|
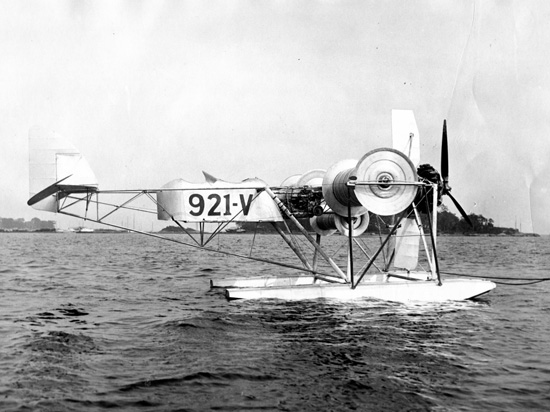
Cyclogyro
The cyclogyro, or cyclocopter, is an aircraft configuration that uses a horizontal-axis cyclorotor as a rotor wing to provide lift and, sometimes, also propulsion and control. In principle, the cyclogyro is capable of VTOL, vertical take off and landing and hovering performance, like a helicopter, while potentially benefiting from some of the advantages of a fixed-wing aircraft. The cyclogyro is distinct from the Flettner airplane, which uses a cylindrical wing rotor to harness the Magnus effect. The cyclogyro's cyclorotor is similar to a Voith Schneider Propeller, Voith Drive, which is a type of propeller used on some boats. They work in almost exactly the same way, except a Voith Drive can produce a force in any direction, whilst a cyclogyro is only designed to produce lift in upwards directions. The other main difference is that Voith Drives work underwater but cyclogyros work in air. Principles of operation The cyclogyro wing resembles a paddle wheel, with airfoil blades re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclorotor
A cyclorotor, cycloidal rotor, cycloidal propeller or cyclogiro, is a fluid propulsion device that converts shaft power into the acceleration of a fluid using a rotating axis perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. It uses several blades with a spanwise axis parallel to the axis of rotation and perpendicular to the direction of fluid motion. These blades are cyclically pitched twice per revolution to produce force (thrust or lift) in any direction normal to the axis of rotation. Cyclorotors are used for propulsion, lift, and control on air and water vehicles. An aircraft using cyclorotors as the primary source of lift, propulsion, and control is known as a cyclogyro or cyclocopter. A unique aspect is that it can change the magnitude and direction of thrust without the need of tilting any aircraft structures. The patented application, used on ships with particular actuation mechanisms both mechanical or hydraulic, is a Voith Schneider Propeller. Operating principle The b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can takeoff and landing, take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-wing aircraft and other hybrid aircraft with powered helicopter rotor, rotors such as cyclogyro, cyclogyros/cyclocopters and gyrodynes. Some VTOL aircraft can operate in other modes as well, such as CTOL (conventional take-off & landing), STOL (short take-off & landing), or STOVL (short take-off & vertical landing). Others, such as some helicopters, can only operate as VTOL, due to the aircraft lacking landing gear that can handle taxiing. VTOL is a subset of V/STOL (vertical or short take-off & landing). Some aerostat, lighter-than-air aircraft also qualify as VTOL aircraft, as they can hover, takeoff and land with vertical approach/departure profiles. Electric vertical takeoff and landing aircraft, or eVTOLs, are being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which Lift (force), lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning Helicopter rotor, rotors. This allows the helicopter to VTOL, take off and land vertically, to hover (helicopter), hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. The Focke-Wulf Fw 61 was the first successful, practical, and fully controllable helicopter in 1936, while in 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale mass production, production. Starting in 1939 and through 1943, Igor Sikorsky worked on the development of the Vought-Sikorsky VS-300, VS-300, which over four iterations, became the basis for modern helicopters with a single main rotor and a single tail rotor. Although most earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flettner Airplane
A Flettner airplane is a type of rotor airplane which uses a Flettner rotor to provide lift. The rotor comprises a spinning cylinder with circular end plates and, in an aircraft, spins about a spanwise horizontal axis. When the aircraft moves forward, the Magnus effect creates lift. Anton Flettner, after whom the rotor is named, used it successfully as the sails of a rotor ship. He also suggested its use as a wing for a rotor airplane. The Butler Ames Aerocycle was built in 1910 and tested aboard a warship. There is no record of it having flown. The Plymouth A-A-2004 was built for Zaparka in 1930 by three anonymous American inventors. It was reported to have made successful flights over Long Island Sound. An inherent safety concern is that if power to the rotating drums were lost—even if thrust was maintained—the aircraft would lose its ability to generate lift as the drum slowed and it would not be able to sustain flight. See also * Cyclogyro * FanWing * Servo tab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voith Schneider Propeller
The Voith Schneider Propeller (VSP) is a specialized marine propulsion system (MPS) manufactured by the Voith Group based on a cyclorotor design. It is highly maneuverable, being able to change the direction of its thrust almost instantaneously. It is widely used on tugs and ferries. Operation From a circular plate, rotating around a vertical axis, a circular array of vertical blades (in the shape of hydrofoils) protrude out of the bottom of the ship. Each blade can rotate itself around a vertical axis. The internal gear changes the angle of attack of the blades in sync with the rotation of the plate, so that each blade can provide thrust in any direction. Unlike the azimuth thruster (where a conventional propeller is rotated about the vertical axis to direct its thrust, allowing a vessel to steer without the use of a rudder), the Voith-Schneider drive merely requires changing the pattern of orientation of the vertical blades. In a marine situation, this provides for a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Edward Caldwell
Jonathan Edward Caldwell (March 24, 1883 – November 8, 1955) was a Canadian-American self-taught aeronautical engineer who designed a series of bizarre aircraft and started public companies in order to finance their construction. None of these was ever successful, and after his last known attempt in the later 1930s he disappeared, apparently to avoid securities fraud charges. His name was later connected with mythical German flying saucers, and he remains a fixture of the UFO genre. Caldwell was born in Hensall, Ontario, Canada, the fifth son (and one of twelve children) of William Thomas Caldwell (1848–1930) and Sarah Alice Chamberlain (1852–1933). He moved to the United States in 1910 and attended Oregon State College, from 1912 to 1913, majoring in mechanical engineering. He formally emigrated from Canada in 1914 and applied for U.S. citizenship in 1915, while working as a farmer in Montana. In the 1920s, according to statements he made later in life, he became i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Whirlwind
The Wright Whirlwind was a family of air-cooled radial aircraft engines built by Wright Aeronautical (originally an independent company, later a division of Curtiss-Wright). The family began with nine-cylinder engines, and later expanded to include five-cylinder and seven-cylinder varieties. Fourteen-cylinder twin-row versions were also developed, but these were not commercially produced. The Whirlwind series was succeeded by more powerful but still air-cooled radial aero engines, notably the Pratt & Whitney Wasp series and the Wright Cyclone series. Description The Whirlwind was a direct descendant of the Lawrance J-1, a nine-cylinder air-cooled radial built by the Lawrance Aero Engine Company for the U.S. Navy. Because the Navy was very enthusiastic about air-cooled radials, but was concerned that Lawrance could not produce enough engines for its needs, it forced Wright to purchase the Lawrance company in 1923 and build the J-1 itself. Wright's J-1 was the first engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VSTOL
A vertical and/or short take-off and landing (V/STOL) aircraft is an airplane able to take-off or land vertically or on short runways. Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft are a subset of V/STOL craft that do not require runways at all. Generally, a V/STOL aircraft needs to be able to hover. Helicopters are not considered under the V/STOL classification as the classification is only used for aeroplanes, aircraft that achieve lift (force) in forward flight by planing the air, thereby achieving speed and fuel efficiency that is typically greater than the capability of helicopters. Most V/STOL aircraft types were experiments or outright failures from the 1950s to 1970s. V/STOL aircraft types that have been produced in large numbers include the F-35B Lightning II, Harrier and V-22 Osprey. A rolling takeoff, sometimes with a ramp ( ski-jump), reduces the amount of thrust required to lift an aircraft from the ground (compared with vertical takeoff), and hence increases t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STOL
A short takeoff and landing (STOL) aircraft is a fixed-wing aircraft that can takeoff/land on short runways. Many STOL-designed aircraft can operate on airstrips with harsh conditions (such as high altitude or ice). STOL aircraft, including those used in scheduled passenger airline operations, can be operated from STOLport airfields that feature short runways. Design STOL aircraft come in configurations such as bush planes, autogyros, and Conventional landing gear, taildraggers, and those such as the de Havilland Canada Dash-7 that are designed for use on conventional airstrips. The PAC P-750 XSTOL, the Daher Kodiak, the de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter and the Wren 460 have STOL capability, needing a short ground roll to get airborne, but are capable of a near-zero ground roll when landing. For any plane, the required runway length is a function of the square of the stall speed (minimum flying speed), and much design effort is spent on minimizing this number. For take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary-wing Aircraft
A rotary-wing aircraft, rotorwing aircraft or rotorcraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings that spin around a vertical mast to generate lift. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that rotorcraft "means a heavier-than-air aircraft that depends principally for its support in flight on the lift generated by one or more rotors." The assembly of several rotor blades mounted on a single mast is referred to as a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a rotorcraft as "supported in flight by the reactions of the air on one or more rotors". Rotorcraft generally include aircraft where one or more rotors provide lift throughout the entire flight, such as helicopters, gyroplanes, autogyros, and gyrodynes Compound rotorcraft augment the rotor with additional thrust engines, propellers, or static lifting surfaces. Some types, such as helicopters, are capable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |