|
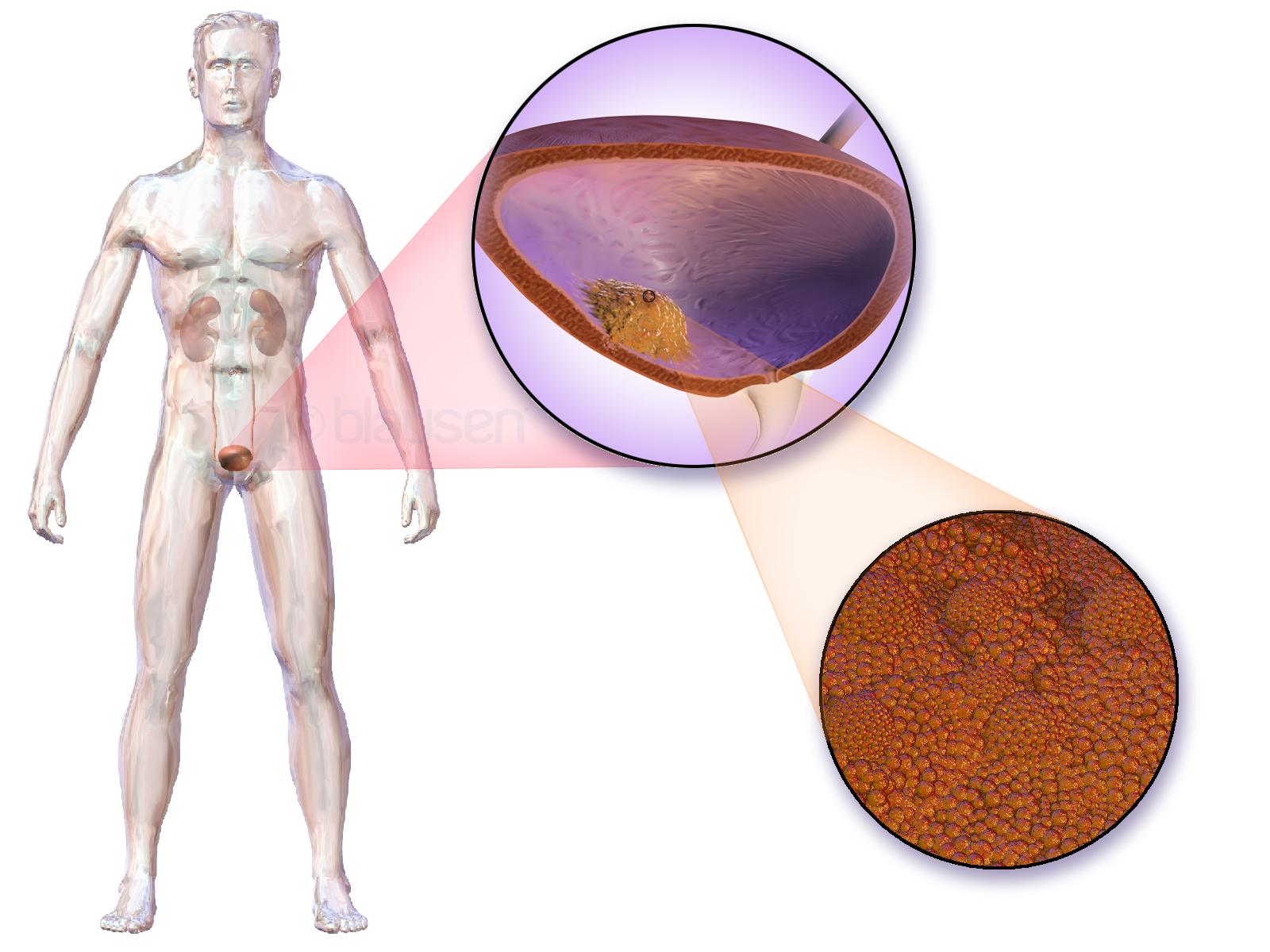
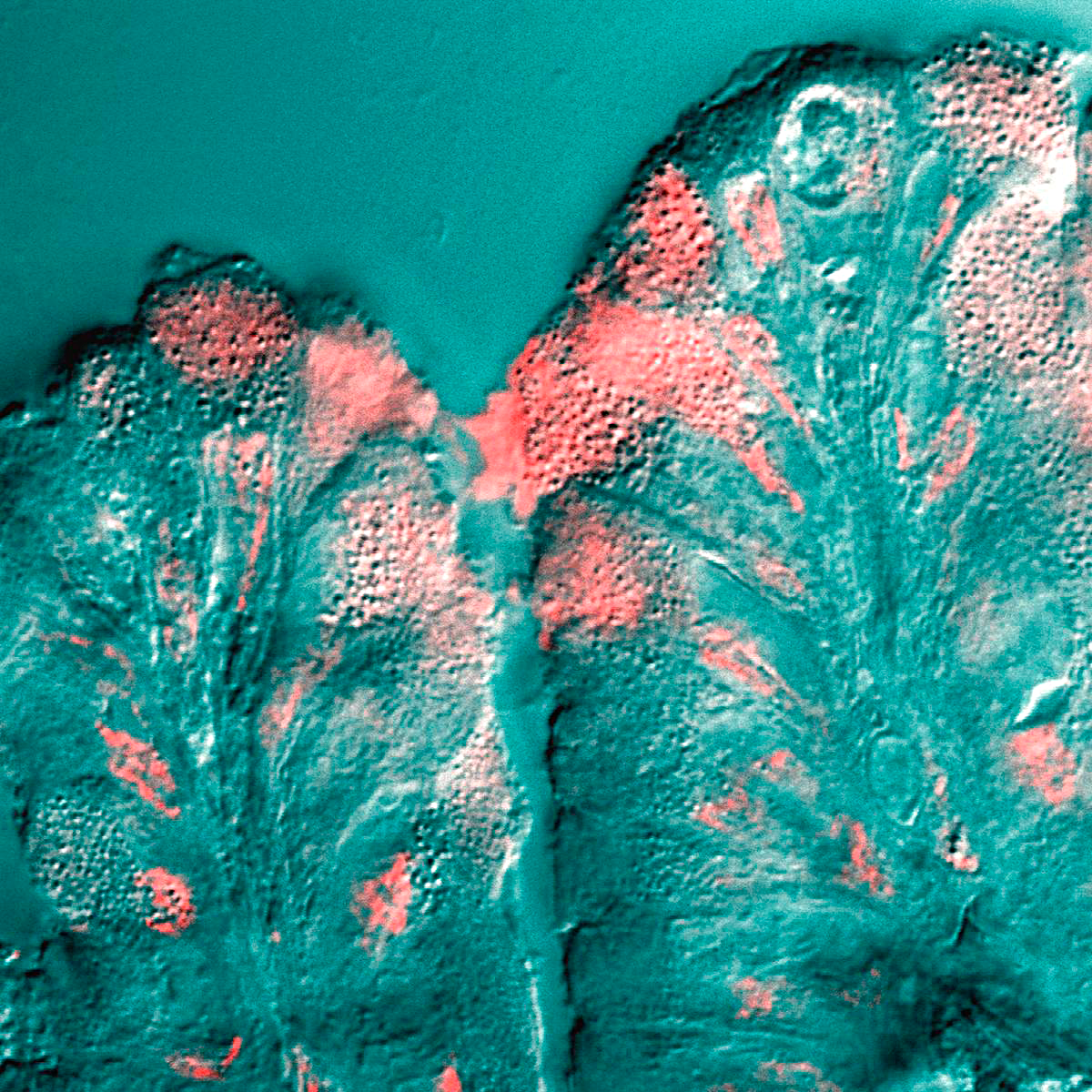
Cystitis Glandularis
Cystitis glandularis is the transformation of mucosal cells lining the urinary bladder. They undergo glandular metaplasia, a process in which irritated tissues take on a different form, in this case that of a gland. The main importance is in the findings of test results, in this case histopathology. They must distinguish a benign metaplastic change from the cancerous condition urothelial cell carcinoma. It is a very common finding in bladder Biopsy, biopsies and Cystectomy, cystectomies, and most often found in the trigone of urinary bladder, trigone area. Cystitis glandularis lesions are usually present as small microscopic foci; however, occasionally it can form raised intramucosal or Polypoidy, polypoid lesions. The cystitis glandularis lesions are within the submucosa. Types There are two main types of cystitis glandularis, non-mucinous and mucinous (intestinal). The difference is in the cellular production of mucin, a normal feature of colonic and intestinal epithelial cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystitis Glandularis At Trigone
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or Abdominal pain, flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear Hematuria, bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes mellitus, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins ( glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most gel-like secretions, serving functions from lubrication to cell signalling to forming chemical barriers. They often take an inhibitory role. Some mucins are associated with controlling mineralization, including nacre formation in mollusks, calcification in echinoderms and bone formation in vertebrates. They bind to pathogens as part of the immune system. Overexpression of the mucin proteins, especially MUC1, is associated with many types of cancer. Although some mucins are membrane-bound due to the presence of a hydrophobic membrane-spanning domain that favors retention in the plasma membrane, most mucins are secreted as principal components of mucus by mucous membranes or are secreted to become a component of saliva. Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrogenic Adenoma
Nephrogenic adenoma is a benign growth typically found in the urinary bladder. It is thought to result from displacement and implantation of renal tubular cells, as this entity in kidney transplant recipients has been shown to be kidney donor derived. This entity should not be confused with the similar-sounding '' metanephric adenoma''. Diagnosis Nephrogenic adenomas are diagnosed under the microscope by pathologist Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...s. Microscopically the tumor shows closely packed small tubular structures in edematous stroma. The tubules show considerable variation in size and shape resembling convoluted tubules of the kidney. The single layer of cells lining the tubules are cuboidal with a scant to moderate amount of cytoplasm. In some areas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Metaplasia
