|
Cytochrome A
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature. History Cytochromes were initially described in 1884 by Charles Alexander MacMunn as respiratory pigments (myohematin or histohematin). In the 1920s, Keilin rediscovered these respiratory pigments and name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Alexander MacMunn
Dr Charles Alexander MacMunn (11 April 1852 – 18 February 1911) was the first to describe the respiratory pigment in blood, known today as Cytochrome1. It was one of the most significant discoveries made by an Irish doctor. Biography MacMunn was born on 11 April 1852 in Easkey, County Sligo, Ireland, the son of James MacMunn MD. He was educated at Trinity College Dublin, graduating BA with honours in 1871, MB in 1872, MD in 1875. He studied under William Stokes. He moved to Wolverhampton in 1873 to work within his cousin's practice, subsequently taking over the practice on his cousin's death. He had a loft of his stable converted to a laboratory work he could carry out work on his spectroscopy when not otherwise engaged with the practice. He was the author of numerous papers on medicine, physiology and biology. His seminal paper was published in 1880 entitled "The Spectroscope in Medicine". He used the spectroscope to study pigments in microorganisms and muscular tissue. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin-endoperoxide Synthase 2
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 ( HUGO PTGS2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTGS2'' gene. In humans it is one of three cyclooxygenases. It is involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, an important precursor of prostacyclin, which is expressed in inflammation. Function PTGS2 (COX-2), converts arachidonic acid (AA) to prostaglandin endoperoxide H2. PTGSs are targets for NSAIDs and PTGS2 (COX-2) specific inhibitors called coxibs. PTGS-2 is a sequence homodimer. Each monomer of the enzyme has a peroxidase and a PTGS (COX) active site. The PTGS (COX) enzymes catalyze the conversion of AA to prostaglandins in two steps. First, hydrogen is abstracted from carbon 13 of arachidonic acid, and then two molecules of oxygen are added by the PTGS2 (COX-2), giving PGG2. Second, PGG2 is reduced to PGH2 in the peroxidase active site. The synthesized PGH2 is converted to prostaglandins ( PGD2, PG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism. ''Photosynthesis'' usually refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms store the chemical energy so produced within intracellular organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism's cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth. Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-dependent Reactions
Light-dependent reactions are certain photochemical reactions involved in photosynthesis, the main process by which plants acquire energy. There are two light dependent reactions: the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and the second occurs at photosystem I (PSI). PSII absorbs a photon to produce a so-called high energy electron which transfers via an electron transport chain to cytochrome ''bf'' and then to PSI. The then-reduced PSI, absorbs another photon producing a more highly reducing electron, which converts NADP to NADPH. In oxygenic photosynthesis, the first electron donor is water, creating oxygen (O2) as a by-product. In anoxygenic photosynthesis, various electron donors are used. Cytochrome ''b6f'' and ATP synthase work together to produce ATP ( photophosphorylation) in two distinct ways. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, cytochrome ''b6f'' uses electrons from PSII and energy from PSI to pump protons from the stroma to the lumen. The resulting proton gradient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multidomain enzymes, in which multiple active site, catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of protein quaternary structure, quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent interactions, non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between Enzyme, enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme Q – Cytochrome C Reductase
The coenzyme Q : cytochrome ''c'' – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome ''bc''1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain (), playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial (cytochrome b) and the nuclear genomes (all other subunits). Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most bacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits (cytochrome B, cytochrome C1, Rieske protein), 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins. Ubiquinol—cytochrome-c reductase catalyzes the chemical reaction :QH2 + 2 ferricytochrome c \rightleftharpoons Q + 2 ferrocytochrome c + 2 H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
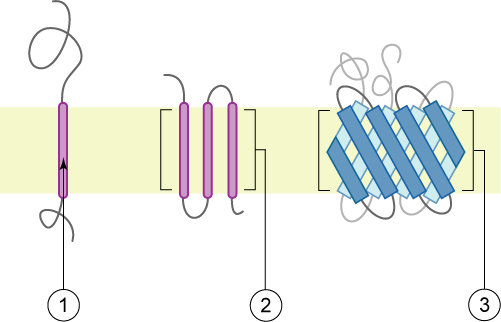
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (forming colloids in water), unlike the fibrous or membrane proteins. There are multiple fold classes of globular proteins, since there are many different architectures that can fold into a roughly spherical shape. The term globin can refer more specifically to proteins including the globin fold. Globular structure and solubility The term globular protein is quite old (dating probably from the 19th century) and is now somewhat archaic given the hundreds of thousands of proteins and more elegant and descriptive structural motif vocabulary. The globular nature of these proteins can be determined without the means of modern techniques, but only by using ultracentrifuges or dynamic light scattering techniques. The spherical structure is induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox reactions are driven by the difference in the Gibbs free energy of reactants and products. The free energy released when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |