|
CyClones
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anticyclone). Cyclones are characterized by inward-spiraling winds that rotate about a zone of low pressure. The largest low-pressure systems are polar vortices and extratropical cyclones of the largest scale (the synoptic scale). Warm-core cyclones such as tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones also lie within the synoptic scale. Mesocyclones, tornadoes, and dust devils lie within the smaller mesoscale. Upper level cyclones can exist without the presence of a surface low, and can pinch off from the base of the tropical upper tropospheric trough during the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere. Cyclones have also been seen on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune. Cyclogenesis is the process of cyclone f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild rain, showers to severe hail, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as Synoptic scale meteorology, large scale (synoptic) Low-pressure area, low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term "cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclones
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe hail, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Cyclone
A subtropical cyclone is a weather system that has some characteristics of both tropical cyclone, tropical and extratropical cyclones. As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were uncertain whether they should be characterized as Tropical cyclone, tropical or extratropical cyclones. They were officially recognized and titled by the National Hurricane Center in 1972. Beginning in 2002, subtropical cyclones began receiving names from the official tropical cyclone lists in the North Atlantic hurricane, North Atlantic basin. Subtropical cyclones are also recognized in the South-West Indian Ocean tropical cyclone, South-West Indian Ocean and South Atlantic tropical cyclone, South Atlantic basins. There are two definitions currently used for subtropical cyclones depending on their location. Across the north Atlantic and southwest Indian Ocean, they require some central Convectional Precipitation, convection fairly near the center surrounding a warming core existing in the mid-levels of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclogenesis
Cyclogenesis is the development or strengthening of Cyclonic rotation, cyclonic circulation in the atmosphere (a low-pressure area). Cyclogenesis is an umbrella term for at least three different processes, all of which result in the development of some sort of cyclone, and at any size from the microscale meteorology, microscale to the synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic scale. * Tropical cyclones form due to latent heat driven by significant thunderstorm activity, developing a warm core. * Extratropical cyclones form as waves along weather fronts before occluding later in their life cycle as cold core cyclones. * Mesocyclones form as warm core cyclones over land, and can lead to tornado formation. Waterspouts can also form from mesocyclones, but more often develop from environments of high instability and low vertical wind shear. The process in which an extratropical cyclone undergoes a rapid drop in atmospheric pressure (24 millibars or more) in a 24-hour period is referred to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
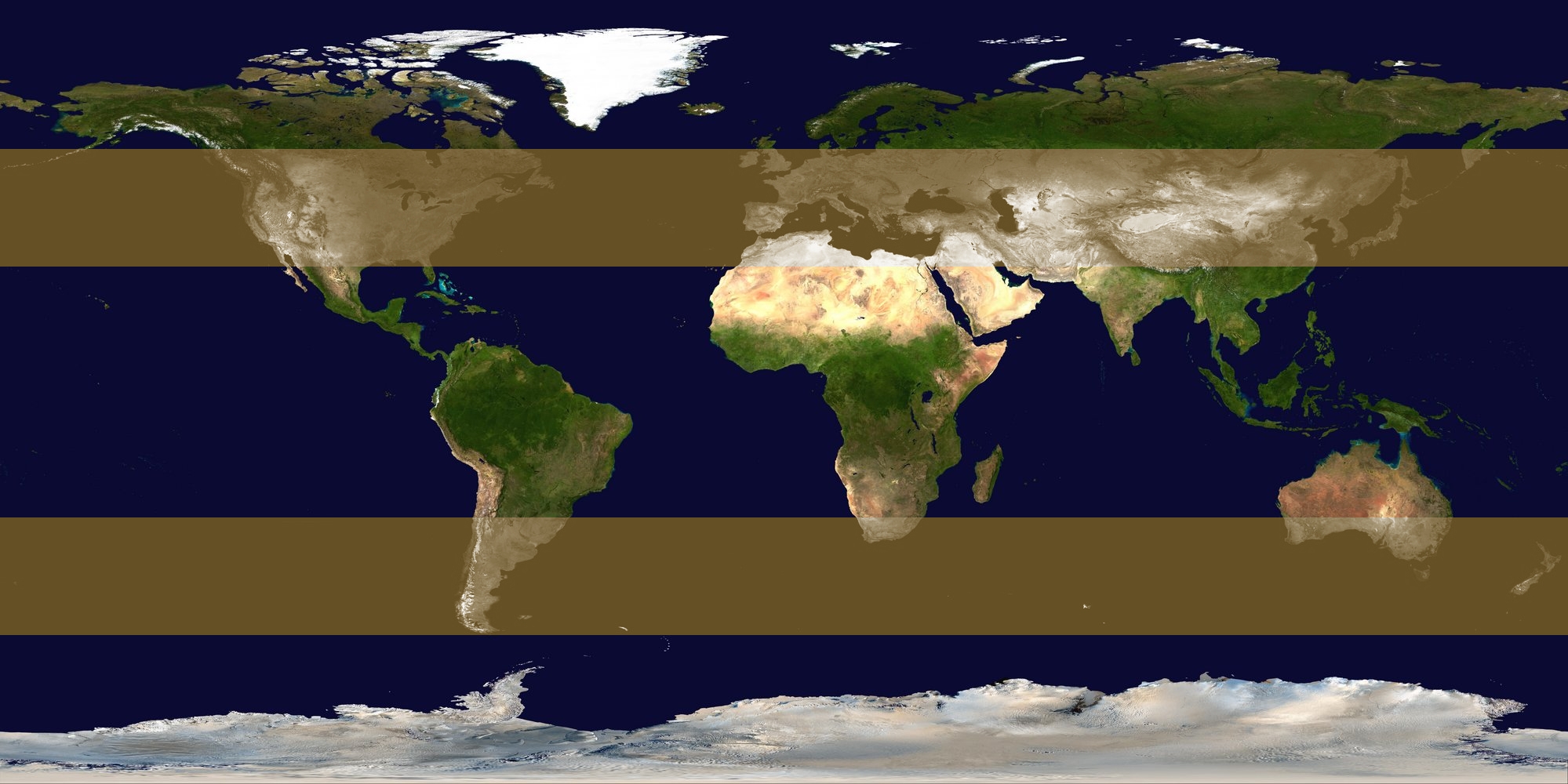
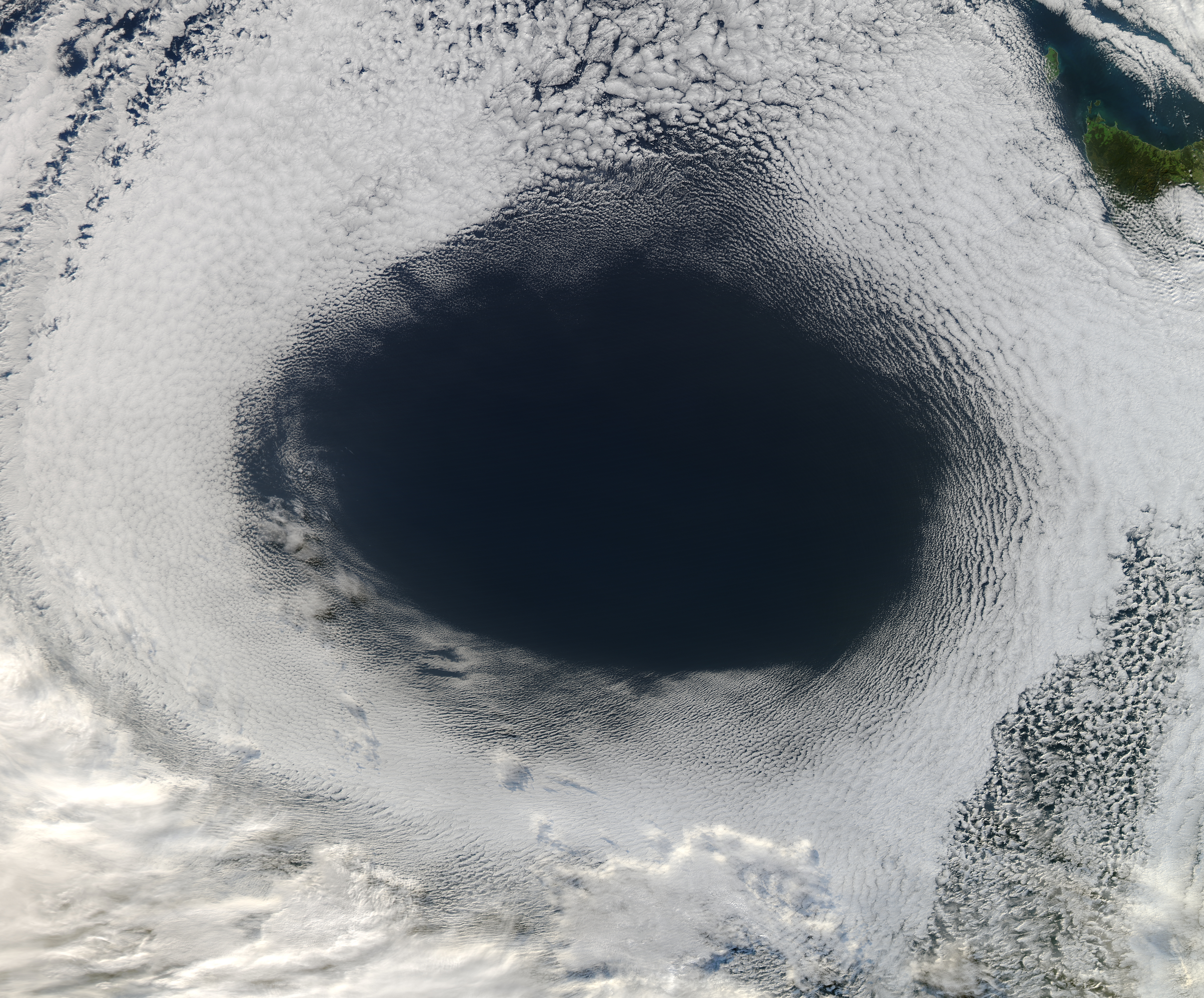
Low Pressure
In meteorology, a low-pressure area (LPA), low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. It is the opposite of a high-pressure area. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). * A secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesocyclone
A mesocyclone is a meso-gamma mesoscale (or storm scale) region of rotation ( vortex), typically around in diameter, most often noticed on radar within thunderstorms. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is usually located in the right rear flank (back edge with respect to direction of movement) of a supercell, or often on the eastern, or leading, flank of a high-precipitation variety of supercell. The area overlaid by a mesocyclone’s circulation may be several miles (km) wide, but substantially larger than any tornado that may develop within it, and it is within mesocyclones that intense tornadoes form. Description Mesocyclones are medium-scale vortices of rising and converging air that circulate around a vertical axis. They are most often associated with a local region of low-pressure. Their rotation is (usually) in the same direction as low pressure systems in a given hemisphere: counter-clockwise in the northern, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, with the only o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
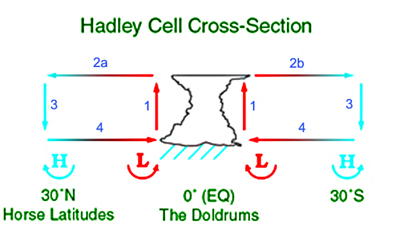
Synoptic Scale
In meteorology, the synoptic scale (also called the large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions (e.g. extratropical cyclones). Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps (such as surface weather analyses) are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word '' synoptic'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "seen together". The Navier–Stokes equations applied to atmospheric motion can be simplified by scale analysis in the synoptic scale. It can be shown that the main terms in horizontal equations are Coriolis force and pressure gradient terms; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Upper Tropospheric Trough
A tropical upper tropospheric trough (TUTT), also known as the mid-oceanic trough, is a trough situated in the upper-level (at about 200 hPa) tropics. Its formation is usually caused by the intrusion of energy and wind from the mid-latitudes into the tropics. It can also develop from the inverted trough adjacent to an upper level anticyclone. TUTTs are different from mid-latitude troughs in the sense that they are maintained by subsidence warming near the tropopause which balances radiational cooling. When strong, they can present a significant vertical wind shear to the tropics and subdue tropical cyclogenesis. When upper cold lows break off from their base, they tend to retrograde and force the development of, or enhance, surface troughs and tropical waves to their east. Under special circumstances, they can induce thunderstorm activity and lead to the formation of tropical cyclones. Location The TUTT is elongated from east-northeast to west-southwest across oceans of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture, construction, weather warnings and disaster management. Along with climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry, meteorology forms the broader field of the atmospheric sciences. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans (notably El Niño and La Niña) are studied in the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Other interdisciplinary areas include biometeorology, space weather and planetary meteorology. Marine weather forecasting relates meteorology to maritime and coastal safety, based on atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorologists study meteorological phenomena driven by solar radiation, Earth's rotation, ocean currents and other factors. These include everyday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often (but not always) visible in the form of a funnel cloud, condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The Tornado records#Highest winds observed in a tornado, most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |