|
Córdoba-Navarco Fault
The Córdoba-Navarco Fault () is a sinistral strike-slip fault in the departments of Colombia, department of Quindío Department, Quindío in west-central Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike (geology), strike of 018.5 ± 4 in the Cordillera Central (Colombia), Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault segment pertaining to the megaregional Romeral Fault System is a set of two faults that are active, causing the major 1999 Armenia, Colombia earthquake, 1999 Armenia earthquake with approximately 1185 fatalities. Etymology The fault is named after Córdoba, Quindío, Córdoba and the Navarco River in Quindío Department, Quindío.Paris et al., 2000a, p.25 Description The fault section is formed by the Córdoba and Navarco Faults, which are eastern strands of Romeral Fault System, south of the city of Armenia, Colombia, Armenia. These faults lie within the epicenter area of the Armenia earthquake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Córdoba, Quindío
Córdoba is a municipality in the eastern part of the department of Quindío, Colombia. It's located 24 km southeast of the departmental capital Armenia. History Córdoba was founded in 1927 by Jesús García and Jesús Buitrago, and became a municipality in 1966 when it split from Calarcá. In 2023 it had an estimated population of 5,888. By population it's the third smallest municipality in Quindío, after Buenavista and Pijao. Geography Córdoba is bounded to the north by the municipality of Calarcá, to the south by Pijao, to the west by Buenavista, and to the east by the department of Tolima. Climate The average temperature of Córdoba is 20 °C with a subtropical highland climate. Tourism Córdoba is home to the National Bamboo and Guadua Investigation Center (). Open to the public, the center shows the potential uses of guadua ''Guadua'' is a Neotropical genus of thorny, clumping bamboo in the grass family, ranging from moderate to very large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike (geology)
In geology, strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the plane orientation or attitude of a planar geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination (or depression angle) measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geological map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the feature's dip by recording the inclination perpendicular to the strike. These can be don ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercalli Intensity Scale
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM, MMI, or MCS) measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location. This is in contrast with the seismic magnitude usually reported for an earthquake. Magnitude scales measure the inherent force or strength of an earthquake — an event occurring at greater or lesser depth. (The "" scale is widely used.) The MMI scale measures intensity of shaking, at any particular location, on the surface. It was developed from Giuseppe Mercalli's Mercalli intensity scale of 1902. While shaking experienced at the surface is caused by the seismic energy released by an earthquake, earthquakes differ in how much of their energy is radiated as seismic waves. They also differ in the depth at which they occur; deeper earthquakes have less interaction with the surface, their energy is spread throughout a larger volume, and the energy reaching the surface is spread across a larger area. Shaking intensity is localised. It generally diminishes with dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Magnitude Scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mwg, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. was defined in a 1979 paper by Thomas C. Hanks and Hiroo Kanamori. Similar to the local magnitude scale, local magnitude/Richter scale () defined by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, it uses a logarithmic scale; small earthquakes have approximately the same magnitudes on both scales. Despite the difference, news media often use the term "Richter scale" when referring to the moment magnitude scale. Moment magnitude () is considered the authoritative magnitude scale for ranking earthquakes by size. It is more directly related to the energy of an earthquake than other scales, and does not saturatethat is, it does not underestimate magnitudes as other scales do in certain conditions. It has become the standard scale used by seismological authorities like the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereira, Colombia
Pereira () is the capital city of the Colombian Departments of Colombia, department of Risaralda Department, Risaralda. It is located in the foothills of the Andean natural region, Andes in a coffee-producing area of Colombia officially known as the "Colombian coffee growing axis, Coffee Axis". Pereira, alongside the rest of the Coffee Axis, form part of UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the "Coffee Cultural Landscape of Colombia"."Colombia green guide Michelin 2012-2013." Michelin. 2012. Accessed at Google Books 29 December 2013. It is the most populated city in the Coffee Axis. Pereira is also part of the Central West Metropolitan Area, which has 735.769 residents and is composed of Pereira and the neighboring cities of Dosquebradas and La Virginia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risaralda Department
Risaralda () is a department of Colombia. It is located in the western central of the country, in the Andean region, It is part of the Coffee axis with Caldas and Quindío. Its capital is Pereira. Risaralda is very well known for the high quality of its coffee, and a booming industry: automotive, clothes, food, trading of goods and services. It was divided from the department of Caldas in 1966. The territory is very mountainous and has many kinds of climates in a very small area. Its proximity to harbours such as Buenaventura on the Pacific Region and to the biggest cities in Colombia – Bogotá, Cali, Medellín – makes it a fast-growing economic centre. Geography Risaralda department with an area of , is located in the central sector of the central Andean region west of the country between two major poles of economic development (department of Antioquia in northern and southern Cauca Valley, extending between the central and western Cordillera), which slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibagué Fault
The Ibagué Fault () is a major dextral slightly oblique strike-slip fault in the department of Tolima in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average east-northeast to west-southwest strike of 067.9 ± 11 cross-cutting the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault is part of a regional shear zone and has been active in historical times, possibly associated with the 1825 Ibagué earthquake and an earthquake in 1942. Etymology The fault is named after Ibagué, the capital of Tolima.Diederix et al., 2006, p.492 Description The Ibagué Fault crosses the central part and eastern slope of the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes, close to the city of Ibagué. The fault strikes west-southwest to east-northeast, controlling the course of the Cocora River. The fault has a well developed fault trace with prominent linear fault ridges (whale backs) as much as long and high, fault scarplets aligned with ridges, sag ponds, fault-controlled d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Scarp
A fault scarp is a small step-like offset of the ground surface in which one side of a fault has shifted vertically in relation to the other. The topographic expression of fault scarps results from the differential erosion of rocks of contrasting resistance and the displacement of land surface by movement along the fault. Differential movement and erosion may occur either along older inactive geologic faults, or recent active faults. Characteristics Fault scarps often involve zones of highly fractured rock and discontinuities of hard and weak consistencies of rock. Bluffs can form from upthrown blocks and can be very steep, as in the case of Pakistan's coastal cliffs. The height of the scarp formation tends to be defined in terms of the vertical displacement along the fault. Active scarp faults may reflect rapid tectonic displacement and can be caused by any type of fault including strike-slip faults. Vertical displacement of ten meters may occur in fault scarps in volcanic bed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
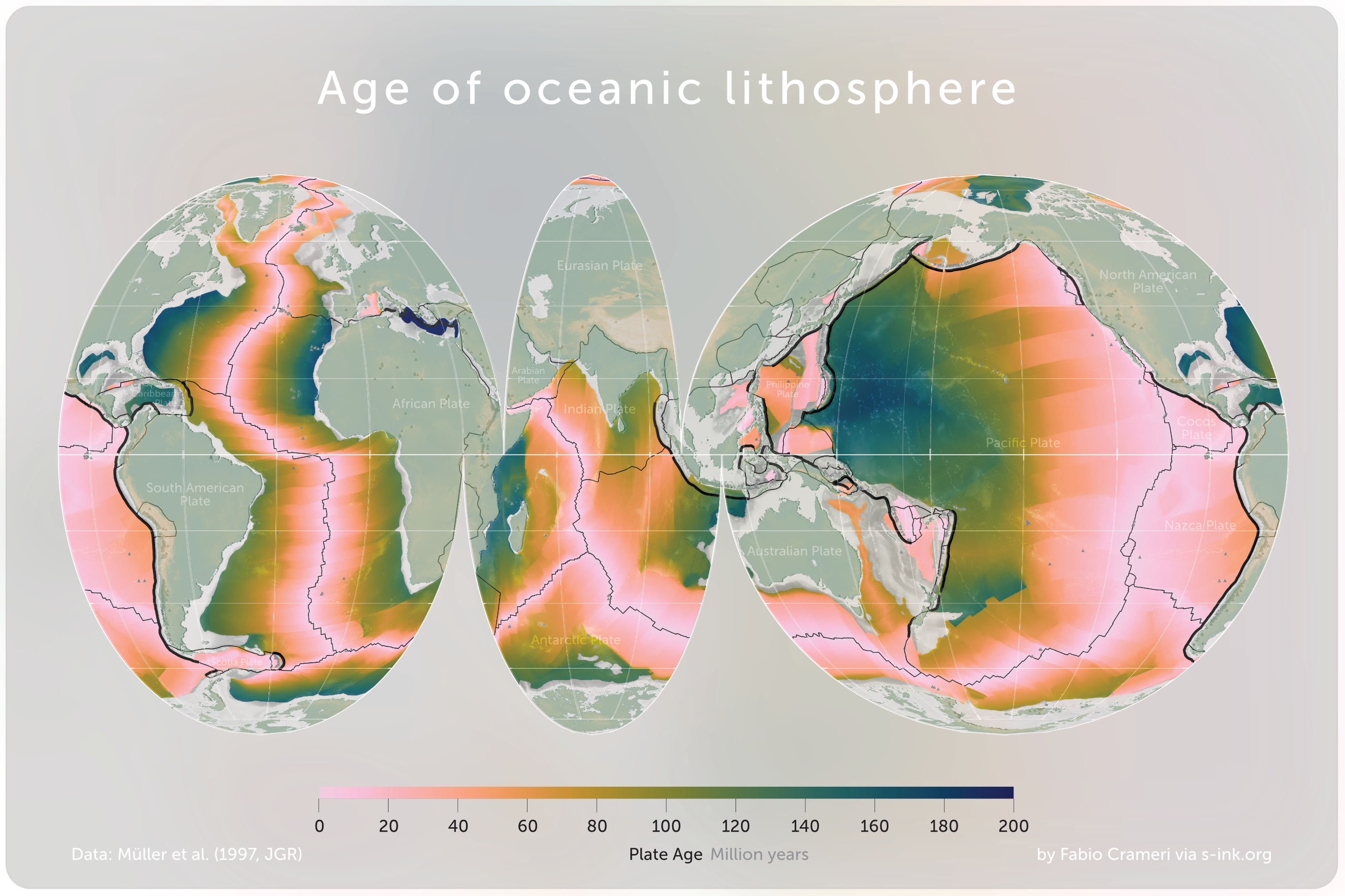
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust lies above the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |