|
Cyclooctasulfur
Octasulfur is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula . It is an odourless and tasteless yellow solid, and is a major industrial chemical. It is the most common allotrope of sulfur and occurs widely in nature.Steudel, R., "Homocyclic Sulfur Molecules", Topics Curr. Chem. 1982, 102, 149. Nomenclature The name octasulfur is the most commonly used for this chemical. It is systematically named ''cyclo''-octasulfur (which is the preferred IUPAC name) and cyclooctasulfane. It is also the final member of the thiocane heterocylic series, where every carbon atom is substituted with a sulfur atom, thus this sulfur allotrope is systematically named octathiocane as well. Structure The chemical consists of rings of 8 sulfur atoms. It adopts a crown conformation with D4d point group symmetry. The S–S bond lengths are equal, at about 2.05 Å. Octasulfur crystallizes in three distinct polymorphs: rhombohedral, and two monoclinic forms, of which only two are stable at standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexathiane
Hexasulfur is an inorganic chemical with the chemical formula . This allotrope was first prepared by M. R. Engel in 1891 by treating thiosulfate with HCl. ''Cyclo''- is orange-red and forms a rhombohedral crystal. It is called ρ-sulfur, ε-sulfur, Engel's sulfur and Aten's sulfur. Another method of preparation involves the reaction of a polysulfane with sulfur monochloride: : (dilute solution in diethyl ether) Nomenclature The name hexasulfur is the most commonly used and preferred IUPAC name and is constructed according to the compositional nomenclature, and cyclohexasulfane. It is also the final member of the thiane heterocyclic series, where every carbon atom is substituted with a sulfur atom, thus the systematic name hexathiane, a valid IUPAC name, is constructed according to the substitutive nomenclature. Another valid IUPAC systematic name ''cyclo''-hexasulfur is constructed according to the additive nomenclature. Structure This chemical consists of rings of 6 sulfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claus Process
The Claus process is the most significant gas desulfurizing process, recovering elemental sulfur from gaseous hydrogen sulfide. First patented in 1883 by the chemist Carl Friedrich Claus, the Claus process has become the industry standard. The multi-step Claus process recovers sulfur from the gaseous hydrogen sulfide found in raw natural gas and from the by-product gases containing hydrogen sulfide derived from refining crude oil and other industrial processes. The by-product gases mainly originate from physical and chemical gas treatment units ( Selexol, Rectisol, Purisol and amine scrubbers) in refineries, natural gas processing plants and gasification or synthesis gas plants. These by-product gases may also contain hydrogen cyanide, hydrocarbons, sulfur dioxide or ammonia. Gases with an H2S content of over 25% are suitable for the recovery of sulfur in straight-through Claus plants while alternate configurations such as a split-flow set up or feed and air preheatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Element Minerals
Native element minerals are those elements that occur in nature in uncombined form with a distinct mineral structure. The elemental class includes metals, intermetallic compounds, alloys, metalloids, and nonmetals. The Nickel–Strunz classification system also includes the naturally occurring phosphides, silicides, nitrides, carbides, and arsenides. Elements The following elements occur as native element minerals or alloys: Nickel–Strunz Classification -01- Native elements This list uses the Classification of Nickel–Strunz ( mindat.org, 10 ed, pending publication). ;Abbreviations: * "*" – discredited (IMA/CNMNC status). * "?" – questionable/doubtful (IMA/CNMNC status). * "REE" – Rare-earth element (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) * "PGE" – Platinum-group element (Ru, Rh, Pd, Os, Ir, Pt) * 03.C Aluminofluorides, 06 Borates, 08 Vanadates (04.H V ,6/sup> Vanadates), 09 Silicates: ** Neso: insular (from Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietary Minerals
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element. Some "minerals" are essential for life, but most are not. ''Minerals'' are one of the four groups of essential nutrients; the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. The five major minerals in the human body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and magnesium. The remaining minerals are called " trace elements". The generally accepted trace elements are iron, chlorine, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, iodine, selenium, and bromine; there is some evidence that there may be more. The four organogenic elements, namely carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen ( CHON), that comprise roughly 96% of the human body by weight, are usually not considered as minerals (nutrient). In fact, in nutrition, the term "mineral" refers more generally to all the other functional and structural elements found in living organisms. Plants obtain minerals from soil. Animals ingest plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology And Pharmacology Of Chemical Elements
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Modern biology is grounded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Chemicals
An agrochemical or agrichemical, a contraction of ''agricultural chemical'', is a chemical product used in industrial agriculture. Agrichemical typically refers to biocides (pesticides including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and nematicides) alongside synthetic fertilizers. It may also include hormones and other chemical growth agents. Though the application of mineral fertilizers and pesticidal chemicals has a long history, the majority of agricultural chemicals were developed from the 19th century, and their use were expanded significantly during the Green Revolution and the late 20th century. Agriculture that uses these chemicals is frequently called conventional agriculture. Agrochemicals are counted among speciality chemicals. Most agrochemicals are products of the petrochemical industry, where chemicals are derivatives of fossil fuels. The production and use of agrochemicals contribute substantially to climate change, both through direct emissions during production, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur (pharmacy)
Sulfur is used in pharmaceutical skin preparations for the treatment of acne and other conditions. It acts as a keratolytic agent and also kills bacteria, fungi, scabies mites and other parasites. Chemically, it is the naturally occurring octasulfur (S8). Forms and uses * ''Flowers of sulfur'' or ''sublimed sulfur'' (Latin: ''sulfur sublimatum'') is the naturally occurring, unpurified form. It comes in yellow flakes and has been used in traditional medicine, traditional and alternative medicine, alternative medicine for humans and animals, as well as in alchemy and sulfuring fruit before Drying (food), drying. * ''Purified sulfur'' (''sulfur depuratum'') is prepared by washing sublimed sulfur with ammonia. It is a fine yellow powder. It was formerly used as a laxative, but this application is rare today. * ''Precipitated sulfur'' (''sulfur praecipitatum'') is prepared by boiling sulfur and calcium oxide in water and then precipitation (chemistry), precipitating with hydrochloric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
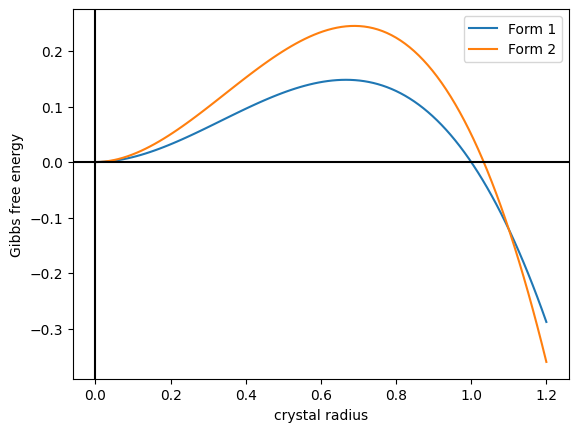
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard State
The standard state of a material (pure substance, mixture or solution) is a reference point used to calculate its properties under different conditions. A degree sign (°) or a superscript ⦵ symbol (⦵) is used to designate a thermodynamic quantity in the standard state, such as change in enthalpy (Δ''H''°), change in entropy (Δ''S''°), or change in Gibbs free energy (Δ''G''°). The degree symbol has become widespread, although the Plimsoll is recommended in standards, see discussion about typesetting below. In principle, the choice of standard state is arbitrary, although the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends a conventional set of standard states for general use. The standard state should not be confused with standard temperature and pressure (STP) for gases, nor with the standard solutions used in analytical chemistry. STP is commonly used for calculations involving gases that approximate an ideal gas, whereas standard state condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with chemical synthesis, synthesis and behavior of inorganic compound, inorganic and organometallic chemistry, organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, pharmaceutical drug, medications, fuels, and agriculture. Occurrence Many inorganic compounds are found in nature as minerals. Soil may contain iron sulfide as pyrite or calcium sulfate as gypsum. Inorganic compounds are also found multitasking as biomolecules: as electrolytes (sodium chloride), in energy storage (Adenosine triphosphate, ATP) or in construction (the polyphosphate backbone in DNA). Bonding Inorganic compounds exhibit a range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). It was originally spelled with Swedish letters, as Ångström and later as ångström (). The latter spelling is still listed in some dictionaries, but is now rare in English texts. Some popular US dictionaries list only the spelling ''angstrom''. The unit's symbol is Å, which is a letter of the Swedish alphabet, regardless of how the unit is spelled. However, "A" or "A.U." may be used in less formal contexts or typographically limited media. The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals, wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, and dimensions of integrated circuit part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |