|
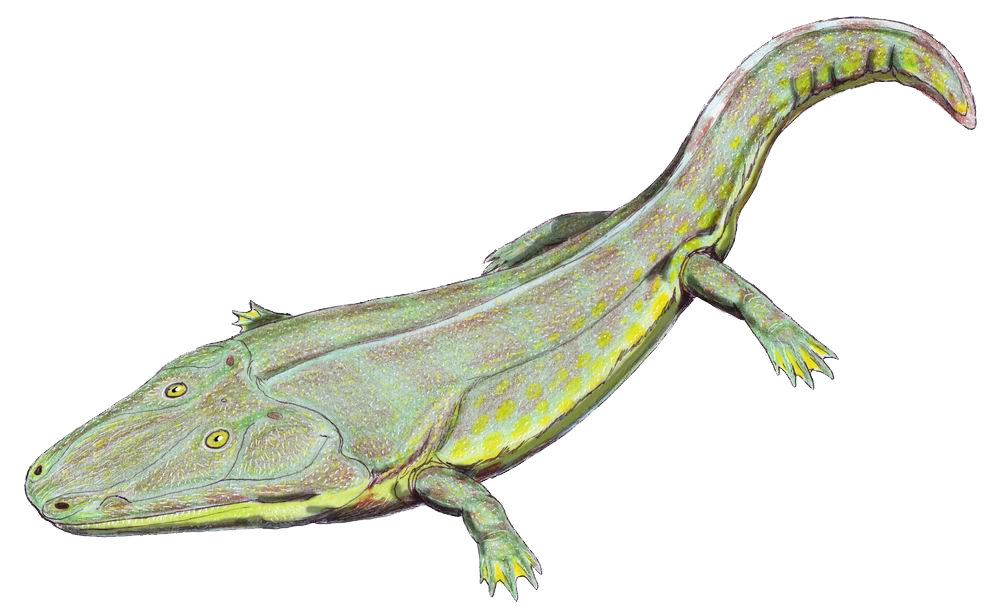
Cyclotosaurus
''Cyclotosaurus'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae. It was of great size for an amphibian, had an elongated skull up to . Etymology The name means "round eared lizard" in Ancient Greek, derived from round openings or fenestrae in the cheeks, which are thought to contain structures of the middle ear. History German naturalist Eberhard Fraas erected the genus ''Cyclotosaurus'' in 1889, with ''C. robustus'' (previously ''Mastodonsaurus robustus'') as the type species. Several species are known, mainly from Germany and Poland in Central Europe, as well as East Greenland and Thailand. The relationships between species is unclear. ''"Labyrinthodon" pachygnathus'' Owen, 1842 and ''"L." leptognathus'' Owen, 1842 were transferred to ''Cyclotosaurus'', as ''C. pachygnathus'' and ''C. leptognathus'', by Paton (1974). However, Damiani (2001) assigned the two species to Mastodonsauroidea indeterminate and Stereospondyli indeterminate. Palaeont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotosaurus Buechneri
''Cyclotosaurus buechneri'' is a species of the temnospondyl genus ''Cyclotosaurus'' from the Upper Triassic ( middle Carnian) of northwestern Germany. The type and only known specimen is a 28 cm long skull that was found in 1975 by Martin Büchner, the former director of the Natural History Museum Bielefeld, at a construction site in Bielefeld-Sieker, Germany. The specimen derives from the Stuttgart Formation The Stuttgart Formation is a geologic formation in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic period. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schilfsandstein Formation
The Stuttgart Formation is a geologic formation in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic period.Stuttgart Formation at .org Fossil content Temnospondyls * ''''Witzmann et al., 2016 * '' C. robustus''Schoch & Milner, 2000 * ''[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleming Fjord Formation
The Fleming Fjord Formation, alternatively called the Fleming Fjord Group is an Upper Triassic geological formation in the northeastern coast of Jameson Land, Greenland. It consists of terrestrial sediments and is known for its fossil content. Description It is of Norian to Rhaetian age and is subdivided into three members; at the base the Edderfugledal Member, followed by the Malmros Klint Member with the Ørsted Dal Member at the top. It was deposited in a large shallow to ephemeral lake. Paleobiota The fauna of Fleming Fjord is diverse, including sauropodomorph dinosaurs, pterosaurs, temnospondyls, mammaliaforms, aetosaurs, and other taxa. Freshwater unionid bivalves and conchostracans have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Fish Lungfish, actinopterygian, and chondrichthyan teeth have been reported from the Malmros Klint Member. Amphibians Reptiles Besides the forms described below, a diverse ichnofauna of small and large tracks has also been reporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart Formation
The Stuttgart Formation is a geologic formation in Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic period.Stuttgart Formation at .org Fossil content Temnospondyls * ''''Witzmann et al., 2016 * '' C. robustus''Schoch & Milner, 2000 * ''[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastodonsauridae
Mastodonsauridae is a family of capitosauroid temnospondyls. Fossils belonging to this family have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The family Capitosauridae is synonymous with Mastodonsauridae. Description Size Mastodonsaurids were generally large amphibians, with some length estimates ranging from 3 to 6 meters. Some genera, like ''Mastodonsaurus'' and ''Cyclotosaurus'' were specially large, reaching at least 4 meters or more. Other genera like ''Parotosuchus'' and '' Paracyclotosaurus'' only reached 2 meters or more in length, but it's still pretty large compared to modern-day amphibians. Distinguishing features Some mastodonsaurids including ''Parotosuchus'' were covered in a scaly skin, unlike the smooth skin of modern-day amphibians, and probably moved with an eel-like motion in the water. Another peculiar mastodonsaurid is ''Sclerothorax'', with unusual features including its elongated neural spines. The neural spines are tallest at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasiejów
Krasiejów (german: Krascheow) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ozimek, within Opole County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately east of Ozimek and east of the regional capital Opole. The village has a population of 2,050. Paleontological localities Abundant skeletons of the Upper Triassic tetrapods (i.e., large Temnospondyli: ''Metoposaurus'' and ''Cyclotosaurus''; reptiles: ''Paleorhinus'', dinosauriformes '' Silesaurus'') were described from the pit. Two paleontological museums and large dinopark (so-called JuraPark) are at Krasiejów. Some microvertebrate fossils, fossil plants, bivalves, crustaceans and fish scales were also collected at the site. History The village was first mentioned in the 13th century, when it was part of Piast-ruled Poland. Its name is of Polish origin, and comes from the Old Polish words ''kraszenie'' or ''krasny''. Later on, the village was also part of Bohemia (Czechia), Prussia and Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastodonsaurus
''Mastodonsaurus'' (meaning "teat tooth lizard") is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Middle Triassic of Europe. It belongs to a Triassic group of temnospondyls called Capitosauria, characterized by their large body size and presumably aquatic lifestyles. ''Mastodonsaurus'' remains one of the largest amphibians known, and may have exceeded 6 meters (20 feet) in length. Description Like those of many other capitosaurs, the head of ''Mastodonsaurus'' was triangular, reaching about in the largest specimens. Narrow grooves on the surface of the skull bones called sulci show it had sensory organs that could detect vibrations and pressure under water, similar to the lateral lines on fish. The large, oval eye sockets are midway along the skull with the nostrils near the tip of the snout. Small ear holes (otic notches) are indented on either side of the back of the skull. The upper surface of the skull bones of ''Mastodonsaurus'' bore an intricate pattern of pits and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart-Feuerbach
Feuerbach is a borough (''Stadtbezirk'') of the city of Stuttgart. Its name is derived from the small river of the same name that flows from the neighboring district of Botnang through Feuerbach. Feuerbach is home to one of Germany's biggest industrial giants and is surrounded by the districts of Zuffenhausen, Bad Cannstatt, Stuttgart-North, Stuttgart-West, Botnang and Weilimdorf. History The remains of a prehistoric settlement were uncovered in 1904, when the pastor of Feuerbach, Richard Kallee excavated, archeologically documented and published a total of 102 Alemannic sandstone tombs and cists. Heinz Krämer: Fertig Feuerbach! Richard Kallee, Pfarrer und Geschichtsforscher '' in German, DRW Verlag, Leinfelden-Echterdingen, 2004, . Was die alten Steine in Feuerbach erzählen'' in German, 1923. Together with his helpers he took great care to recover 760 artifacts from these Alemannic graves: skulls and bones, coins, pottery shards, combs, necklaces, belts, locks, swords, sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasensandstein Formation
The Blasensandstein is a Carnian geologic member in Bavaria, Germany. It is part of the Hassberge Formation The Hassberge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Bavaria, Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic Period (geology), period.Hassberge Formation The Hassberge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Bavaria, Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic Period (geology), period.Hassberge Formation The Hassberge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Bavaria, Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic Period (geology), period.Hassberge Formation The Hassberge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation in Bavaria, Germany. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carnian stage of the Triassic Period (geology), period.Hassberge Formation The Hassberge Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebrach
Ebrach is a municipality with market rights in the Upper Franconian district of Bamberg and the seat of the ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' (municipal association) of Ebrach. Geography Ebrach lies between Bamberg in the east and Würzburg in the west. It is located in the Steigerwald on the river Mittlere Ebrach. Constituent communities Ebrach’s main and namesake centre is by far the biggest of its ''Ortsteile'' with a population of 1,078. The market community furthermore has these outlying centres, each given here with its own population figure: *Buch bei Ebrach: 55 *Eberau bei Ebrach: 122 *Großbirkach: 68 *Großgressingen: 251 *Hof bei Ebrach: 15 *Kleinbirkach: 36 *Kleingressingen: 40 *Meierei bei Ebrach: 7 *Neudorf bei Ebrach: 93 *Schmerb: 4 *Winkelhof: 6 The community also has five traditional rural land units, known in German as ''Gemarkungen'', named Buch, Ebrach, Großbirkach, Großgressingen and Neudorf bei Ebrach, the same names as five of the constituent communities (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |