|
Cyfeilliog
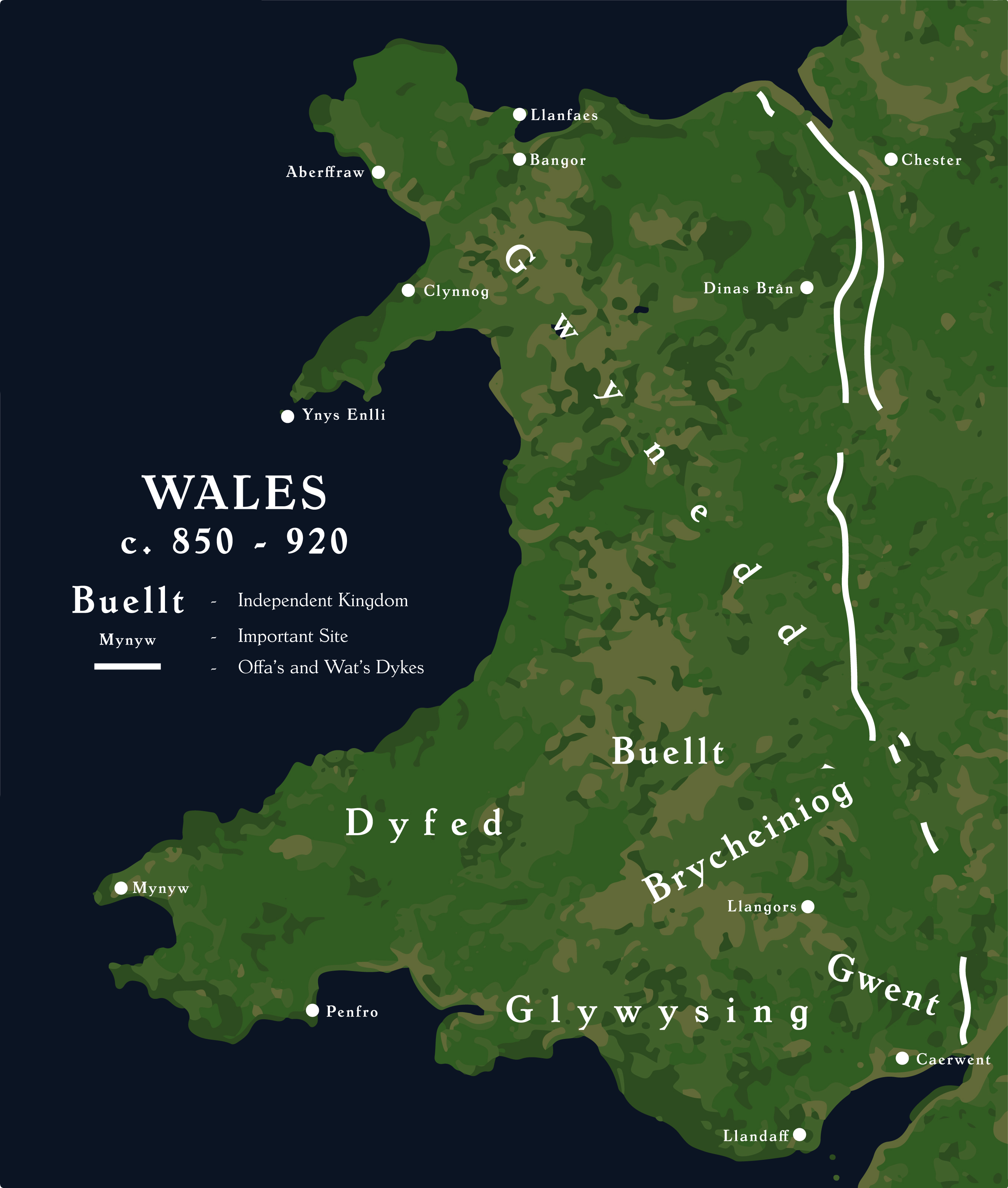
Cyfeilliog () or Cyfeiliog (, in Old Welsh ''Cemelliauc''; probably died 927) was a bishop in south-east Wales. The location and extent of his diocese is uncertain, but lands granted to him are mainly close to Caerwent, suggesting that his diocese covered Kingdom of Gwent, Gwent. There is evidence that his diocese extended into Ergyng (now south-west Herefordshire). He is recorded in charters dating from the mid-880s to the early tenth century. In 914 he was captured by the Vikings and ransomed by Edward the Elder, King of the Anglo-Saxons, for 40 pounds of silver. Edward's assistance is regarded by historians as evidence that he inherited the overlordship of his father, Alfred the Great, over the south-east Welsh kingdoms. Cyfeilliog is probably the author of a cryptogram (encrypted text) which was added as a marginal note to the ninth-century collection of poetry known as the Juvencus Manuscript. Composing the cryptogram would have required knowledge of Latin and Greek. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvencus Manuscript
The Juvencus Manuscript (Cambridge, Cambridge University Library, MS Ff. 4.42; ) is one of the main surviving sources of Old Welsh. Unlike much Old Welsh, which is attested in manuscripts from later periods and in partially updated form, the Welsh material in the Juvencus Manuscript was written during the Old Welsh period itself; the manuscript provides the first attestation of many Welsh words. Around the second half of the ninth century, someone copied two Old Welsh poems into the margins: a nine-stanza ''englyn'' poem on the wonders of God's creation (generally known as the 'Juvencus nine'), and, on folios 25–26, a three-stanza poem which seems to represent a warrior lamenting his misfortunes (known as the 'Juvencus three'). These are the earliest surviving ''englynion''. The parts of the manuscript containing the 'Juvencus three' were cut out of the manuscript and stolen in the early eighteenth century by the antiquary Edward Lhuyd (1660-1709), but were found after his death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward The Elder
Edward the Elder (870s?17 July 924) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin Æthelwold ætheling, Æthelwold, who had a strong claim to the throne as the son of Alfred's elder brother and predecessor, Æthelred I. Alfred had succeeded Æthelred as king of Wessex in 871, and almost faced defeat against the Danish Vikings until his decisive victory at the Battle of Edington in 878. After the battle, the Vikings still ruled Northumbria, Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia and eastern Mercia, leaving only Wessex and western Mercia under Anglo-Saxon control. In the early 880s Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians, the ruler of western Mercia, accepted Alfred's lordship and married his daughter Æthelflæd, and around 886 Alfred adopted the new title King of the Anglo-Saxons as the ruler of all Anglo-Saxons not subject to D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval South-east Wales Map Lloyd
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire—came unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg. Name and early history Glywysing is said in medieval Welsh tradition to be named after Glywys, supposedly an early king of the region. In reality, the name probably comes from '' Glevum'', the Roman name for what is now Gloucester, via a Latin name *''Glevenses'' ('people of Glevum') or *''Glevensis'' ('person from Glevum'). Thus the name suggests that the kingdom was named after invaders or migrants, or a particular ruler, from Glevum. According to 12th-century sources, after the death of Glywys, the kingdom was divided into three cantrefs named for his sons: Penychen, Gwynllwg, and Gorfynydd. These were typically ruled together by the head of the family and sometimes treated as appenage subkingdoms. Location The borders changed over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ffernfael Ap Meurig
Ffernfael ap Meurig or Ffyrnfael or Fernmail, fl. 880s, was king of Gwent in southeast Wales jointly with his brother Brochfael ap Meurig. Asser says in his biography of Alfred the Great that "Brochfael and Ffyrnfael, (sons of Meurig and kings of Gwent), driven by the might and tyrannical behaviour of Ealdorman Æthelred and the Mercians, petitioned King Alfred of their own accord, in order to obtain lordship and protection from him in the face of their enemies". In early medieval Wales, it was common for brothers to share the kingship. Brochfael and Ffernfael are both listed in the Book of Llandaff The Book of Llandaff (; , ', or '), is the cartulary of the cathedral of Llandaff, a 12th-century compilation of documents relating to the history of the diocese of Llandaff in Wales. It is written primarily in Latin but also contains a signific ... as witnesses to a charter of their father, but Ffernfael does not witness any surviving charter of his own, whereas several show Bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hywel Ap Rhys (Glywysing)
Hywel ap Rhys ('Hywel son of Rhys') (ruled 886) was a king of Glywysing (either in part or in its entirety) in South Wales. His sons Arthfael and Owain were probably responsible for the reünification of the realm of Morgannwg.Charles-Edwards, T. Wales and the Britons, 3501064', p. 495. Oxford Univ. Press, 2012. Accessed 20 Feb 2013. His grandsons, Owain's sons, Gruffydd ab Owain (died c. 935 at the hands of troops from Ceredigion) and Cadwgan ab Owain (died c. 949 0r 951, "murdered by the Saxons") ruled as joint kings of Glywysing from c. 930 until their deaths, before the surviving brother Morgan Hen ab Owain (d. 974), having previously ruled as King of Gwent, brought the territories together under him as the Kingdom of Morgannwg. The Houelt Cross A cross in the collection of ancient stones at St Illtyd's Church, Llantwit Major has been identified with Hywel. The ''Houelt Cross'' has a Latin inscription written in half-uncial Latin which has consistently been interpreted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asser
Asser (; ; died 909) was a Welsh people, Welsh monk from St David's, Kingdom of Dyfed, Dyfed, who became Bishop of Sherborne (ancient), Bishop of Sherborne in the 890s. About 885 he was asked by Alfred the Great to leave St David's and join the circle of learned men whom Alfred was recruiting for his court. After spending a year at Caerwent because of illness, Asser accepted. In 893, Asser wrote a biography of Alfred, called the ''Life of King Alfred''. The manuscript survived to modern times in only one copy, which was part of the Cotton library. That copy was destroyed in a fire in 1731, but transcriptions that had been made earlier, together with material from Asser's work which was included by other early writers, have made it possible to reconstruct the work. The biography is the main source of information about Alfred's life and provides far more information about Alfred than is known about any other early English ruler. Asser assisted Alfred in his translation of Grego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886. The Anglo-Saxons believed that Wessex was founded by Cerdic and Cynric of the Gewisse, though this is considered by some to be a legend. The two main sources for the history of Wessex are the West Saxon Genealogical Regnal List and the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (the latter of which drew on and adapted an early version of the List), which sometimes conflict. Wessex became a Christianity, Christian kingdom after Cenwalh () was baptised and was expanded under his rule. Cædwalla later conquered Kingdom of Sussex, Sussex, Kingdom of Kent, Kent and the Isle of Wight. His successor, Ine of Wessex, Ine (), issued one of the oldest surviving English law codes and established a second West Saxon bishopric. The throne subsequently passed to a series of kings wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelred, Lord Of The Mercians
Æthelred (died 911) became Lord of the Mercians in England shortly after the death or disappearance of Mercia's last king, Ceolwulf II, in 879. He is also sometimes called the Ealdorman of Mercia. Æthelred's rule was confined to the western half, as eastern Mercia was then part of the Viking-ruled Danelaw. His ancestry is unknown. He was probably the leader of an unsuccessful Mercian invasion of Wales in 881, and soon afterwards he acknowledged the lordship of King Alfred the Great of Wessex. This alliance was cemented by the marriage of Æthelred to Alfred's daughter Æthelflæd. In 886, Alfred took possession of London, which had suffered greatly from several Viking occupations. Alfred then handed London over to Æthelred, as it had traditionally been a Mercian town. In 892, the Vikings renewed their attacks, and the following year, Æthelred led an army of Mercians, West Saxons and Welsh to victory over a Viking army at the Battle of Buttington. He spent the next thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
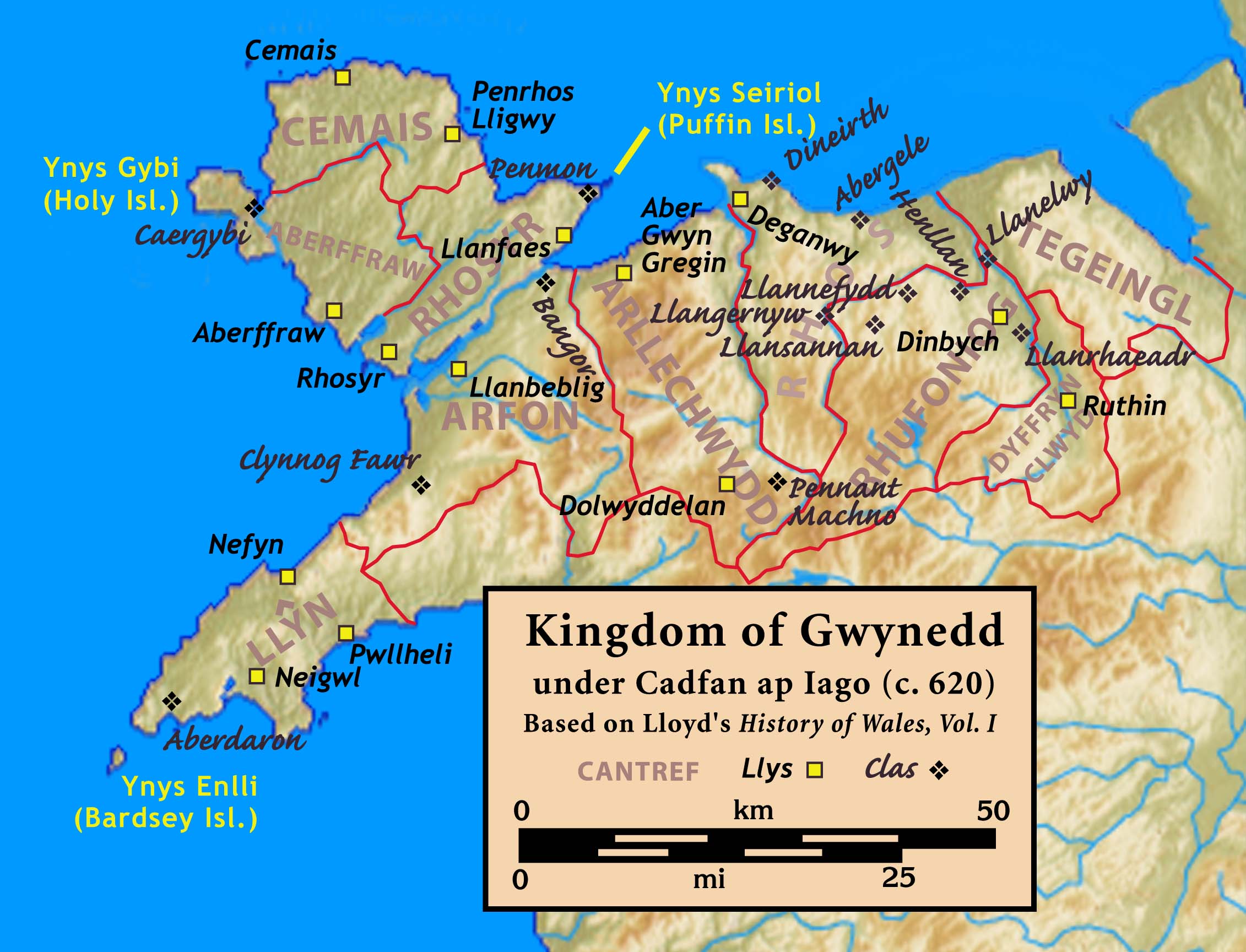
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodri Mawr
Rhodri ap Merfyn, commonly known as , was a Welsh king whose legacy has impacted the history of Wales. Rhodri rose to power during a tumultuous era, where the fate of Welsh kingdoms was often determined by the power of their leaders. Early life Rhodri was born in the 9th century on the Isle of Man. Rhodri was the son of Merfyn Frych, Merfyn, who, under enigmatic circumstances, assumed the kingship of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd following the death of Hywel ap Rhodri Molwynog, Hywel ap Caradog in 825. Rhodri ascended to the throne of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd following the passing of his father, Merfyn Frych, Merfyn, in the year 844. Reign Rhodri's reign unfolded against a tumultuous backdrop, as Wales confronted escalating Vikings, Viking incursions. Among Rhodri's earliest recorded achievements was his defeat and killing of Gorm, a Danes, Danish chieftain, in a battle on Anglesey in 856. This victory garnered international acclaim, reaching the ears of Charles the Bald whos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |