|
Curt Von François
Curt Karl Bruno von François (2 October 1852 – 28 December 1931) was a German geographer, cartographer, Schutztruppe officer and commissioner of the German colonial empire, imperial colonial army of the German Empire, particularly in German South West Africa (today's Namibia) where he was responsible on behalf of Kaiser for the foundation of the city of Windhoek on 18 October 1890 and the harbor of Swakopmund on 4 August 1892. Life François was born in Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg of French Huguenot ancestry. He was the son of Prussian Army, Prussian general Bruno von François, who was killed in the battle of Spicheren. Curt's younger brother Hermann von François (1856–1933) served as a general in World War I and was one of the key contributors to the German victory at the 1914 Battle of Tannenberg (1914), Battle of Tannenberg. The writer Louise von François was his aunt. Like his ancestors, young Curt von François joined the Prussian Cadet Corps. He served as a soldie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Colonial Governors Of South West Africa
This article lists the colonial governors of South West Africa. South West Africa was the colonial predecessor of the modern day Namibia, Republic of Namibia from when the territory was controlled by the German Empire (as German South West Africa) and the Union of South Africa. The title of the position changed a number of times. Under German rule, the title of the position went from Commissioner (1884–1893) to Provincial Governor () (1893–1898) to Governor (1898–1915). Under South African rule, the title was Administrator (1915–1977) and Administrator-General (1977–1990). After the United Nations terminated South Africa's mandate to govern South West Africa, the UN appointed United Nations Commissioner for Namibia, commissioners of its own. They had no authority and South Africa refused to recognize them, and are not included here. List * Dates in italics indicate ''de facto'' continuation of office German South West Africa South West Africa See also * Presi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swakopmund
Swakopmund ("Mouth of the Swakop River, Swakop") is a city on the coast of western Namibia, west of the Namibian capital Windhoek via the B2 road (Namibia), B2 main road. It is the capital of the Erongo Region, Erongo administrative district. It has 75,921 inhabitants. The city is situated at the edge of the Namib Desert and is the fourth largest population centre in Namibia. Swakopmund is a popular beach resort and characterized by 19th century German colonial architecture. The city was founded in 1892 as the main harbour for German South West Africa. Buildings in the city include the Altes Gefängnis, Swakopmund, Altes Gefängnis, a prison designed by Heinrich Bause in 1909. The Woermannhaus, built in 1906 with a prominent tower (Damara tower), is now a public library. Attractions in Swakopmund include the Swakopmund Museum, the National Marine Aquarium of Namibia, the Crystal Gallery. Activities like quad biking, camel rides, sky diving, paragliding, and desert day trips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
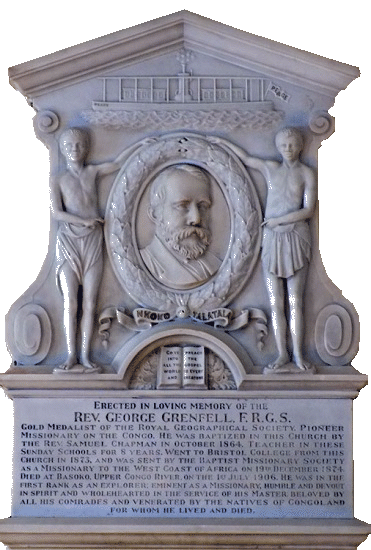
George Grenfell
George Grenfell (21 August 1849, in Sancreed, Cornwall – 1 July 1906, in Basoko, Congo Free State (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo) was a Cornish missionary and explorer. Early years Grenfell was born at Sancreed, near Penzance, Cornwall. After the family moved to Birmingham he was educated at a branch of King Edward's school. Though his parents were Anglicans he soon joined Heneage Street Baptist Chapel, where he was admitted to membership by baptism on 7 Nov. 1864. He founded the Birmingham Young Men’s Baptist Missionary Society. After leaving school, he was apprenticed to a firm of hardware and machinery merchants. Influenced by the likes of David Livingstone, Grenfell's ambition was to become a missionary so in September 1873 he entered the Baptist College, Stokes Croft, Bristol. On 10 Nov. 1874 the Baptist Missionary Society accepted him for work in Africa. In December 1874, he went as a Baptist missionary to Cameroon, West Africa, with Alfred Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
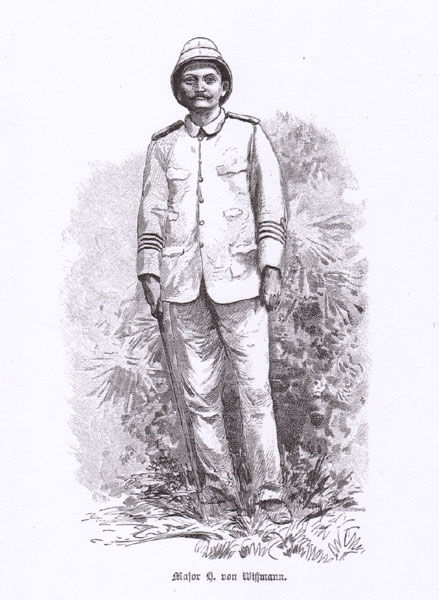
Hermann Wissmann
Hermann Wilhelm Leopold Ludwig Wissmann, after 1890 Hermann von Wissmann (4 September 1853 – 15 June 1905), was a German explorer and administrator in Africa. Biography Born in Frankfurt an der Oder, Wissmann was enlisted in the Prussian Army in 1870 and was commissioned a Lieutenant four years later. Wissmann served Mecklenburg in Füsilierregiment No. 90 posted at Rostock. During this time he had to serve a four-month prison sentence for wounding an opponent in a duel. An 1879 chance meeting with the explorer Dr. Paul Pogge changed his life. Granted a leave of absence from the army, in 1880, Wissmann accompanied explorer Paul Pogge on a journey through the Congo Basin. In the eastern Congo, Pogge and Wissmann parted company. Pogge stayed to build an agricultural research station for a Congolese chief, while Wissmann trekked to the Indian Ocean via present-day Tanzania. He was awarded the 1888 Founder's Medal of the Royal Geographical Society for his explorations. Afterwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
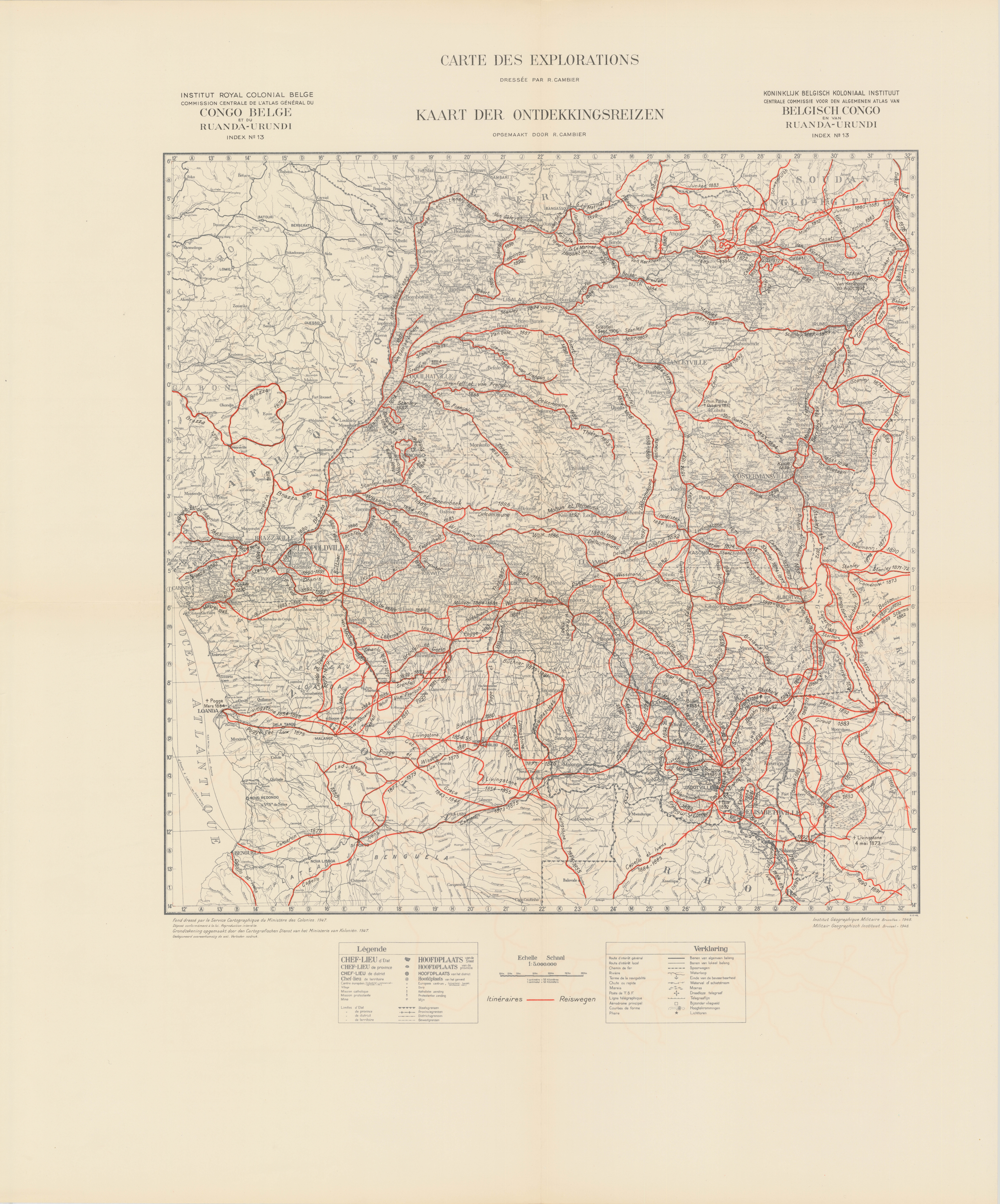
Colonisation Of The Congo
Colonization of the Congo Basin refers to the European colonization of the Congo Basin of tropical Africa. It was the last part of the continent to be colonized. By the end of the 19th century, the Basin had been carved up by European colonial powers into the Congo Free State, the French Congo and the Portuguese Congo (modern Cabinda Province of Angola). Early European exploration One by one the other great mysteries had been explored: * The coasts by Prince Henry the Navigator's Portuguese sailors in the 15th century. * The Blue Nile by James Bruce in 1773. * The remote upper Niger by Mungo Park in 1796. * The vast Sahara by competitors Laing, Caillié, and Clapperton in the 1820s. * The fever-ridden mangroves of the lower Niger by the brothers Richard and John Lander in 1830. * Southern Africa and the Zambezi by Livingstone and John Clafton in the 1850s. * The upper Nile by Burton, Speke, and Baker in a succession of expeditions between 1857 and 1868. Though the Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
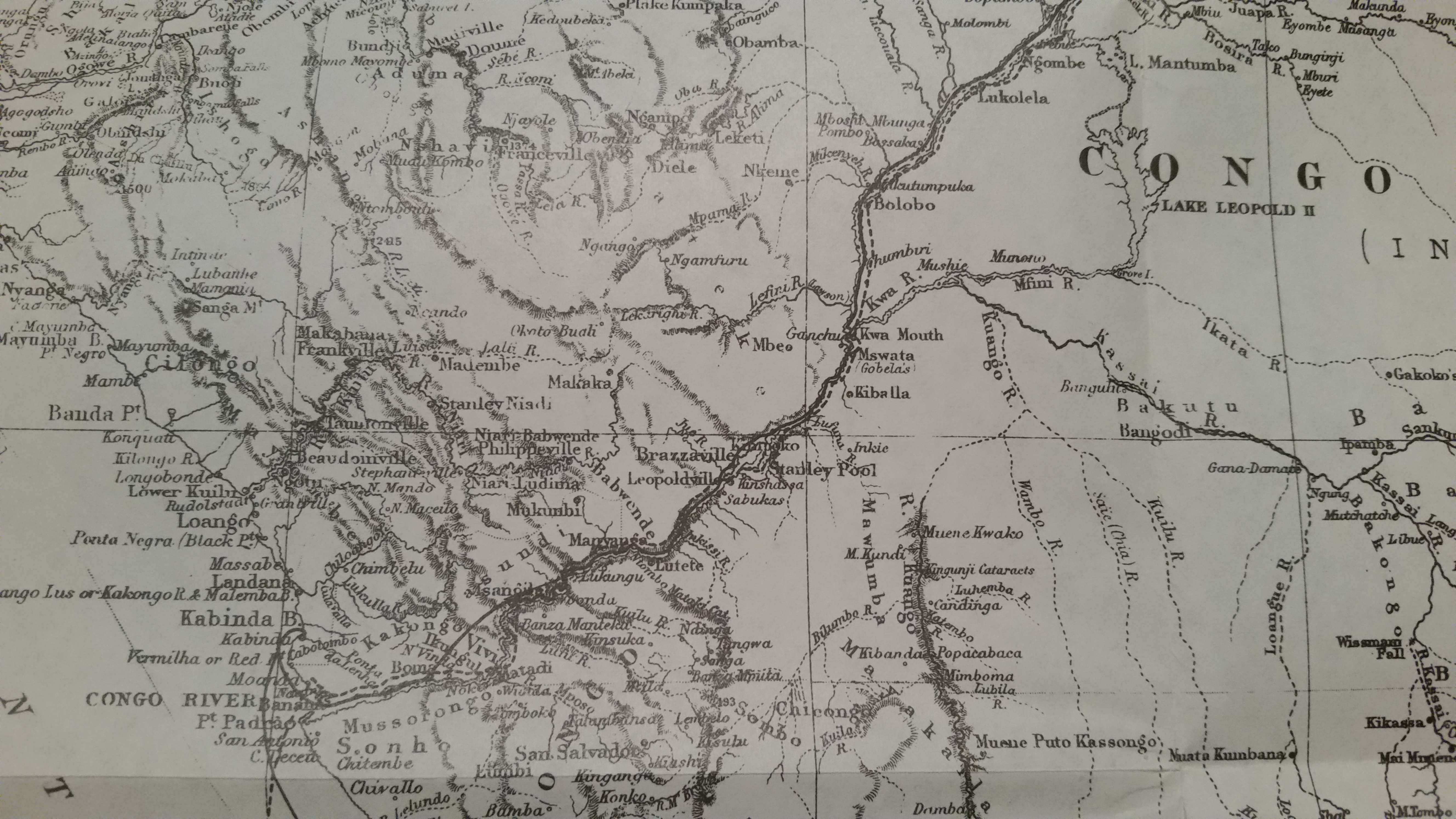
Kasai River
The Kasai River (, ; called Cassai in Angola) is a left bank tributary of the Congo River, located in Central Africa. The river begins in central Angola and flows to the east until it reaches the border between Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it turns north and serves as the border until it flows into the DRC. From Ilebo, between the confluences with Lulua river and Sankuru river, the Kasai river turns to a westerly direction. The lower stretch of the river, from the confluence with Fimi river until it joins the Congo at Kwamouth northeast of Kinshasa, is also known as the Kwa(h) River. The Kasai basin consists mainly of equatorial rainforest areas, which provide an agricultural land in a region noted for its infertile, sandy soil. It is a tributary of Congo river and diamonds are found in it. Around 60% of diamonds in Belgium go from Kasai river for cutting and shaping. Exploration Henry Morton Stanley reached the confluence on 9 March 1877, calli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the insignia of the medieval Teutonic Order and borne by its knights from the 13th century. As well as being a military medal, it has also been used as an emblem by the Prussian Army, the Imperial German Army, and the of the Weimar Republic, while the ''Balkenkreuz'' (bar cross) variant was used by the ''Wehrmacht''. The Iron Cross is now the emblem of the , the modern German armed forces. King Frederick William III of Prussia established the Iron Cross award on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Louise, who was the first person to receive it (posthumously). The Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Spicheren
The Battle of Spicheren, also known as the ''Battle of Forbach'', was a battle during the Franco-Prussian War. The German victory compelled the French to withdraw to the defenses of Metz. The Battle of Spicheren, on 6 August, was the second of three critical French defeats. General (later field marshal) Helmuth von Moltke had originally planned to keep Bazaine's army on the Saar river until he could attack it with the 2nd Army in front and the 1st Army on its left flank, while the 3rd Army closed towards the rear. The aging General von Steinmetz made an overzealous, unplanned move, leading the 1st Army south from his position on the Moselle. He moved straight toward the town of Spicheren, cutting off Prince Frederick Charles from his forward cavalry units in the process. Background The French declared war before their troops were in position to invade Germany. The Germans, commanded by Field Marshal von Moltke, began to assemble into three armies, which were to invade Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 January 1871, the conflict was caused primarily by France's determination to reassert its dominant position in continental Europe, which appeared in question following the decisive Austro-Prussian War, Prussian victory over Austria in 1866. According to some historians, Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck deliberately provoked the French into declaring war on Prussia in order to induce four independent southern German states—Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Grand Duchy of Hesse, Hesse-Darmstadt—to join the North German Confederation. Other historians contend that Bismarck exploited the circumstances as they unfolded. All agree that Bismarck recognized the potential for new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tannenberg (1914)
The Battle of Tannenberg, also known as the Second Battle of Tannenberg, was fought between Russia and Germany between 23 and 30 August 1914, the first month of World War I. The battle resulted in the almost complete destruction of the Russian Second Army and the suicide of its commanding general, Alexander Samsonov. A series of follow-up battles ( First Masurian Lakes) led to the ousting of the First Army from East Prussia. The battle is particularly notable for fast rail movements by the German Eighth Army, enabling them to concentrate against each of the two Russian armies in turn, first delaying the First Army and then destroying the Second before once again turning on the First days later. It is also notable for the failure of the Russians to encode their radio messages, broadcasting their daily marching orders in the clear, which allowed the Germans to make their movements with the confidence they would not be flanked. The almost miraculous outcome brought consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |