|
Cylinder Head Porting
Cylinder head porting refers to the process of modifying the intake and exhaust ports of an internal combustion engine to improve their air flow. Cylinder heads, as manufactured, are usually suboptimal for racing applications due to being designed for maximum durability. Ports can be modified for maximum power, minimum fuel consumption, or a combination of the two, and the power delivery characteristics can be changed to suit a particular application. Port modifications When a modification is decided upon through testing with an air flow bench, the original port wall material can be reshaped by hand with die grinders or by numerically controlled milling machines. For major modifications the ports must be welded up or similarly built up to add material where none existed. The Ford two-liter F2000 engine in stock trim equipped with the head shown above was capable of delivering 115 horsepower at 5500 rpm for a BMEP of 136 psi. This aftermarket Pro Stock racing head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intake
An intake (also inlet) is an opening, structure or system through which a fluid is admitted to a space or machine as a consequence of a pressure differential between the outside and the inside. The pressure difference may be generated on the inside by a mechanism, or on the outside by ram pressure or hydrostatic pressure. Flow rate through the intake depends on pressure difference, fluid properties, and intake geometry. Intake refers to an opening, or area, together with its defining edge profile which has an associated entry loss, that captures pipe flow from a reservoir or storage tank. Intake refers to the capture area definition and attached ducting to an aircraft gas turbine engine or ramjet engine and, as such, an intake is followed by a compressor or combustion chamber. It may instead be referred to as a diffuser (other), diffuser. For an automobile engine the components through which the air flows to the engine cylinders, are collectively known as an intake syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or r⋅min−1) is a unit of rotational speed (or rotational frequency) for rotating machines. One revolution per minute is equivalent to hertz. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a physical quantity called ''rotation'' (or ''number of revolutions''), dimensionless, whose instantaneous rate of change is called ''rotational frequency'' (or ''rate of rotation''), with units of reciprocal seconds (s−1). A related but distinct quantity for describing rotation is ''angular frequency'' (or ''angular speed'', the magnitude of angular velocity), for which the SI unit is the radian per second (rad/s). Although they have the same dimensions (reciprocal time) and base unit (s−1), the hertz (Hz) and radians per second (rad/s) are special names used to express two different but proportional ISQ quantities: frequency and angular frequency, respectively. The conversions between a frequency and an angular frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golf Ball
A golf ball is a ball designed to be used in golf. Under the rules of golf, a golf ball has a mass no more than , has a diameter not less than , and performs within specified velocity, distance, and symmetry limits. Like golf clubs, golf balls are subject to testing and approval by The R&A (formerly part of the Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews) and the United States Golf Association, and those that do not conform with regulations may not be used in competitions ''(Rule 5–1)''. History Early balls It is commonly believed that hard wooden, round balls, made from hardwoods such as beech and box, were used for golf from the 14th through the 17th centuries. Though wooden balls were no doubt used for other similar contemporary stick and ball games, there is no definite evidence that they were actually used in golf in Scotland. It is equally likely, if not more so, that leather balls filled with cows' hair were used, imported from the Netherlands from at least 1486 onwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a Boundary (thermodynamic), bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces a No-slip condition, no-slip boundary condition (zero velocity at the wall). The flow velocity then monotonically increases above the surface until it returns to the bulk flow velocity. The thin layer consisting of fluid whose velocity has not yet returned to the bulk flow velocity is called the velocity boundary layer. The air next to a human is heated, resulting in gravity-induced convective airflow, which results in both a velocity and thermal boundary layer. A breeze disrupts the boundary layer, and hair and clothing protect it, making the human feel cooler or warmer. On an aircraft wing, the velocity boundary layer is the part of the flow close to the wing, where viscosity, viscous forces distort the surrounding non-viscous flow. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement (engine), displacement. It is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and increase power outputs, especially with reduced engine dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
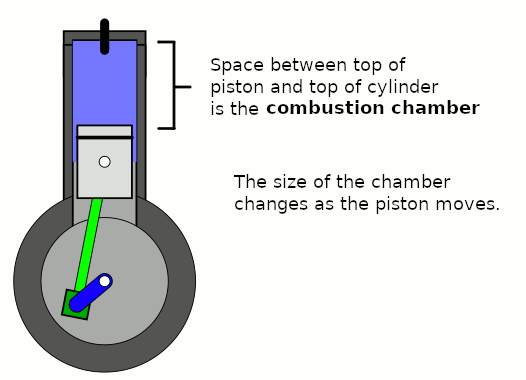
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol engine, petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Centre (engineering)
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either furthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as top dead centre (TDC) while the latter is known as bottom dead centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
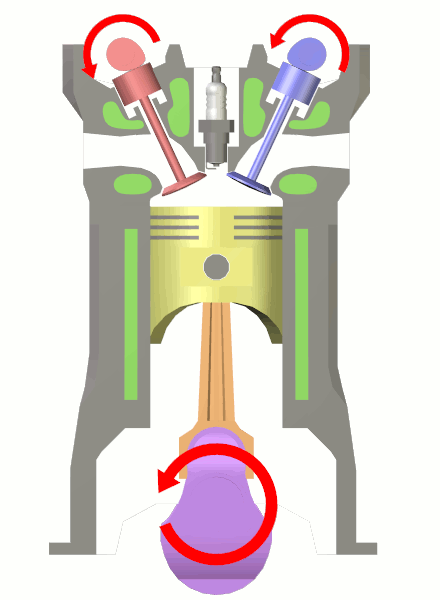
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting (metalworking), casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft is located within the engine block and held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecting Rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a reciprocating engine, piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank (mechanism), crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaft. The connecting rod is required to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the piston. In its most common form, in an internal combustion engine, it allows pivoting on the piston end and rotation on the shaft end. The predecessor to the connecting rod is a mechanic linkage used by water mills to convert rotating motion of the water wheel into reciprocating motion. The most common usage of connecting rods is in internal combustion engines or on steam engines. __TOC__ Origins A connecting rod crank has been found in the Celtic Oppida at Paule in Brittany, dated to 69 BC. The predecessor to the connecting length is the Linkage (mechanical), mechanical linkage used by List of Roman wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elasticity (solid mechanics), elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in dry air (sea level 14.7 psi) is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in dry air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in Earth's atmosphere, air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |