|
Cytomegalovirus Colitis
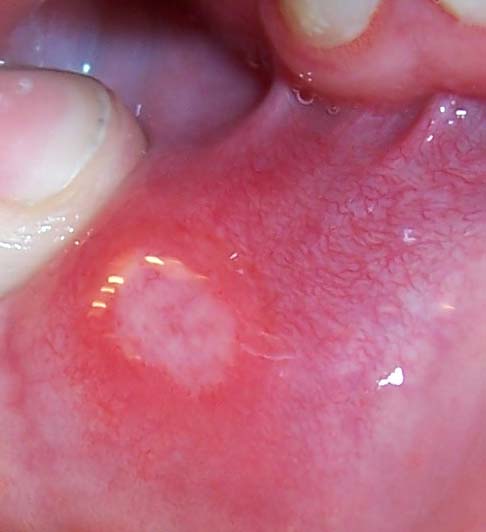
Cytomegalovirus colitis (CMV colitis) is an inflammation of the colon. Causes The infection is spread by saliva, urine, respiratory droplets, sexual contact, and blood transfusions. Most people are exposed to the virus in their lifetime, but it usually produces mild or no symptoms in healthy people. However, serious CMV infections can occur in people with weakened immune systems. This includes patients receiving chemotherapy for cancer and patients on immune-suppressing medicines following an organ transplant. In rare instances, more severe CMV infection involving the gastrointestinal tract has been reported in people with a healthy immune system. Risk factors The systemic use of corticosteroids in the context of inflammatory bowel disease can promote CMV infection in the colon. The corticosteroids used as a primary treatment for flare-up events of inflammatory bowel disease reduce the autoimmune activity of the T lymphocytes and monocytes that contribute to the inflammation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a micros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evidence. Several methods can be used to detect antibodies and antigens, including ELISA, agglutina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. While the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointestinal tract, possibly targeting microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
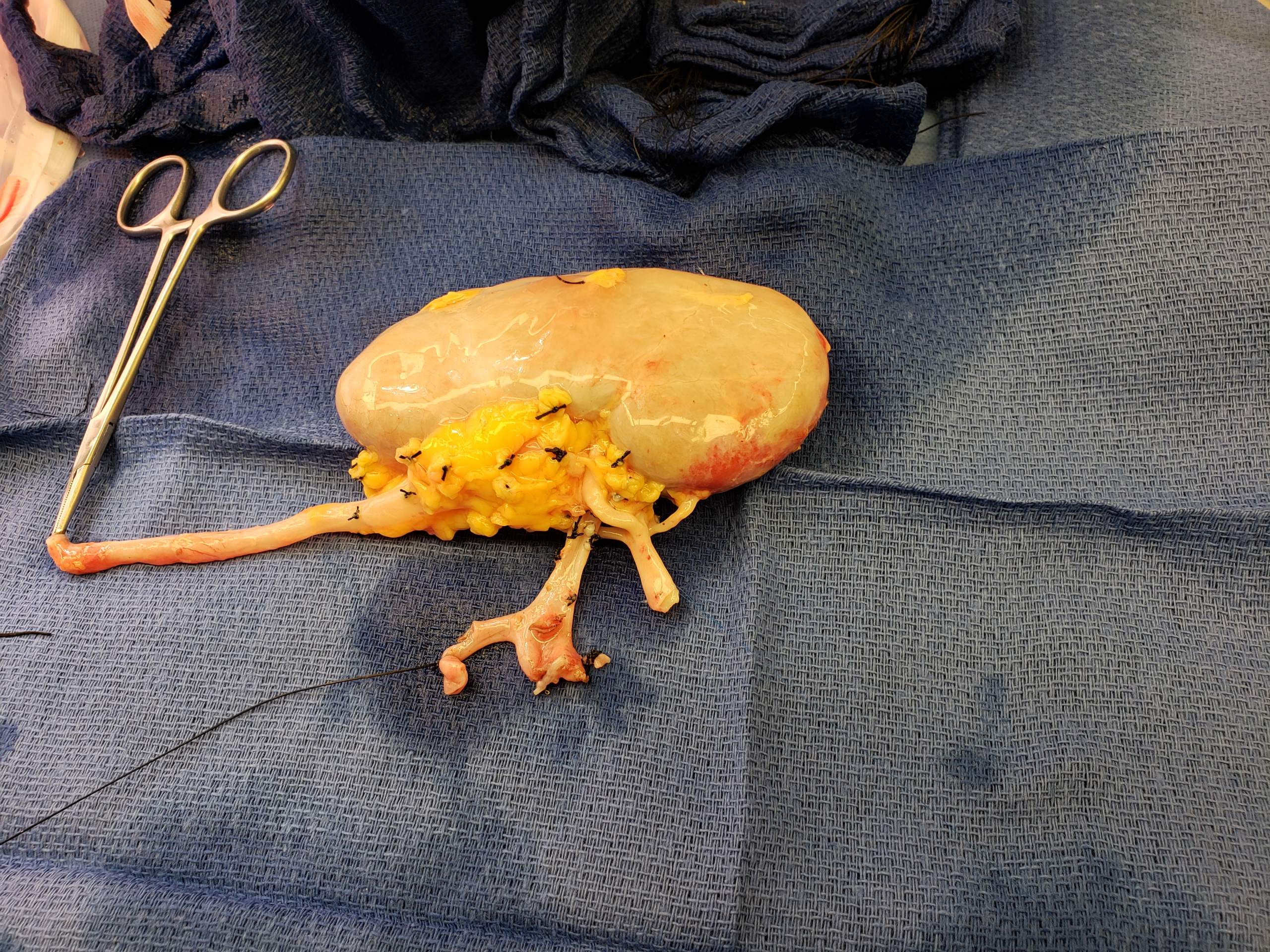
Colectomy
Colectomy ('' col-'' + '' -ectomy'') is bowel resection of the large bowel ( colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection (partial colectomy). In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy ('' procto-'' + ''colectomy'') denotes that the rectum is included. Indications Some of the most common indications for colectomy are: * Colon cancer * Diverticulitis and diverticular disease of the large intestine * Trauma * Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. Colectomy neither cures nor eliminates Crohn's disease, instead only removing part of the entire diseased large intestine. A colectomy is considered a "cure" for ulcerative colitis because the disease attacks only the large intestine and therefore will not be able to flare up again if the entire large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (''e.g.,'' ulceration, polyps) and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected colorectal cancer lesions. Colonoscopy can remove polyps smaller than one millimeter. Once polyps are removed, they can be studied with the aid of a microscope to determine if they are precancerous or not. Colonoscopy is similar to sigmoidoscopy—the