Squamous metaplasia is a benign non-cancerous change (metaplasia) of surfacing lining cells (epithelium) to a squamous morphology. Location Common sites for squamous metaplasia include the bladder and cervix. Smokers often exhibit squamous metaplasia in the linings of their airways. These changes don't signify a specific disease, but rather usually represent the body's response to stress or irritation. Vitamin A deficiency or overdose can also lead to squamous metaplasia. Uterine cervix In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the endocervix, as it is composed of simple columnar epithelium, whereas the ectocervix is composed of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007) ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 716-720 Significance Squamous metaplasia may be seen in the context of benign lesions (e.g., atypical polypoid adenomyoma), chronic irrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystitis Cystica
Cystitis cystica is an uncommon chronic reactive inflammatory disease that is believed to be brought on by a tumor, calculi, infection, or obstruction of the urothelium. Cystitis glandularis is a proliferative progression of cystitis cystica that is distinguished by urothelial glandular metaplasia. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of cystitis cystica and associated pathologies are not specific. They could exhibit vague symptoms akin to those of numerous other urinary illnesses and ailments. Symptoms include suprapubic or perianal pain, hematuria, urine retention, lower urinary tract symptoms such as incomplete emptying, urgency, and frequency, and obstructive urinary symptoms. Causes Although many affected individuals share a common feature of chronic irritation, infection, or inflammation, the exact cause of cystitis cystica remains unknown. Potential causes include chronic Urinary tract infections, in-dwelling catheters, mechanical irritation, chronic bladder outlet obstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina Propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital tract. The lamina propria is a thin layer of loose (areolar) connective tissue, which lies beneath the epithelium, and together with the epithelium and basement membrane constitutes the mucosa. As its Latin name indicates, it is a characteristic component of the mucosa, or the mucosa's "own special layer." Thus, the term mucosa or mucous membrane refers to the combination of the epithelium and the lamina propria. The connective tissue of the lamina propria is loose and rich in cells. The cells of the lamina propria are variable and can include fibroblasts, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, eosinophilic leukocytes, and mast cells. It provides support and nutrition to the epithelium, as well as the means to bind to the underlying t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in their urine. Those suspected of having bladder cancer typically have their bladder inspected by a thin medical camera, a procedure called cystoscopy. Suspected tumors are removed and examined to determine if they are cancerous. Based on how far the tumor has spread, the cancer case is assigned a stage 0 to 4; a higher stage indicates a more widespread and dangerous disease. Those whose bladder tumors have not spread outside the bladder have the best prognoses. These tumors are typically surgically removed, and the person is treated with chemotherapy or one of several immune-stimulating therapies. Those whose tumors continue to grow, or whose tumors have penetrated the bladder muscle, often have their bladder surgically removed ( radical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is called ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Stone
A bladder stone is a stone found in the urinary bladder. Signs and symptoms Bladder stones are small mineral deposits that can form in the bladder. In most cases bladder stones develop when the urine becomes very concentrated or when one is dehydrated. This allows for minerals, such as calcium or magnesium salts, to crystallize and form stones. Bladder stones vary in number, size and consistency. In some cases bladder stones do not cause any symptoms and are discovered as an incidental finding on a plain radiograph. However, when symptoms do occur, these may include severe lower abdominal and back pain, difficult urination, frequent urination at night, fever, painful urination and blood in the urine. The majority of individuals who are symptomatic will complain of pain which comes in waves. The pain may also be associated with nausea, vomiting and chills. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraplegia
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organ (anatomy), organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal Tissue (biology), tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucinous
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus covers the epithelial cells that interact with outside environment, serves to protect the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, to help in move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |