 – 30 November 1846) was a German entrepreneur, diplomat, economist and political theory, political theorist who developed the Economic nationalism, nationalist theory of political economy in both Europe and t ...
and
Karl Ludwig Bruck. These were mostly based on economic issues.
''
Mitteleuropa
(), meaning Middle Europe, is one of the German terms for Central Europe. The term has acquired diverse cultural, political and historical connotations. University of Warsaw, Johnson, Lonnie (1996) ''Central Europe: Enemies, Neighbors, Friends' ...
'' may refer to a historical concept or a contemporary German definition of Central Europe. As a historical concept, the German term ''Mitteleuropa'' (or alternatively its literal translation into English, ''Middle Europe'') is an ambiguous German concept. According to
Fritz Fischer ''Mitteleuropa'' was a scheme in the era of the
Reich of 1871–1918 by which the old imperial elites had allegedly sought to build a system of German economic, military and political domination from the northern seas to the Near East and from the Low Countries through the steppes of Russia to the Caucasus. Later on, Professor Fritz Epstein argued the threat of a Slavic "Drang nach Westen" (Western expansion) had been a major factor in the emergence of a ''Mitteleuropa'' ideology before the Reich of 1871 ever came into being.
In Germany, the word's connotation was also sometimes linked to the pre-war German provinces east of the
Oder-Neisse line.
The term "Mitteleuropa" conjures up negative historical associations among some people although the Germans have not played an exclusively negative role in the region. Most Central European Jews embraced the enlightened German humanistic culture of the 19th century. Jews at the turn of the 20th century became representatives of what many consider to be Central European culture at its best, but the Nazi conceptualisation of "Mitteleuropa" sought to destroy that culture. The term "Mitteleuropa" is widely used in German education and media without a negative meaning, especially since the end of communism. Many people from the
new states of Germany
The new states of Germany () are the five re-established states of the former German Democratic Republic (GDR) that unified with the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) with its 10 "old states" upon German reunification on 3 October 1990.
Th ...
do not identify themselves as being part of Western Europe and therefore prefer the term "Mitteleuropa".
Central Europe during World War II
During World War II, Central Europe was largely occupied by Nazi Germany. Many areas were a battle area and were devastated. The mass murder of the Jews depopulated many of their centuries-old settlement areas or settled other people there and their culture was wiped out. Both
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
and
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
diametrically opposed the centuries-old Habsburg principles of "live and let live" with regard to ethnic groups, peoples, minorities, religions, cultures and languages and tried to assert their own ideologies and power interests in Central Europe. There were various Allied plans for state order in Central Europe for post-war. While Stalin tried to get as many states under his control as possible,
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
preferred a Central European Danube Confederation to counter those countries against Germany and Russia. There were also plans to add Bavaria and Württemberg to an enlarged Austria. There were also various resistance movements around
Otto von Habsburg that pursued that goal. The group around the Austrian priest
Heinrich Maier also planned in that direction, which also successfully helped the Allies to wage war by, among other things, forwarding production sites and plans for
V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
s,
Tiger tanks and aircraft to the United States. Otto von Habsburg tried to relieve Austria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary and northern Yugoslavia (particularly the territories of present-day Croatia and Slovenia) from German and Soviet influence and control. There were various considerations to prevent German and Soviet power in Europe after the war. Churchill's idea of reaching the area around Vienna before the Russians via an operation from the Adriatic had not been approved by the Western Allied chiefs of staff. As a result of the military situation at the end of the war, Stalin's plans prevailed and much of Central Europe came under Soviet control.
Central Europe behind the Iron Curtain

Following
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, parts of Central Europe became part of the
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
. The boundary between the two blocks was called the
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. On the east side of the Iron Curtain were countries connected to the So ...
. Austria, Switzerland and Yugoslavia remained neutral.
The post-World War II period brought blocking of research on Central Europe in the
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries, as its every result proved the dissimilarity of Central Europe, which was inconsistent with the
Stalinist doctrine. On the other hand, the topic became popular in Western Europe and the United States, much of the research being carried out by immigrants from Central Europe. Following the
Fall of Communism, publicists and historians in Central Europe, especially the anti-communist opposition, returned to their research.
According to Karl A. Sinnhuber (''Central Europe: Mitteleuropa: Europe Centrale: An Analysis of a Geographical Term'')
most Central European states were unable to preserve their political independence and became
Soviet satellites. Besides Austria, Switzerland and Yugoslavia, only the marginal European states of
Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
,
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
,
Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
and Sweden preserved their political sovereignty to a certain degree, being left out of any military alliances in Europe.
The opening of the
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. On the east side of the Iron Curtain were countries connected to the So ...
between Austria and Hungary at the
Pan-European Picnic on 19 August 1989 then set in motion a peaceful chain reaction, at the end of which there was no longer an
East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
and the Eastern Bloc had disintegrated. It was the largest escape movement from East Germany since the Berlin Wall was built in 1961. After the picnic, which was based on an idea by
Otto von Habsburg to test the reaction of the USSR and Mikhail Gorbachev to an opening of the border, tens of thousands of media-informed East Germans set off for Hungary. The leadership of the GDR in East Berlin did not dare to completely block the borders of their own country and the USSR did not respond at all.
This broke the bracket of the Eastern Bloc and Central Europe subsequently became free from communism.
Roles
According to American professor
Ronald Tiersky, the 1991 summit held in
Visegrád attended by the
Czechoslovak, Hungarian and Polish presidents was hailed at the time as a major breakthrough in Central European cooperation, but the
Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
became a vehicle for coordinating Central Europe's road to the European Union, while development of closer ties within the region languished.
American professor
Peter J. Katzenstein
Peter Joachim Katzenstein Fellow of the British Academy, FBA (born February 17, 1945) is a German-American political scientist. He is the Walter S. Carpenter, Jr. Professor of International Studies at Cornell University. Katzenstein has made inf ...
described Central Europe as a way station in a Europeanization process that marks the transformation process of the
Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
countries in different, though comparable ways. According to him, in Germany's contemporary public discourse "Central European identity" refers to the civilizational divide between Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. He argued that there is no precise way to define Central Europe and that the region may even include Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia and Serbia.
Definitions
The issue of how to name and define the Central European area is subject to debates. Very often, the definition depends on the nationality and historical perspective of its author. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. It was understood as a contact zone between the Southern and Northern areas, and later the Eastern and Western areas of Europe. Thinkers portrayed "Central Europe" either as a separate region, or a buffer zone between these regions.
In the early nineteenth century, the terms "Middle" or "Central" Europe (known as "Mitteleuropa" in German and "Europe centrale" in French) were introduced in geographical scholarship in both German and French languages. At first, these terms were linked to the regions spanning from the Pyrenees to the Danube, which, according to German authors, could be united under German authority. However, after the Franco-Prussian war of 1870, the French began to exclude France from this area, and later the Germans also adopted this perspective by the end of World War I.
The concept of "Central" or "Middle Europe", understood as a region with German influence, lost a significant part of its popularity after WWI and was completely dismissed after WWII. Two defeats of Germany in the world wars, combined with the division of Germany, an almost complete disappearance of German-speaking communities in these countries, and the Communist-led isolation of Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Lithuania, Poland and Yugoslavia from the Western world, turned the concept of "Central/Middle Europe" into an anachronism. On the other side, the non-German areas of Central Europe were almost universally regarded as "Eastern European" primarily associated with the Soviet sphere of influence in the late 1940s–1980s.
For the most part, this geographical framework lost its attraction after the end of the Cold War. A number of Post-Communist countries rather re-branded themselves in the 1990s as "Central European.", while avoiding the stained wording of "Middle Europe," which they associated with German influence in the region. This reinvented concept of "Central Europe" excluded Germany, Austria and Switzerland, reducing its coverage chiefly to Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Lithuania and Yugoslavia.
Academic
The main proposed regional definitions, gathered by Polish historian
Jerzy Kłoczowski and others, include:
* West-Central and
East-Central Europe – this conception, presented in 1950, distinguishes two regions in Central Europe: the German West-Centre and the East-Centre covered by a variety of nations ''from
Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
to
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
'', placed between the great empires of
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
, Germany, Italy and the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
.
* Central Europe as a region comprising countries in
mainland Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by so ...
speaking
West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germ ...
(Austria,
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Germany, the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
and Switzerland) and
West Slavic languages (the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Poland).
* Central Europe as the area of the cultural heritage of the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
– Ukrainian, Belarusian and Lithuanian historians, in cooperation (since 1990) with Polish historians, insist on the importance of this concept.

* Central Europe as the area of the former Habsburg monarchy – a concept which is popular in large parts of
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
.
* A concept underlining the links connecting
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
,
Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
with Russia and treating the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
together with the whole
Slavic Orthodox population as one entity – this position is taken by Russian historiographers.
* A concept putting the accent on links with the West, especially from the 19th century and the grand period of liberation and formation of Nation-states, an idea that is represented by the
South-Eastern states, which prefer the enlarged concept of the "East Centre" expressing their links with
Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
.
Former University of Vienna professor Lonnie R. Johnson points out criteria to distinguish Central Europe from Western, Northern, Eastern and Southern Europe:
* One criterion for defining Central Europe is the frontiers of medieval empires and kingdoms that largely correspond to the religious frontiers between
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
Western and Central Europe and
Orthodox Eastern Europe. Following that criterion, the pagans of Central Europe were converted to Catholicism, but in Eastern and Southeastern Europe, they were brought into the fold of the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
.
He also thinks that Central Europe is a dynamic historical concept, not a static spatial one. For example, a fair share of
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
and
Right-bank Ukraine
The Right-bank Ukraine is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts o ...
are in Eastern Europe today, but years ago, they were in the
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
. Johnson's study on Central Europe received acclaim and positive reviews in the scientific community. However, according to the Romanian researcher
Maria Bucur, the very ambitious project suffers from the weaknesses imposed by its scope (almost 1600 years of history).
Encyclopedias, gazetteers, dictionaries
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
defines Central Europe as: Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Liechtenstein, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland. ''
The Columbia Encyclopedia
The ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' is a one-volume encyclopedia produced by Columbia University Press and, in the last edition, sold by the Gale Group. First published in 1935, and continuing its relationship with Columbia University
Columb ...
'' includes: Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Slovakia and Switzerland. While it does not have a single article defining Central Europe,
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
includes the following countries in Central Europe in one or more of its articles: Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Lithuania,
Poland, Romania,
Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland.
The
French ''Encyclopédie Larousse'' defines Central Europe as a region comprising Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland.
The German Encyclopaedia ''Meyers Grosses Taschenlexikon'' (''Meyers Big Pocket Encyclopedia''), 1999, defines Central Europe as the central part of Europe with no precise borders to the East and West. The term is mostly used to denominate the territory between the
Schelde to
Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
and from the
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
to the
Moravian Gate.
The German (Standing Committee on Geographical Names), which develops and recommends rules for the uniform use of geographical names, proposes two sets of boundaries. The first follows international borders of current countries. The second subdivides and includes some countries based on cultural criteria. In comparison to some other definitions, it is broader, including Luxembourg, Estonia, Latvia, and in the second sense, the
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
and parts of Belarus, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Italy, and France.
According to ''Meyers Enzyklopädisches Lexikon'', Central Europe is a part of Europe composed of Austria,
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Germany, Hungary,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
,
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Poland,
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Switzerland, and northern marginal regions of Italy and Yugoslavia (northern states –
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
and
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
), as well as northeastern France.
Geographical

There is no general agreement either on what geographic area constitutes Central Europe, nor on how to further subdivide it geographically.
At times, the term "Central Europe" denotes a geographic definition as the
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
region in the heart of the continent, including the language and culture areas which are today included in the states of Austria,
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
,
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary,
Moldova
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe, with an area of and population of 2.42 million. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. ...
, Poland, Romania,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Slovakia, Slovenia,
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
and usually also Germany.
Governmental and standards organisations
The terminology EU11 countries refer the Central,
Eastern and
Baltic European member states which accessed in 2004 and after: in 2004 Czech Republic, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Poland, Slovenia, and Slovakia; in 2007 Bulgaria, Romania; and in 2013 Croatia.
The EU-funded
Interreg
Interreg is a series of programmes to stimulate cooperation between regions in and out of the European Union (EU), funded by the European Regional Development Fund. The first Interreg started in 1989. Interreg IV covered the period 2007–2013. I ...
region "Central Europe" includes the following countries and regions:
* Austria
* Croatia
* Czechia
* Germany: Berlin, Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Saxony, Thuringia, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
* Hungary
* Italy: Lombardy, Trentino - Alto Adige, Aosta Valley, Veneto, Emiglia Romagna, Liguria, Friuli - Venezia Giulia
* Poland
* Slovakia
* Slovenia

The
Central European Free Trade Agreement
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA in 2006 expanded to Albania, Bo ...
includes the following countries:
*
Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
* Bosnia and Herzegovina
*
Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
* Moldova
* Montenegro
*
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
* Serbia
Map gallery
File:Central Europe Katzenstein.png, Central Europe according to Peter J. Katzenstein
Peter Joachim Katzenstein Fellow of the British Academy, FBA (born February 17, 1945) is a German-American political scientist. He is the Walter S. Carpenter, Jr. Professor of International Studies at Cornell University. Katzenstein has made inf ...
(1997):
File:Visegrad group countries.png, According to ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. M ...
'' and Ronald Tiersky, a strict definition of Central Europe means the Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
.
File:Central Europe (Meyers Grosses Taschenlexikon).PNG, The Central European Countries according to Meyers Grosses Taschenlexikon (1999):
File:Central Europe (Brockhaus).PNG, Middle Europe (Brockhaus Enzyklopädie, 1998)
File:Central-Europe-SwanseaUniv.png, Central Europe according to Swansea University professors Robert Bideleux and Ian Jeffries (1998)
File:Central Europe (Mayers Enzyklopaedisches Lexikon).PNG, Central Europe according to Meyers Enzyklopaedisches Lexikon (1980)
States
The choice of states that make up ''Central Europe'' is an ongoing source of controversy. Although views on which countries belong to Central Europe are vastly varied, according to many sources (see section
Definitions
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definit ...
) the region includes some or all of the states listed in the sections below:
*
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
*
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
*
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
*
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
*
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
*
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
*
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
*
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
*
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
*
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
*
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
Depending on the context, Central European countries are sometimes not seen as a specific group, but sorted as either Eastern or Western European countries.
In this case Austria, Germany, Liechtenstein and Switzerland are often placed in Western Europe, while Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Lithuania, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia are placed in Eastern Europe.
Croatia is alternatively placed in Southeastern Europe.
Additionally, Hungary
and Slovenia
are sometimes included in the region.
Lithuania is alternatively placed in Northeastern Europe.

Other countries and regions
Some sources also add regions of neighbouring countries for historical reasons, or based on geographical and/or cultural reasons:
*
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
(as a former part of the Habsburg monarchy and Yugoslavia, alternatively placed in Southern or Southeast Europe)
*
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
(considered to have been part of extended definitions of 'Mitteleuropa', alternatively placed in Eastern, Northeastern or Northern Europe)
*Italy (
South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
,
Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
,
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and
Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
,
Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
, Lombardy, and
Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
or all of
Northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmo ...
)
*
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
(considered to have been part of extended definitions of 'Mitteleuropa')
*
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(
Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, along with
Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
,
Crișana
Crișana (, , ) is a geographical and historical region of Romania named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Romania, the term is sometimes extended to include areas ...
,
Maramureș
( ; ; ; ) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, along parts of the upper Tisza River drainage basin; it covers the Maramureș Depression and the ...
,
Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
[Klaus Peter Berger]
The Creeping Codification of the New Lex Mercatoria
Kluwer Law International, 2010, p. 132 and
Muntenia
Muntenia (, also known in English as Greater Wallachia) is a historical region of Romania, part of Wallachia (also, sometimes considered Wallachia proper, as ''Muntenia'', ''Țara Românească'', and the rarely used ''Valahia'' are synonyms in Ro ...
along with
Oltenia
Oltenia (), also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions – with the alternative Latin names , , and between 1718 and 1739 – is a historical province and geographical region of Romania in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Da ...
)
*Russia (
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
)
*
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
(primarily
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
and
Northern Belgrade, alternatively placed in Southeast Europe)
*
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
(
Transcarpathia,
and Northern
Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided betwe ...
)
Geography

Geography defines Central Europe's natural borders with the neighbouring regions to the north across the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, namely Northern Europe (or
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
), and to the south across the
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, the
Apennine peninsula (or Italy), and the
Balkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
across the
Soča
Soča (, in Slovene) or Isonzo (, in Italian; other names: ; ; or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies in the Trenta Valley in the Julian Alps ...
–
Krka–
Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
–Danube line. The borders to Western Europe and Eastern Europe are geographically less defined, and for this reason the
cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and historical boundaries migrate more easily west–east than south–north.
Southwards, the
Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
is bounded by the rivers
Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
and
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
– and their respective floodplains. The
Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
stretches over the following countries:
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
,
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
,
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
,
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
,
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
,
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
and
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
, and touches borders of
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
and
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
("peri- Pannonian states").
South of the
Eastern Alps
The Eastern Alps are usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley, up to the Splügen Pass at the Main chain of the Alps, Alpine divide, and down the Liro (Como), Liro River to Lake Como in the south. ...
(spanning Austria, Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein, Slovenia and Switzerland), the
Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern Europe, Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia ...
extend for 650 kilometres along the coast of the
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
(northwest-southeast), from the
Julian Alps
The Julian Alps (, , , , ) are a mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps that stretches from northeastern Italy to Slovenia, where they rise to 2,864 m at Mount Triglav, the highest peak in Slovenia. A large part of the Julian Alps is inclu ...
in the northwest down to the Šar-Korab massif, north–south. According to the
Freie Universität Berlin
The Free University of Berlin (, often abbreviated as FU Berlin or simply FU) is a public university, public research university in Berlin, Germany. It was founded in West Berlin in 1948 with American support during the early Cold War period a ...
, this
mountain chain
A mountain chain is a row of high mountain summits, a linear sequence of interconnected or related mountains,Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, p 87. . or a contiguous ridge of mountains within a larger mo ...
is classified as
South Central European. The city of
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
in this area, for example, expressly sees itself as a ''città mitteleuropea''. This is particularly because it lies at the interface between the
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
,
Slavic,
Germanic,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
and
Jewish culture
Jewish culture is the culture of the Jewish people, from its formation in ancient times until the current age. Judaism itself is not simply a faith-based religion, but an orthopraxy and Ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligion, pertaining to deed, ...
on the one hand and the geographical area of the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and the
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
on the other. A geographical and cultural assignment is made.
The Central European
flora region stretches from Central France (the
Massif Central) to the Northern
Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, Central
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(
Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains ...
) and Southern
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
.
Demography
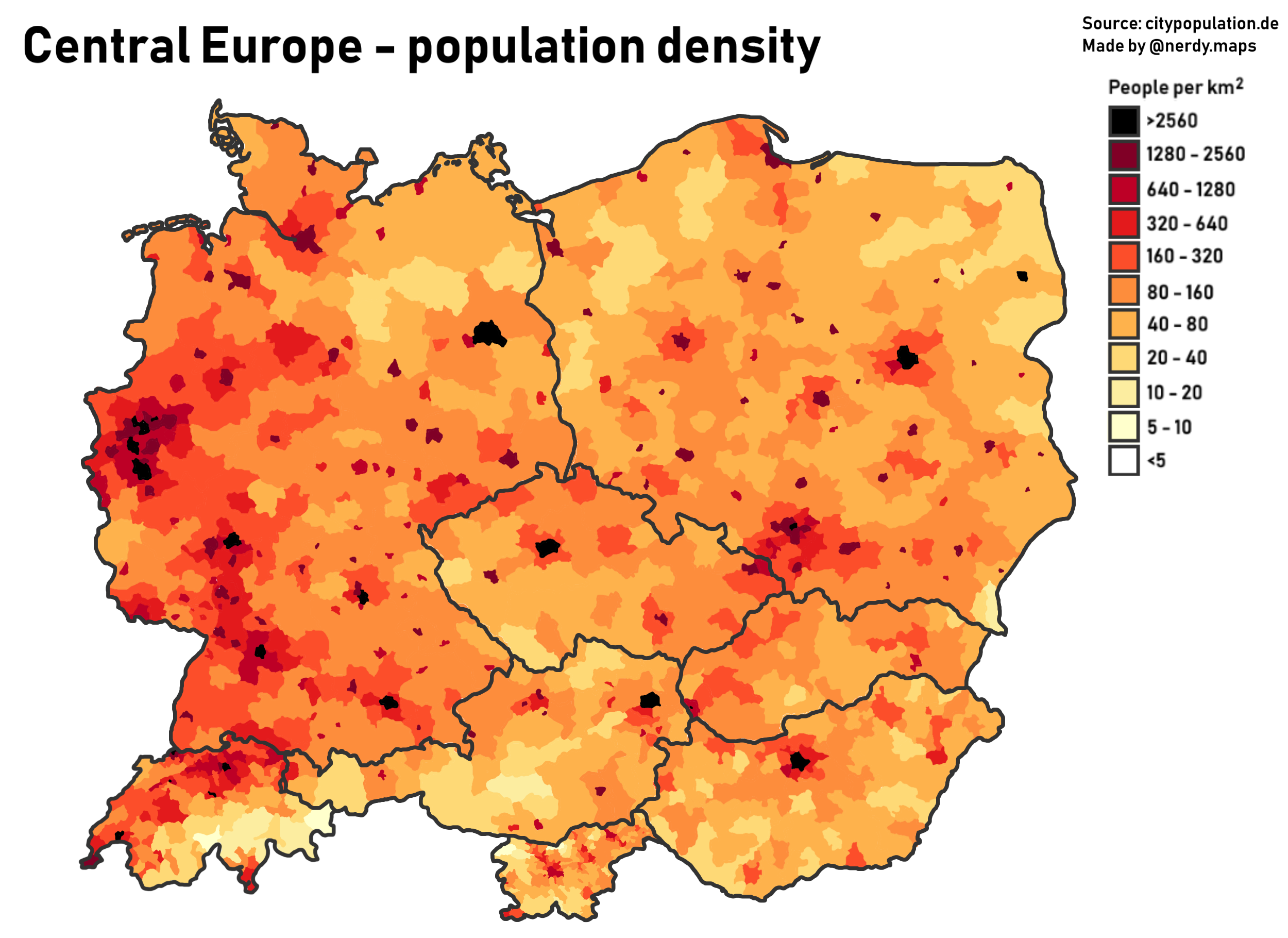

Central Europe is one of the continent's most populous regions. It includes countries of varied sizes, ranging from tiny Liechtenstein to Germany, the second largest European country by population. Demographic figures for countries entirely located within notion of Central Europe ("the core countries") number around 173 million people, out of which around 82 million are residents of Germany. Other populations include: Poland with around 38.5 million residents, Czech Republic at 10.5 million, Hungary at 10 million, Austria with 9.2 million, Switzerland with 8.5 million, Slovakia at 5.4 million, Croatia with 4.3 million, Lithuania with 2.9 million, Slovenia with 2.1 million and Liechtenstein at a bit less than 40,000.
If the countries which are sometimes also included in Central Europe were counted in, partially or in whole – Romania (20 million), Latvia (2 million), Estonia (1.3 million), Serbia (7.1 million) – this would contribute around an additional 30.4 million, although this figure would vary depending on whether a regional or integral approach is used. If smaller, western and eastern historical parts of Central Europe would be included in the demographic corpus, a further 20 million people of different nationalities would also be added in the overall count, surpassing a total of 200 million people.
Economy
Currencies
Currently, the members of the
Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
include Austria, Croatia, Germany, Lithuania, Slovakia, and Slovenia. The Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland use their own currencies (
koruna,
forint,
Polish złoty
The złoty (alternative spelling: ''zloty''; Polish: ''polski złoty'', ;The nominative plural, used for numbers ending in 2, 3 and 4 (except those in 12, 13 and 14), is ; the genitive plural, used for all other numbers, is abbreviation: z� ...
, respectively), but are obliged to adopt the Euro. Switzerland uses its own currency (
Swiss franc
The Swiss franc, or simply the franc, is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) iss ...
), as does Serbia (
dinar
The dinar () is the name of the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, with a more widespread historical use. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was bor ...
) and Romania (
Romanian leu).
Human Development Index

In 2018, Switzerland topped the HDI list among Central European countries, also ranking No. 2 in the world. Serbia rounded out the list at No. 11 (67 world).
Globalisation

The
index of globalization in Central European countries (2016 data): Switzerland topped this list as well (#1 world).
Prosperity Index
Legatum Prosperity Index
The Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the Legatum Institute, an independent educational charity founded and part-funded by the private investment firm Legatum. The ranking is based on a variety of factors including wealt ...
demonstrates an average and high level of prosperity in Central Europe (2018 data). Switzerland topped the index (#4 world).
Corruption
Most countries in Central Europe tend to score above the average in the
Corruption Perceptions Index
The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) is an index that scores and ranks countries by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, as assessed by experts and business executives. The CPI generally defines corruption as an "abuse of entr ...
(2018 data), led by Switzerland, Germany, and Austria.
Rail

Central Europe contains the continent's earliest railway systems, whose greatest expansion was recorded in Austrian, Czech,
German, Hungarian and Swiss territories between 1860-1870s. By the mid-19th century Berlin, Vienna,
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The ...
,
Pest and
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
were focal points for network lines connecting industrial areas of
Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
,
Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, Bohemia, Moravia and Lower Austria with the Baltic (
Kiel
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Ba ...
,
Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
) and Adriatic (
Rijeka
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman dialect, Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the List of cities and towns in Croatia, third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Ba ...
, Trieste). By 1913, the combined length of the railway tracks of Austria and Hungary reached . By 1936, 70% of the
Swiss Federal Railway network had undergone electrification.
Rail infrastructure in Central Europe remains the densest in the world. Railway density as of 2022, with total length of lines operated (km) per 1,000 km2, from highest to lowest is Switzerland (129.2), the Czech Republic (120.7), Germany (108.8), Hungary (85.0), Slovakia (74.0), Austria (66.5), Poland (61.9), Slovenia (59.6), Serbia (49.2), Croatia (46.3) and Lithuania (29.4).
River transport and canals
Before the first railroads appeared in the 1840s, river transport constituted the main means of communication and trade. Earliest canals included Plauen Canal (1745), Finow Canal, and also
Bega Canal (1710) which connected
Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
to
Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; #Name, see below for other names) is the List of cities in Serbia, second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pannoni ...
and
Belgrade
Belgrade is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin, Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. T ...
via the Danube. The most significant achievement in this regard was the facilitation of navigability on the Danube from the
Black sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to
Ulm in the 19th century.
The economies of Central Europe tend to demonstrate
high complexity. Industrialisation reached Central Europe relatively early beginning with Germany and the
Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands (, ) is a historical-geographical term which denotes the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia out of which Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic and Slovakia, were formed. ...
near the end of the 18th century.
The industrialization of the cities of Romania and Serbia started in the
interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
, and did not make significant progress until the post ww2 era.
Agriculture
Central European countries are some of the most significant food producers in the world. Germany is the world's largest
hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to whic ...
producer with 34.27% share in 2010,
[Gnel Gabrielyan, ]
Domestic and Export Price Formation of U.S. Hops
'' School of Economic Sciences at Washington State University. PDF file, direct download 220 KB. Retrieved 25 April 2014. Slovenia is one of the world's leading producers of honey. Serbia is the world's 2nd largest producer of
plums
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are often called prunes, though in the United States they may be labeled as 'dried plums', especially during the 21st century.
Plums are likely to have been ...
and 2nd largest producer of
raspberries.
Business
Central European business has a regional organisation, Central European Business Association (CEBA), founded in 1996 in New York as a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting business opportunities within Central Europe and supporting the advancement of professionals in America with a Central European background.
Tourism
Central European countries, especially Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany and Switzerland are some of the most competitive tourism destinations.
Education
Languages
Education performance
Student performance has varied across Central Europe, according to the
Programme for International Student Assessment
The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is a worldwide study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in member and non-member nations intended to evaluate educational systems by measuring 15-year ...
. In the 2012 study, countries scored medium, below or over the average scores in three fields studied.
Higher education
Universities
The first university established east of France and north of the Alps was in
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
in 1348 by
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV (; ; ; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus (, ), was H ...
. The
Charles University
Charles University (CUNI; , UK; ; ), or historically as the University of Prague (), is the largest university in the Czech Republic. It is one of the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest universities in the world in conti ...
was modeled upon the
University of Paris
The University of Paris (), known Metonymy, metonymically as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, from 1150 to 1970, except for 1793–1806 during the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated wit ...
and initially included the faculty of law, medicine, philosophy, and theology.
Central European University
In 1991,
Ernest Gellner proposed the establishment of a truly Central European institution of higher learning in Prague (1991–1995). Eventually, the
Central European University (CEU) project was taken on and financially supported by the philanthropist
George Soros
George Soros (born György Schwartz; August 12, 1930) is an American investor and philanthropist. , he has a net worth of US$7.2 billion, Note that this site is updated daily. having donated more than $32 billion to the Open Society Foundat ...
, who had provided an endowment of US$880 million, making the university one of the wealthiest in Europe. Over its 30-year history CEU has become one of the most internationally diverse and recognisable universities in the world. For example, as of 2019, 1217 students were enrolled in the university, of which 962 were international students, making the student body the fourth most international in the world. CEU offers highly selective programs with a student to faculty ratio of 7:1. In 2021, the admission rate into its programs was 13%. CEU has thus become a leading global university in Europe promoting a distinctively Central European perspective while emphasizing academic rigor, applied research, and academic honesty and integrity. CEU is a founding member of CIVICCA, a group of prestigious European higher education institutions in the social sciences, humanities, business management and public policy, such as
Sciences Po
Sciences Po () or Sciences Po Paris, also known as the Paris Institute of Political Studies (), is a public research university located in Paris, France, that holds the status of ''grande école'' and the legal status of . The university's unde ...
(France),
The London School of Economics and Political Science
The London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE), established in 1895, is a public research university in London, England, and a member institution of the University of London. The school specialises in the social sciences. Founded ...
(UK),
Bocconi University
Bocconi University or Università Bocconi (formally known in Italian language, Italian as ''Università Commerciale Luigi Bocconi'' – Luigi Bocconi Commercial University) is a private university in Milan, Italy. The university is consistently ...
(Italy) and the
Stockholm School of Economics (Sweden).
Culture and society
Research
Research centres of Central European literature include
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
(Cambridge, MA), Purdue University, and Central European Studies Programme (CESP),
Masaryk University
Masaryk University (MU) (; ) is the second largest university in the Czech Republic, a member of the Compostela Group and the Utrecht Network. Founded in 1919 in Brno, it now consists of ten faculties and 35,115 students. It is named after To ...
,
Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, Czech Republic.
Architecture
Religion
Central European countries are mostly
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
(Austria, Croatia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Poland and Slovenia) or historically both Catholic and
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
(the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
, Germany, Hungary, Slovakia and Switzerland). Large Protestant groups include
Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
,
Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
, and the
Unity of the Brethren affiliates. Significant populations of
Eastern Catholicism and
Old Catholic
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches, or Old Catholic movement, designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the Great C ...
ism are also prevalent throughout Central Europe.
Orthodox Christianity is a minority denomination observed to varying extents across Central Europe.
Central Europe has been the center of the
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
movement for centuries, with the majority of Protestants suppressed and annihilated during the
Counterreformation.
Historically, people in
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
in today's Czech Republic were some of the first Protestants in Europe. As a result of the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
following the
Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (; ; 1618–1620) was an uprising of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemian Estates of the realm, estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power dispu ...
, many
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
were either killed, executed (see for
Old Town Square execution
Old Town Square execution () was the execution of 27 Bohemian leaders (three Nobility, noblemen, seven knights and 17 Burgher (social class), burghers) of the Bohemian Revolt by the Austrian House of Habsburg that took place on 21 June 1621 at th ...
), forcibly turned into Roman Catholics, or emigrated to
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
and the
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
. In the aftermath of the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, the number of inhabitants in the
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
decreased from three million to only 800,000 from multiple factors, including devastating ongoing battles such as the significant
Battle of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years.
It was fought on 8 November 16 ...
and the
Battle of Prague (1648). However, in recent years, most Czechs report as overwhelmingly non-religious, with some describing themselves as Catholic (10.3%).
Before the
Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
(1941–45), there was also a sizeable
Ashkenazi Jewish
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally spe ...
community in the region, numbering approximately 16.7 million people. Poland and Lithuania had the largest Jewish populations in Europe as a percentage of their total populations, with Jews constituting 9.5% of the Polish population and 7.6% of the Lithuanian population in 1933.
Certain countries in Central Europe, particularly the Czech Republic, Germany and Switzerland have sizeable
atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
and
non-religious
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, ration ...
populations. In 2021, 48% of the Czech population declared that they had no religion. In 2022, 43.8% of the German population declared that they had no religion. Meanwhile, 33.5% of the Swiss population stated that they were not affiliated with any religion.
Cuisine
Central European cuisine has evolved over centuries because of social and political change and is generally diverse. However, the national cuisines of western Central Europe share notable similarities, as do the cuisines of eastern Central Europe. Sausages, salamis and cheeses are popular in most of Central Europe, with the earliest evidence of cheesemaking in the archaeological record dates back to 5,500 BCE (
Kuyavia
Kuyavia (; ), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with th ...
region, Poland). Other popular food items in Central Europe include soups, stews, pickled and fermented vegetables.
Schnitzel
Schnitzel () is a thin slice of meat. The meat is usually thinned by pounding with a meat tenderizer. Most commonly, the meat is breaded before frying. Breaded schnitzel is popular in many countries and is made using veal, pork, Chicken as foo ...
,
goulash
Goulash () is a meal (not quite stew or soup) made of meat and vegetables seasoned with paprika and other spices. Originating in Hungary, goulash is a common meal predominantly eaten in Central Europe but also in other parts of Europe. It is on ...
and
cabbage rolls are popular in the region.
Another common feature among Central European cuisines, particularly Austrian, Croatian, Lithuanian, Slovenian and Swiss cuisine, is the use of wild ingredients in traditional dishes, spanning from wild herbs to mushrooms and berries. Beer consumption is also prominent in parts of Central Europe, where the Czech Republic has the highest
beer consumption per capita globally, followed by Austria, with Germany coming 4th. The cuisines of Central European countries that are included in broader definitions of Eastern Europe share similarities and traditions with other Eastern European cuisines. This is particularly evident in the cuisines of Lithuania and Poland, which feature dishes like
borscht
Borscht () is a sour soup, made with meat stock, vegetables and seasonings, common in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. In English, the word ''borscht'' is most often associated with the soup's variant of Ukrainian origin, made with red b ...
,
pierogi
Pierogi ( ; ) are filled dumplings made by wrapping Leavening, unleavened dough around a Stuffing, filling and cooked in boiling water. They are occasionally flavored with a savory or sweet garnish. Typical fillings include potato, cheese, ...
and
sour rye soup.
Human rights
Generally, the countries in the region have been progressive on the issue of human rights: death penalty is illegal in all of them, corporal punishment is outlawed in most of them and people of both genders can vote in elections. However, Central European countries are divided on the subject of
same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal Legal sex and gender, sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 ...
and abortion. Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, and Poland also have a history of participation in the CIA's extraordinary rendition and detention program, according to the
Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is an American grantmaking network founded by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the world, with the s ...
.
Literature
Regional writing tradition revolves around the turbulent history of the region, as well as its cultural diversity. Its existence is sometimes challenged. Specific courses on Central European literature are taught at
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
,
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and
Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University (, UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by Casimir III the Great, King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and one of the List of oldest universities in con ...
as well as cultural magazines dedicated to regional literature. Angelus Central European Literature Award is an award worth 150,000.00 PLN (about $50,000 or £30,000) for writers originating from the region. Likewise, the
Vilenica International Literary Prize is awarded to a Central European author for "outstanding achievements in the field of literature and essay writing".
Media
Sport
There is a number of Central European Sport events and leagues. They include:
*Central European Tour Miskolc GP (Hungary)*
*Central European Tour Budapest GP (Hungary)
*2008 Central Europe Rally (Romania and Hungary)*
*2023 Central Europe Rally (Germany, Austria and Czech Republic)
*Central European Football League (Austria, Croatia, Hungary, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia and Turkey)
*Central European International Cup (Austria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Switzerland and Yugoslavia; 1927–1960)
*Central Europe Throwdown*
Football is one of the most popular sports. Countries of Central Europe hosted several major competitions. Germany hosted two FIFA World Cups (1974 FIFA World Cup, 1974 and 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006) and two UEFA European Championships (UEFA Euro 1988, 1988 and UEFA Euro 2024, 2024). Yugoslavia hosted the UEFA Euro 1976 before the competition expanded to 8 teams. Recently, the UEFA Euro 2008, 2008 and UEFA Euro 2012, 2012 UEFA European Championships were held in Austria & Switzerland and Poland & Ukraine respectively.
Politics
Organisations
Central Europe is a birthplace of regional political organisations:
*
Central European Defence Cooperation
The Central European Defence Cooperation (CEDC) is a military collaboration consisting of the Central European states of Austria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia and Slovenia. Poland has an observer status in this cooperative frame ...
*
Central European Free Trade Agreement
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA in 2006 expanded to Albania, Bo ...
*
Central European Initiative
*
Centrope
*Middleeuropean Initiative
*Three Seas Initiative
*
Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
File:CEDC.svg, Central European Defence Cooperation
The Central European Defence Cooperation (CEDC) is a military collaboration consisting of the Central European states of Austria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia and Slovenia. Poland has an observer status in this cooperative frame ...
File:CEFTA 1992.PNG, CEFTA founding states
File:CEFTA 2003.PNG, CEFTA members in 2003, before joining the EU
File:Central European Free Trade Agreement.svg, Current CEFTA members
File:CEI members.svg, Central European Initiative
File:Three Seas Initiative.svg, Three Seas Initiative
File:Visegrad group countries.svg, Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four or the V4) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, e ...
Democracy Index

Central Europe is a home to some of world's oldest democracies. However, most of them have been impacted by totalitarianism, particularly Fascism and Nazism. Germany and Italy occupied all Central European countries, except Switzerland. In all occupied countries, the Axis powers suspended democracy and installed puppet regimes loyal to the occupation forces. Also, they forced conquered countries to apply racial laws and formed military forces for helping German and Italian struggle against Communists. After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, almost the whole of Central Europe (the Eastern and Middle part) had been transformed into communist states, most of which had been occupied and later allied with the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, often against their will through forged referendum (such as the 1946 Polish people's referendum, Polish people's referendum in 1946) or force (northeast Germany, Poland, Hungary et alia). Nevertheless, those experiences have been dealt in most of them. Most Central European countries score very highly in the Democracy Index.
Global Peace Index

In spite of its turbulent history, Central Europe is currently one of world's safest regions. Most Central European countries are in top 20%.
Central European Time

The time zone is a standard time, which is one hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. Countries using CET include:
* Albania
* Andorra
* Austria
* Belgium
* Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Croatia
* Czech Republic
* Denmark
* France
* Germany
* Hungary
* Italy
* Luxembourg
* Monaco
* Montenegro
* Netherlands
* North Macedonia
* Norway
* Poland
* San Marino
* Slovakia
* Slovenia
*Serbia
* Sweden
* Switzerland
* Vatican City
In popular culture
Central Europe is mentioned in the 35th episode of ''Lovejoy'', entitled "The Prague Sun", filmed in 1992. While walking over the well-regarded and renowned Charles Bridge in Prague, the main character, Lovejoy, says: "I've never been to Prague before. Well, it is one of the great unspoiled cities in Central Europe. Notice: I said: 'Central', not 'Eastern'! The
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
are a bit funny about that, they think of Eastern Europeans as ''turnip heads''."
Wes Anderson's Oscar-winning film ''The Grand Budapest Hotel'' depicts a fictional grand hotel located somewhere in Central Europem, which is in actuality modelled on the Grandhotel Pupp in Karlovy Vary in the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
. The film is a celebration of 1920s and 1930s Central Europe with its artistic splendor and societal sensibilities.
See also
* Central and Eastern Europe
* Geographical midpoint of Europe
* Life zones of central Europe
* Międzymorze (Intermarum)
References
General and cited references
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Shared Pasts in Central and Southeast Europe, 17th–21st Centuries. Eds. G. Demeter, P. Peykovska. 2015
Further reading
* Ágh, Attila. ''Declining Democracy in East-Central Europe: The Divide in the EU and Emerging Hard Populism'' (Edward Elgar Publishing, 2019).
* Baldersheim, Harald, ed. ''Local democracy and the processes of transformation in East-Central Europe'' (Routledge, 2019).
*
*
* Centre of Central European Studies, ''Agrarianism in Central and Eastern Europe in the 19th and 20th Centuries'' (2013
online review
*
* Gardner, Hall, ed. ''Central and South-central Europe in Transition'' (Praeger, 2000)
*
*
* Lederer, David. ''Early Modern Central European History'' (2011
online review by Linnéa Rowlatt*
*
*
*
*
* 'Mapping Central Europe' i
hidden europe 5, pp. 14–15 (November 2005)
External links
''Journal of East Central Europe''Central European Political Science Association's journal "Politics in Central Europe"CEU Political Science Journal (PSJ)Central European Journal of International and Security Studies
Central European Political Studies ReviewMaps of Europe and European countriesCENTRAL EUROPE 2020
Central Europe Economy
{{Authority control
Central Europe,
Regions of Europe
 Following
Following  * Central Europe as the area of the former Habsburg monarchy – a concept which is popular in large parts of
* Central Europe as the area of the former Habsburg monarchy – a concept which is popular in large parts of  There is no general agreement either on what geographic area constitutes Central Europe, nor on how to further subdivide it geographically.
At times, the term "Central Europe" denotes a geographic definition as the
There is no general agreement either on what geographic area constitutes Central Europe, nor on how to further subdivide it geographically.
At times, the term "Central Europe" denotes a geographic definition as the  Geography defines Central Europe's natural borders with the neighbouring regions to the north across the
Geography defines Central Europe's natural borders with the neighbouring regions to the north across the 
 Most countries in Central Europe tend to score above the average in the
Most countries in Central Europe tend to score above the average in the