difference being related to which parts of the colon each can examine. A colonoscopy allows an examination of the entire colon (1,200–1,500mm in length). A sigmoidoscopy allows an examination of the distal portion (about 600mm) of the colon, which may be sufficient because benefits to cancer survival of colonoscopy have been limited to the detection of lesions in the distal portion of the colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-reactivity, cross-react and bind more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with chronic kidney disease, end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluation to make sure that they are healthy enough to undergo transplant surgery. If they are deemed a good candidate, they can be placed on a waiting list to receive a kidney from a deceased donor. Once they are placed on the waiting list, they can receive a new kidney very quickly, or they may have to wait many years; in the United States, the average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
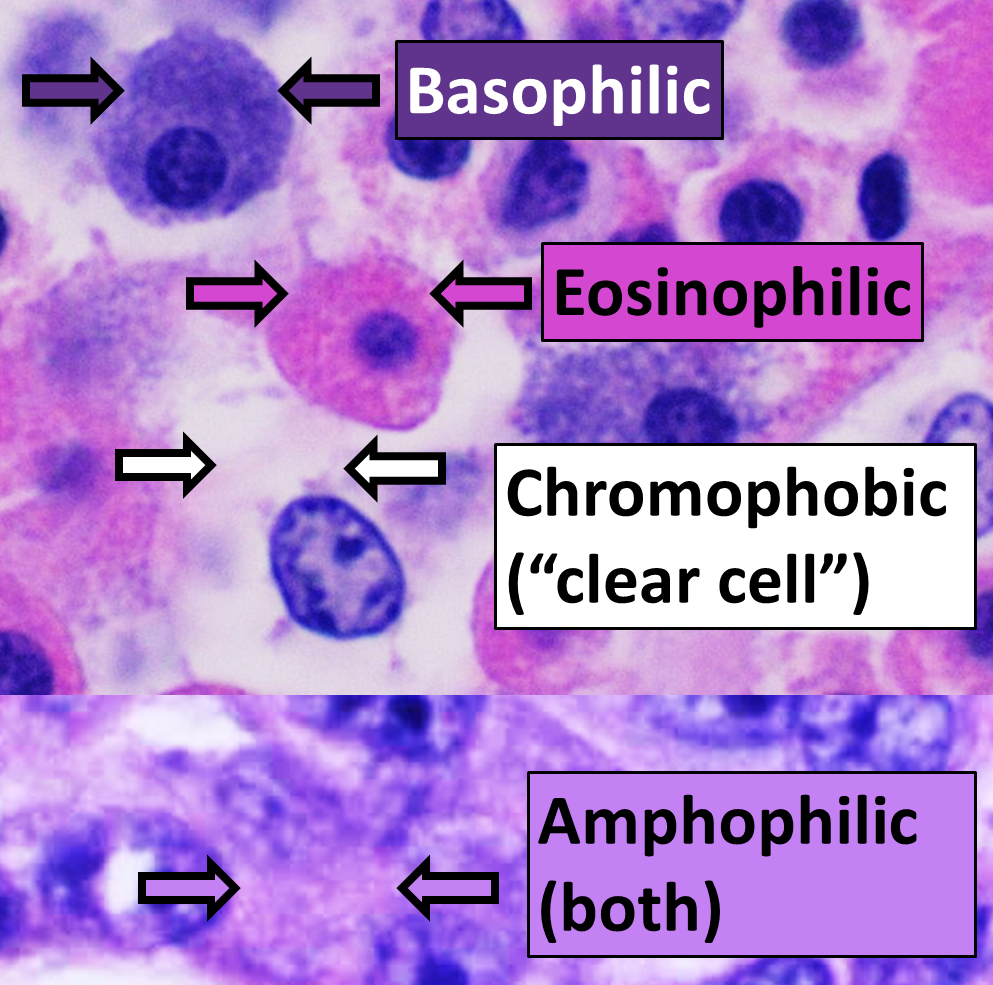
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
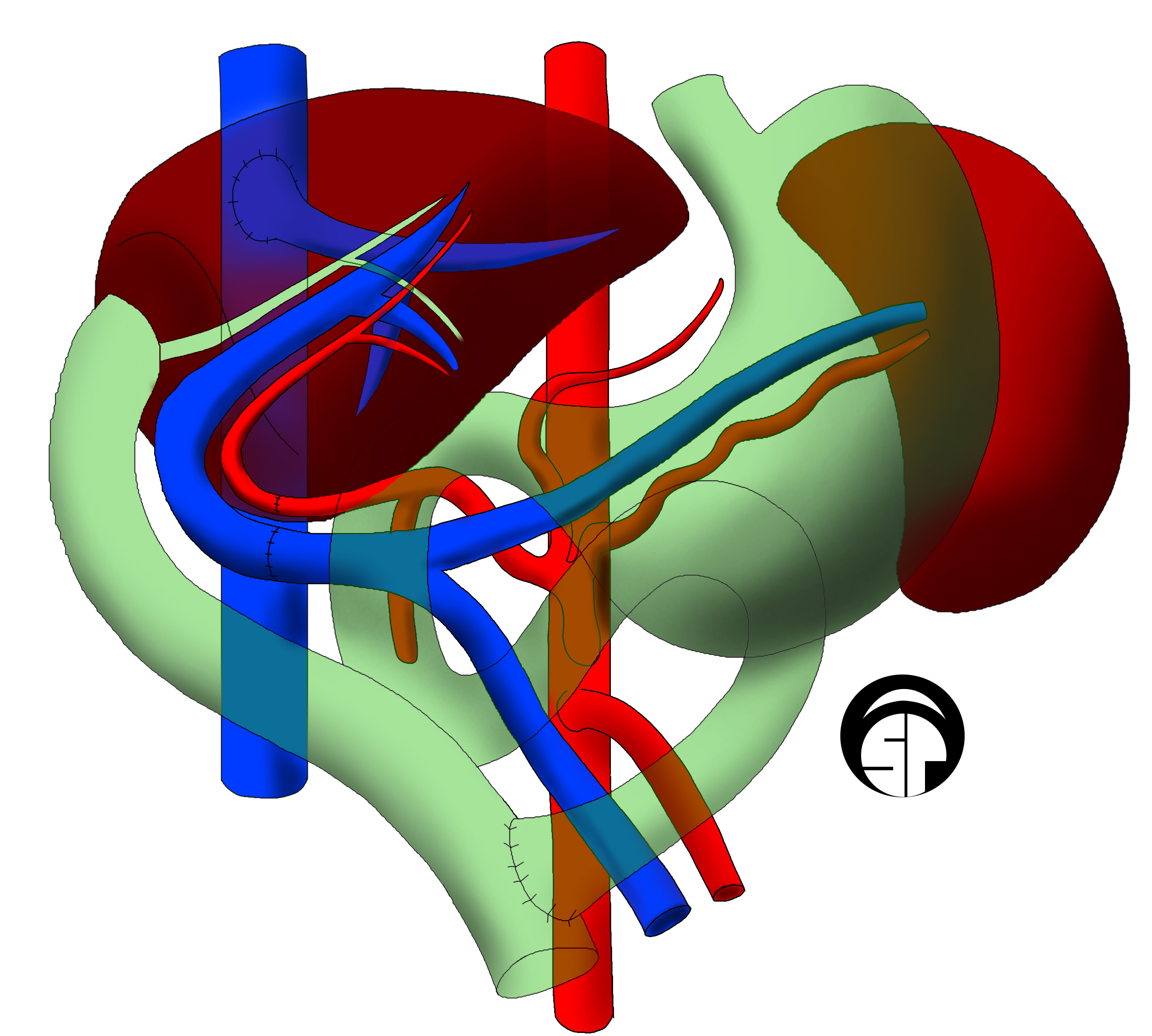
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person ( allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppressive Drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |