|
Cyclonic Niño
Cyclonic Niño is a climatological phenomenon that has been observed in climate models where tropical cyclone activity is increased. Increased tropical cyclone activity mixes ocean waters, introducing Cold wake, cooling in the upper layer of the ocean that quickly dissipates and warming in deeper layers that lasts considerably more, resulting in a net warming of the ocean. In climate simulations of the Pliocene, this net warming is then transported by ocean currents and part of it ends up in the Eastern Pacific, warming it relative to the Western Pacific Ocean, Western Pacific and thus creating El Niño-like conditions. Reconstructed temperatures in the Pliocene have shown an El Niño-like pattern of ocean temperatures that may be explained by increased tropical cyclone activity and thus increased temperatures in the Eastern Pacific. Some of the heat is transported away from the tropics and may be responsible for past episodes of warmer-than-usual climate, such as in the Eocene and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chan-hom 2003-05-23 0314Z
The name Chan-hom has been used to name four tropical cyclones in the Western North Pacific Ocean. The name refers to a type of tree and was submitted by Laos. * Typhoon Chan-hom (2003) (T0303, 04W), strong storm that stayed away from land * Typhoon Chan-hom (2009) (T0902, 02W, Emong), formed off Vietnam, reached typhoon status before landfall in the Philippines * Typhoon Chan-hom (2015) (T1509, 09W, Falcon), a large typhoon which affected several countries in eastern Asia * Typhoon Chan-hom (2020) (T2014, 16W), a typhoon that brushed Japan {{DEFAULTSORT:Chan-Hom Pacific typhoon set index articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area are Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson, Arizona, Tucson. Before 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of New Mexico's pueblos and Santa Fe de Nuevo México#Regions and municipalities, Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Sst Anomaly
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the |
Earth's Energy Budget
Earth's energy budget (or Earth's energy balance) is the balance between the energy that Earth receives from the Sun and the energy the Earth loses back into outer space. Smaller energy sources, such as Earth's internal heat, are taken into consideration, but make a tiny contribution compared to solar energy. The energy budget also takes into account how energy moves through the climate system. The Sun heats the equatorial tropics more than the polar regions. Therefore, the amount of solar irradiance received by a certain region is unevenly distributed. As the energy seeks equilibrium across the planet, it drives interactions in Earth's climate system, i.e., Earth's water, ice, atmosphere, rocky crust, and all living things. The result is Earth's climate. Earth's energy budget depends on many factors, such as atmospheric aerosols, greenhouse gases, surface albedo, clouds, and land use patterns. When the incoming and outgoing energy fluxes are in balance, Earth is in radiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Altimeter
Satellite geodesy is geodesy by means of artificial satellites—the measurement of the form and dimensions of Earth, the location of objects on its surface and the figure of the Earth's gravity field by means of artificial satellite techniques. It belongs to the broader field of space geodesy. Traditional geodetic astronomy, astronomical geodesy is ''not'' commonly considered a part of satellite geodesy, although there is considerable overlap between the techniques. The main goals of satellite geodesy are: # Determination of the figure of the Earth, positioning, and navigation (geometric satellite geodesy) # Determination of geoid, gravity of Earth, Earth's gravity field and its temporal variations (dynamical satellite geodesy or satellite physical geodesy) # Measurement of geodynamics, geodynamical phenomena, such as Crust (geology), crustal dynamics and polar motion Satellite geodetic data and methods can be applied to diverse fields such as navigation, hydrography, oceanogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Heat Content
Ocean heat content (OHC) or ocean heat uptake (OHU) is the energy absorbed and stored by oceans, and is thus an important indicator of global warming. Ocean heat content is calculated by measuring ocean temperature at many different locations and depths, and integrating the areal density of a change in enthalpic energy over an ocean basin or entire ocean. Between 1971 and 2018, a steady upward trendNOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, Assessing the Global Climate in 2024, published online January 2025, Retrieved on March 2, 2025 from https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/news/global-climate-202413. in ocean heat content accounted for over 90% of Earth's excess energy from global warming. Scientists estimate a 1961–2022 warming trend of 0.43±0.08W/m², accelerating at about 0.15±0.04W/m² perdecade. By 2020, about one third of the added energy had propagated to depths below 700 meters. In 2024, the world's oceans were again the hottest in the historical record and excee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
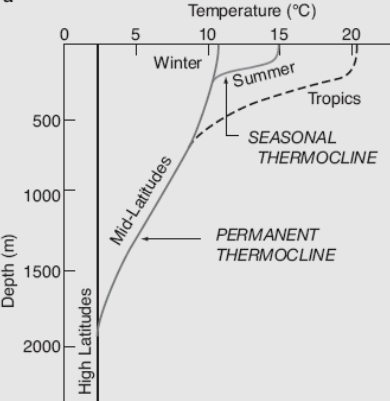
Thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) with a high gradient of distinct temperature differences associated with depth. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below. Depending largely on season, latitude, and turbulent mixing by wind, thermoclines may be a semi-permanent feature of the body of water in which they occur, or they may form temporarily in response to phenomena such as the radiative heating/cooling of surface water during the day/night. Factors that affect the depth and thickness of a thermocline include seasonal weather variations, latitude, and local environmental conditions, such as tides and currents. Oceans Most of the heat energy of the sunlight that strikes the Earth is absorbed in the first few centimeters at the ocean's surface, which hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Wake
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system A storm is any disturbed state of the natural environment or the atmosphere of an astronomical body. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm) ... with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |